.
History Consolidated / Convair
Convair R3Y Tradewind

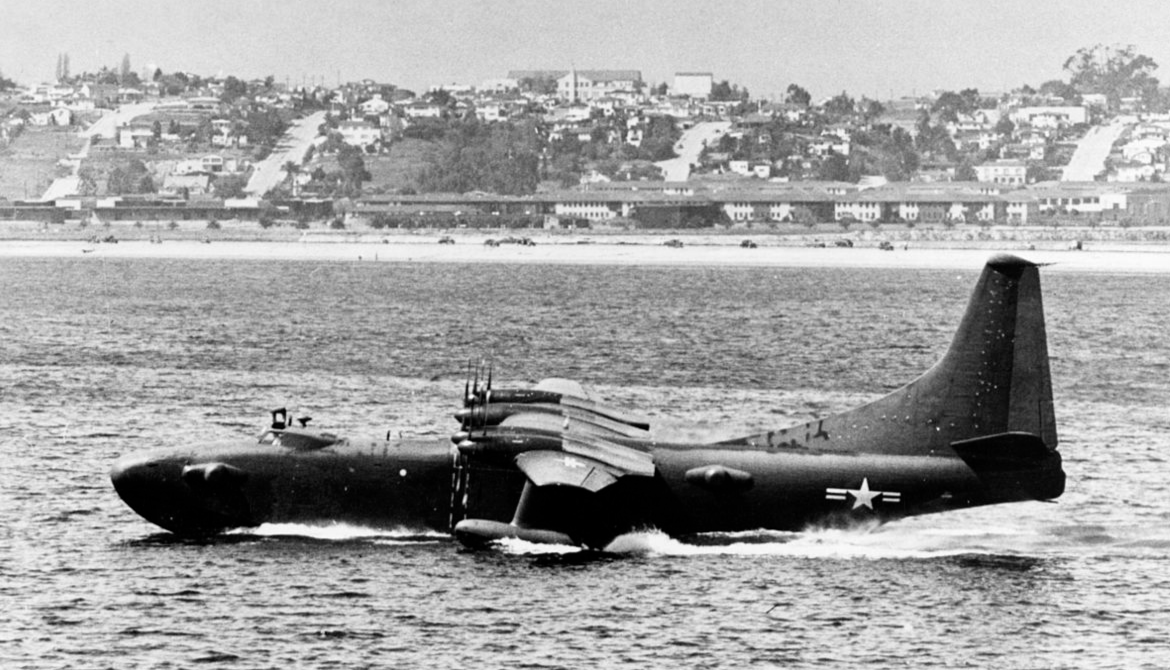
The Convair R3Y Tradewind was an American 1950s turboprop-powered flying boat designed and built by Convair.
Operational service
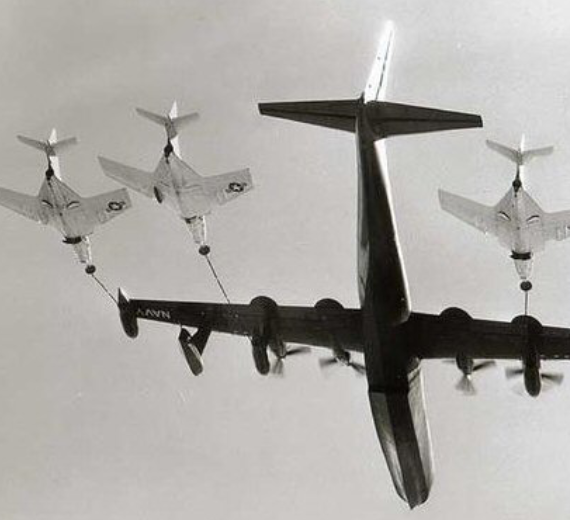
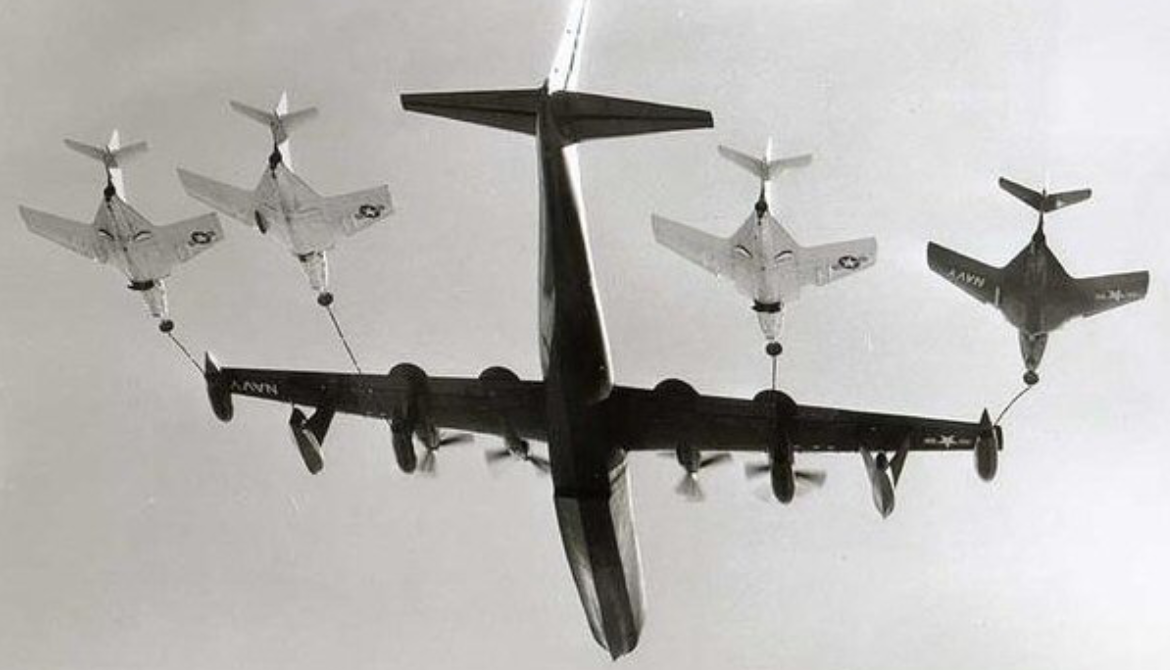
R3Y-2 Tradewind refuels a record four fighters in flight, 1956
The R3Y set a transcontinental seaplane record of 403 mph (649 km/h) in 1954 by utilizing the speed of high-altitude jetstream winds. This record still stands.
