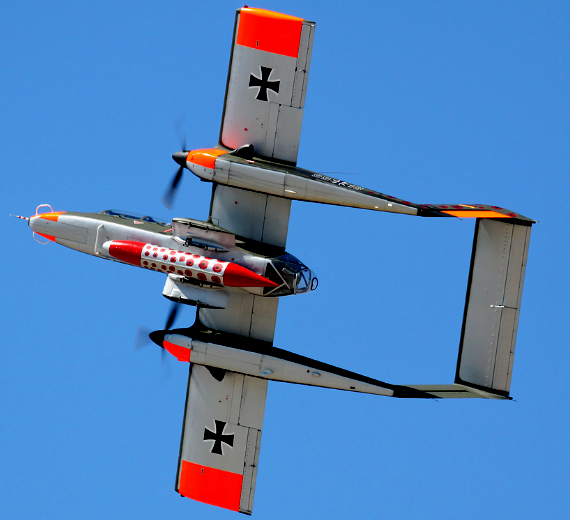
North American /
Rockwell OV-10 Bronco
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Light attack and observation aircraft |
National origin United States
Manufacturer North American Rockwell
First flight 16 July 1965
Introduction October 1969
Retired US (1995)
Status In limited service (2015–present)
Primary users United States Marine Corps (historical)
United States Air Force (historical)
United States Navy (historical)
Philippine Air Force
Produced 1965–1986
Number built 360
.
History North American / Rockwell
Rockwell OV-10 Bronco
First flight 16 July 1965
Introduction October 1969
Produced 1965–1986
The aircraft was initially conceived in the early 1960s through an informal collaboration between W.H. Beckett and Colonel K.P. Rice, U.S. Marine Corps, who met at Naval Air Weapons Station China Lake, California, and who also happened to live near each other. The original concept was for a rugged, simple, close air support aircraft integrated with forward ground operations. At the time, the U.S. Army was still experimenting with armed helicopters, and the U.S. Air Force was not interested in close air support.
