Consolidated / Convair
Consolidated PT-1 Trusty
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Primary Trainer |
| Manufacturer | Consolidated |
| Designer | Colonel Virginius E. Clark |
| Primary users | United States Army Air ServiceUnited States Navy Siam U.S. Army National Guard |
| Number built | 221 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1923 |
| Introduction date | 1921 |
| Developed into | Consolidated PT-3 |
History Consolidated / Convair
Consolidated PT-1 Trusty Model One
nickname "Trusty"
Manufactured 1923, Introduction date 1921

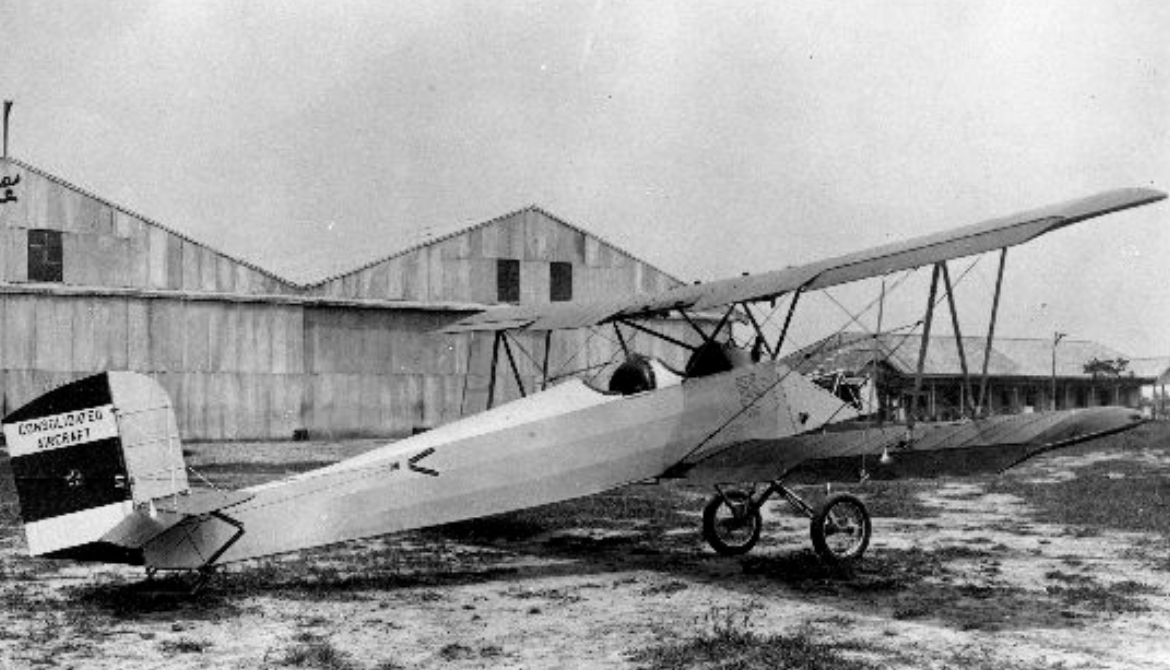
The Consolidated PT-1 Trusty (company designation Model 1) was a biplane primary trainer used by the United States Army Air Service (USAAS).
In 1921, Colonel Virginius Clark, chief designer of the Dayton-Wright Company, designed the Chummy sporting biplane.[1] The airframe was advanced in its use of the new Clark Y thick-section airfoil and a welded fuselage framework of chrome-molybdenum steel tubing. A departure from the all-wood structures found in other trainers, the structure proved sturdy and dependable. It was offered to the USAAS as a replacement for the Curtiss JN-4D trainer, with a choice of Le Rhone or Clerget rotary piston engines.
In 1922, the Army ordered three TA-3 (Trainer, Air-cooled, Type 3) machines for evaluation with the Le Rhone engine and dual controls. Evaluation showed that the type had the makings of a good trainer, but was somewhat lacking in power, so in 1923 Dayton-Wright modified one TA-3 with a more powerful 110 hp (82 kW) Le Rhone.
Variants

NMUSAF
- TA-3
- Dayton-Wright (Trainer, Air-cooled type 3), 13 built, 80 hp (60 kW) Le Rhone 9C rotary engine, wingspan 30 ft 11 in (9.4 m), Length 22 ft 7 in (6.9 m), gross weight 1,753 lb (795 kg)
- TA-5
- Single TA-3 with Lawrance J-1 engine used for tests of a single-wheel landing gear arrangement in 1923.
- TW-3
- Dayton-Wright (Trainer, Water-cooled type 3), two built, 150 hp (112-kW) Wright-Hispano I engine wingspan 34 ft 9 in (10.6 m), Length 25 ft 7 in (7.8 m), gross weight 2,447 lb (1019 kg)
- TW-3
- Consolidated (Trainer, Water-cooled type 3), 20 built, 180 hp (134 kW) Wright-Hispano E engine wingspan 34 ft 9 in (10.6 m), Length 26 ft 9 in (8.1 m), gross weight 2,407 lb (1,092 kg)
- PT-1
- Consolidated (Primary Trainer number 1), 221 built, 180 hp (134 kW) Wright-Hispano E (V-720) engine
- XPT-2
- PT-1 with 225 hp (168 kW) Wright R-790 (J-5) engine, wingspan 34 ft 7 in (10.5 m), Length 28 ft 4 in (8.6 m), gross weight 2,427 lb (1,100 kg)
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Consolidated / Convair / Vultee
Consolidated PT-1 Trusty Model One
nickname "Trusty"
Manufactured 1923
Introduction date 1921


Consolidated Convair Vultee
Consolidated PT-1 Trusty
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 27 ft 9.25 in (8.4646 m)
- Wingspan: 34 ft 5.5 in (10.503 m)
- Height: 9 ft 10 in (3.00 m)
- Wing area: 284 sq ft (26.4 m2)
Powerplant
- Empty weight: 1,805 lb (819 kg)
- Gross weight: 2,577 lb (1,169 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Wright-Hispano E V-8 water-cooled piston engine, 180 hp (130 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed-pitch propeller
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 92 mph (148 km/h, 80 kn) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 79 mph (127 km/h, 69 kn)
- Range: 350 mi (560 km, 300 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 13,450 ft (4,100 m)
- Rate of climb: 690 ft/min (3.5 m/s)
Links to Youtube & Others
The "Camel" may be regarded as the prototype of the Consolidated response to the USAAS's 1924 requirement for a new primary trainer. In the early summer of 1924.
Consolidated PT-1 Trusty Model One
In 1922, the Army ordered three TA-3 (Trainer, Air-cooled, Type 3) machines for evaluation with the Le Rhone engine and dual controls.
Youtube Link
The Consolidated PT-1 Trusty (company designation Model 1) was a biplane primary trainer used by the United States Army Air Service (USAAS)