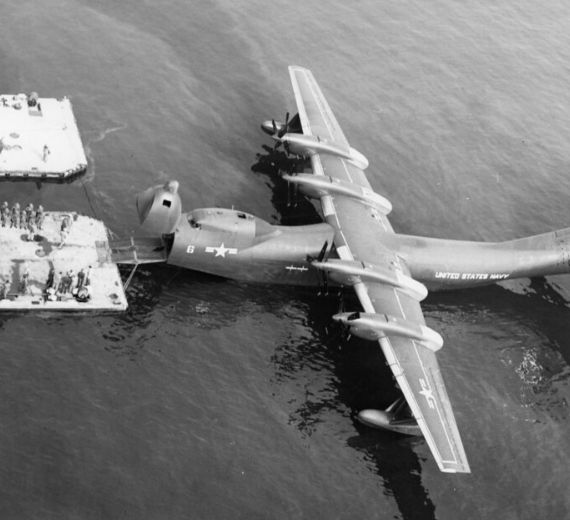
After service trials the aircraft were delivered to a U.S. Navy air transport squadron, VR-2, on 31 March 1956. Problems with the engine/propeller combination led to the ending of Tradewind operations and the unit was disbanded on 16 April 1958.
The six R3Y-2s were converted into four-point in-flight tankers using the probe-and-drogue method. In September 1956 one example was the first aircraft to successfully refuel four others simultaneously in flight in 1956, refueling four Grumman F9F Cougars.