The concept aircraft was to operate from expedient forward air bases using roads as runways. Speed was to be from very slow to medium subsonic, with much longer loiter times than a pure jet. Efficient turboprop engines would give better performance than piston engines. Weapons were to be mounted on the centerline to get efficient unranged aiming.0
ftTake off Distance
0
nmMAX RANGE
0
Km/HAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
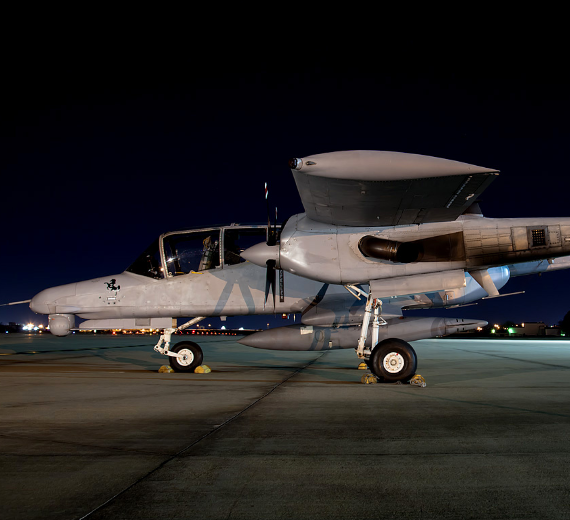
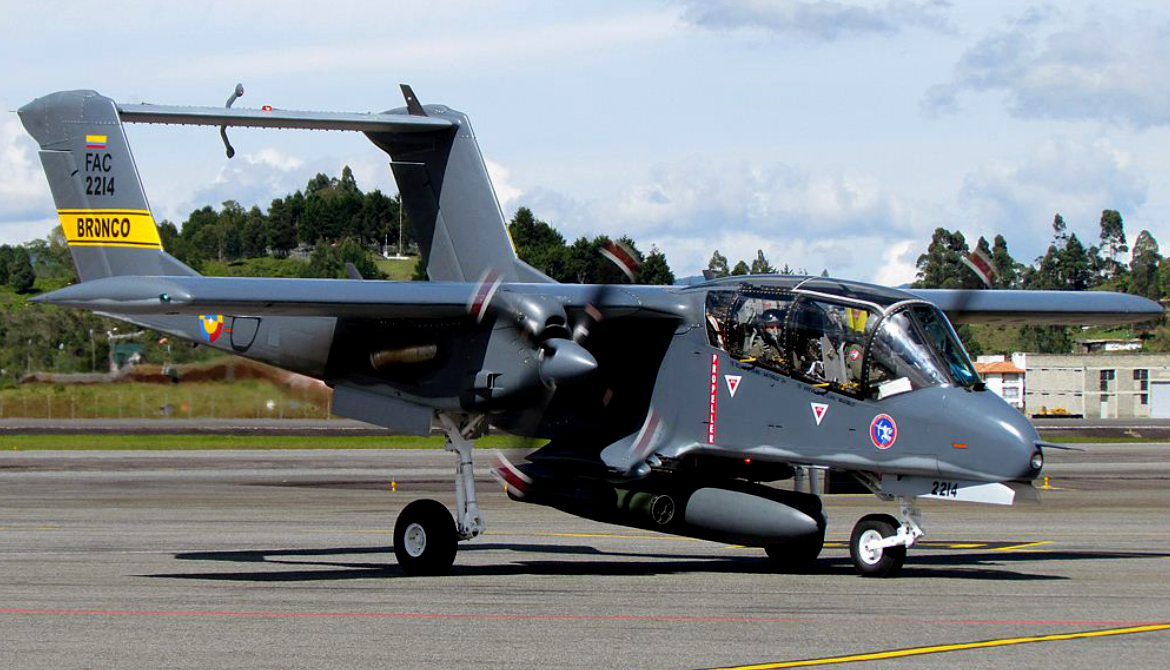
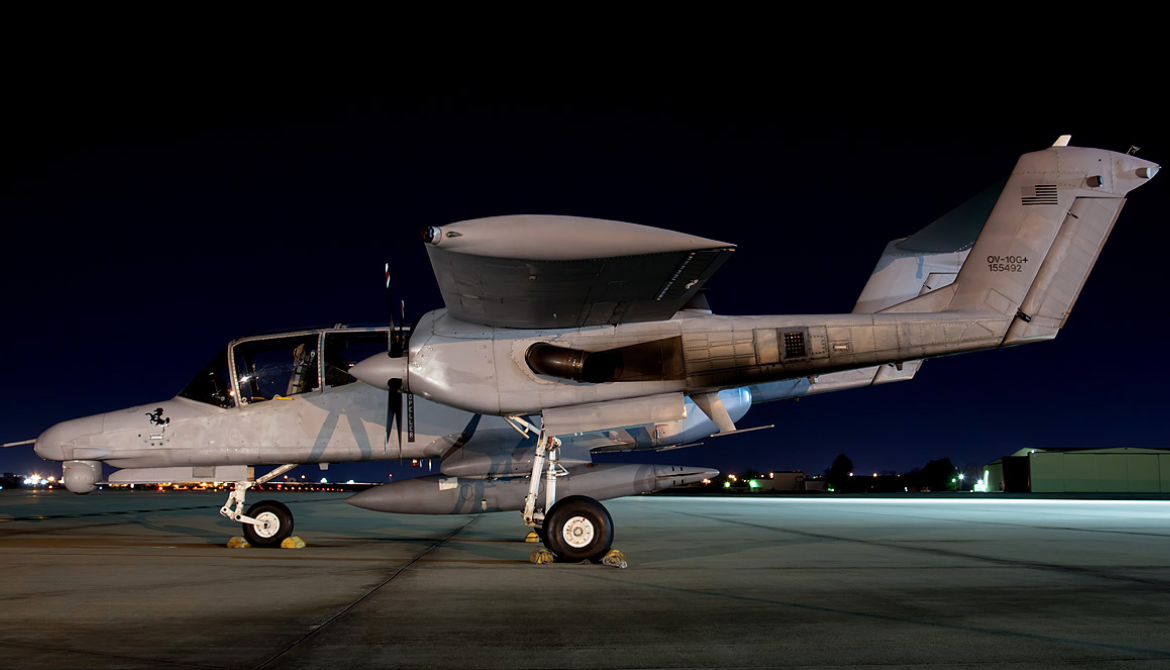
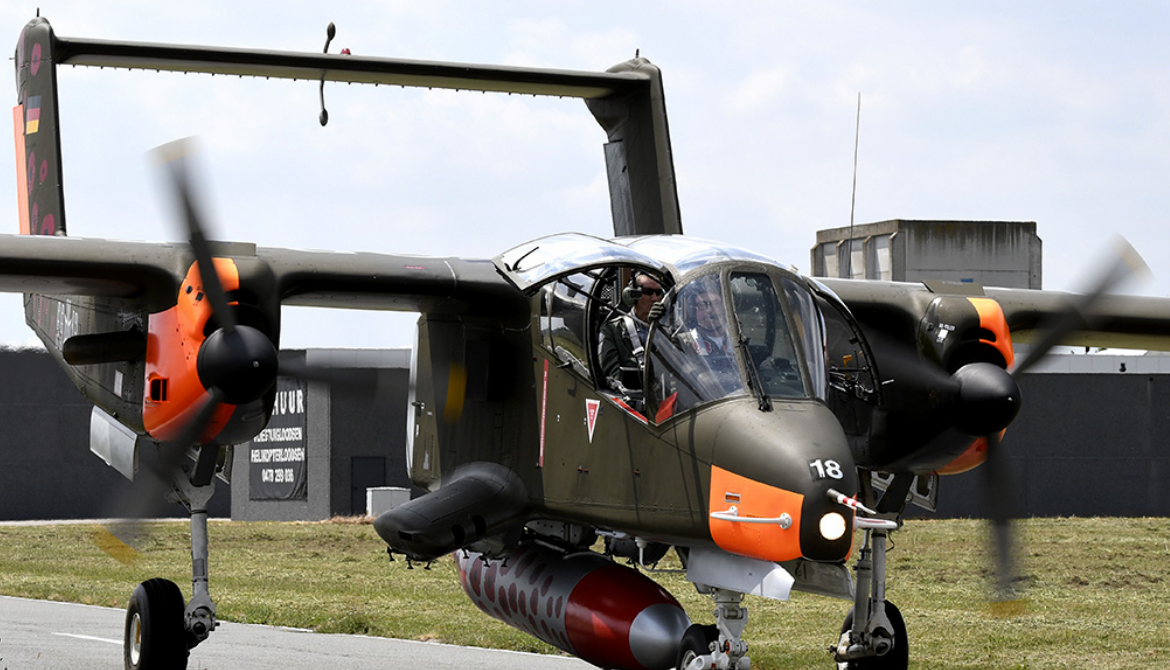
Photo Gallery
Rockwell OV-10 Bronco


North American /
Rockwell OV-10 Bronco
First flight 16 July 1965 Introduction October 1969
Produced 1965–1986
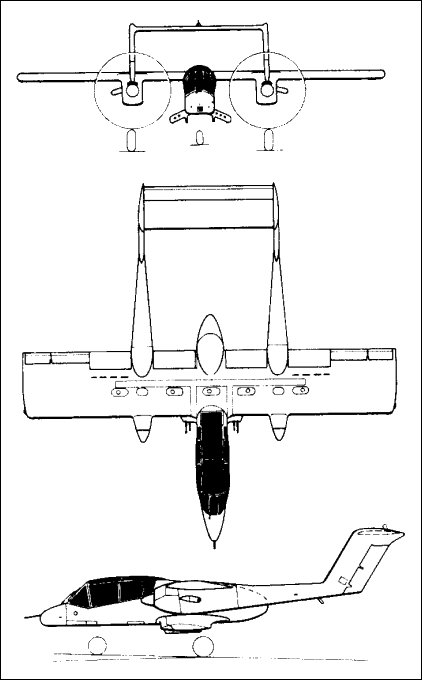
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: cargo compartment for personnel (no seats) or 3,200 lb (1,451 kg) of freight
- Length: 44 ft 0 in (13.41 m)
- Wingspan: 40 ft 0 in (12.19 m)
- Height: 15 ft 2 in (4.62 m)
- Wing area: 291.0 sq ft (27.03 m2)
Powerplant
- Fuel capacity: 252 US gal (210 imp gal; 950 L) internal
- Powerplant: 2 × Garrett T76-G-420/421 turboprop engines, 1,040 shp (780 kW) each equivalent
- Propellers: 3-bladed Hamilton Standard, 8 ft 6 in (2.59 m) diameter constant-speed fully feathering propellers