Design and development

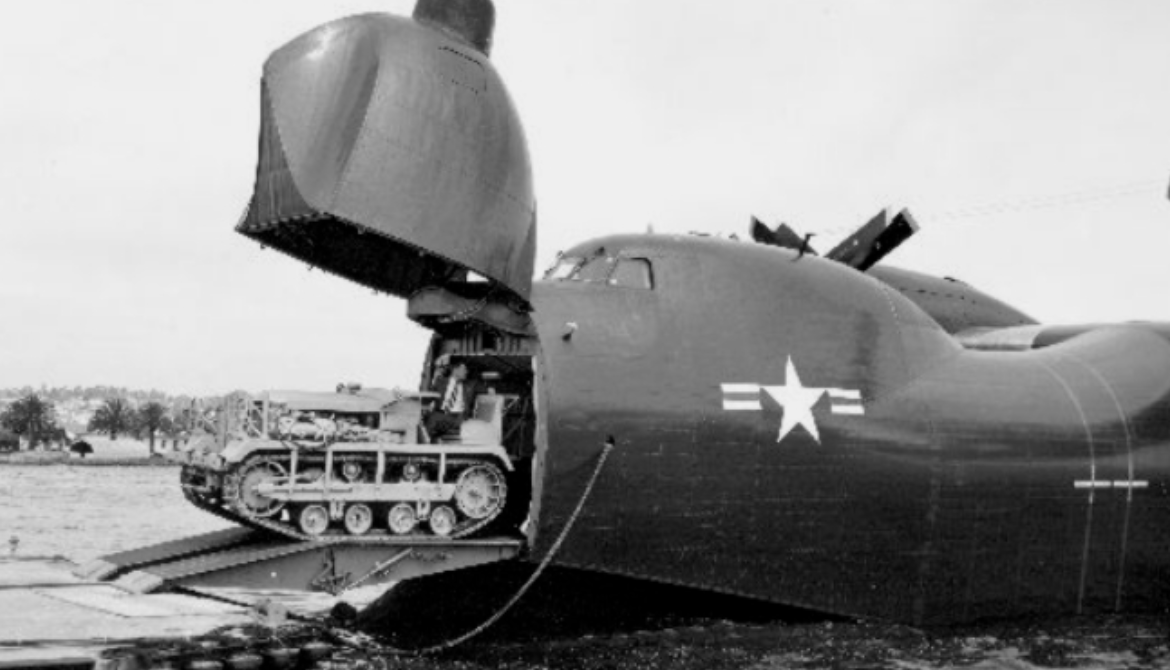
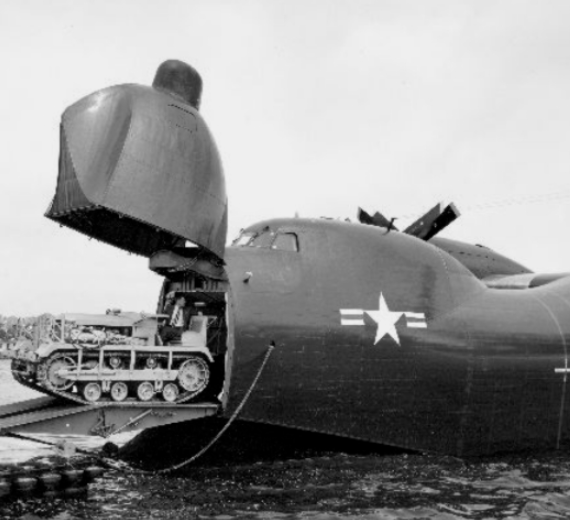
Convair received a request from the United States Navy in 1945 for the design of a large flying boat using new technology developed during World War II, especially the laminar flow wing and still-developing turboprop technology. Their response was the Model 117. It was a large high-wing flying boat with Allison T40 engines driving six-bladed contra-rotating propellers. It had a sleek body with a single-step hull and a slender high-lift wing with fixed floats. The Navy ordered two prototypes on 27 May 1946. Designated XP5Y-1, the first aircraft first flew on 18 April 1950 at San Diego. In August the aircraft set a turboprop endurance record of eight hours six minutes. The Navy decided not to proceed with the patrol boat version, instead directing that the design should be developed into a passenger and cargo aircraft.