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 250 kn (290 mph, 460 km/h) at sea level
- Combat range: 198 nmi (228 mi, 367 km)
- Ferry range: 1,200 nmi (1,400 mi, 2,200 km) with auxiliary fuel
- Service ceiling: 30,000 ft (9,100 m)
- Rate of climb: 3,020 ft/min (15.3 m/s)
- Take-off run: 740 ft (226 m)
- Take-off distance to 50 ft (15 m): 1,120 ft (341 m)
Armament
- Guns: 1 × 20 mm (0.79 in) M197 electric cannon (YOV-10D) or 4 × 7.62×51 mm M60C machine guns (OV-10D/D+)
- Hardpoints: 5 fuselage and 2 underwing , with provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets: 7- or 19-tube launchers for 2.75 in (70 mm) FFARs/WAFARs or 2- or 4-tube launchers for 5 in (127 mm) FFARs or WAFARs
- Missiles: AIM-9 Sidewinder on wings only
- Bombs: up to 500 lb (227 kg)
Links to Youtube & Others
The North American Rockwell OV-10 Bronco is an American twin-turboprop light attack and observation aircraft.
COIN Combat Aircraft
The North American Rockwell OV-10 Bronco is an American twin-turboprop light attack and observation aircraft
Youtube Link
In May 2015, the Pentagon initiated a secret program dubbed Combat Dragon II. Its purpose: to test the viability of the low-cost, Vietnam-era OV-10 Bronco in combat scenarios against ISIS.














.svg.png)