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Consolidated / Convair / Vultee
Convair R3Y Tradewind


Consolidated Convair Vultee
Convair R3Y Tradewind
General characteristics
- Crew: 7 flight crew + cabin crew / loadmasters
- Capacity: 80 pax / 72 litter patients with 8 medical staff
-
-
-
- R3Y-2: 103 pax / 92 litter patients with 12 medical staff
-
-
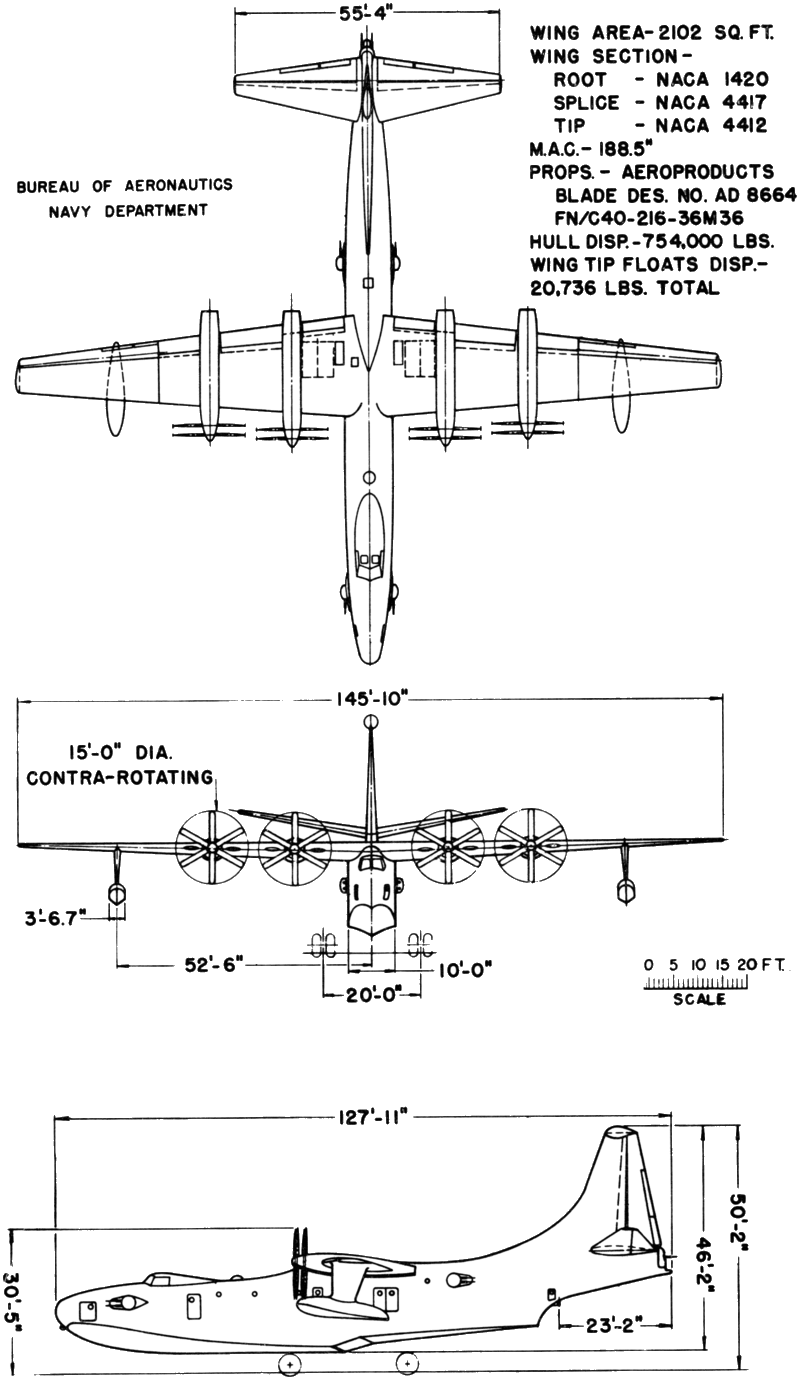
- Length: 139 ft 8.3 in (42.578 m)
-
-
-
- R3Y-2: 141 ft 1.7 in (43 m)
-
-
- Wingspan: 145 ft 9.7 in (44.442 m)
- Width: 12 ft 6 in (3.81 m) maximum hull beam
- Height: 49 ft 0 in (14.94 m) keel to fin tip
-
-
-
- 51 ft 5.2 in (16 m) on beaching gear
-
-
- Wing area: 2,100.7 sq ft (195.16 m2)
Powerplant
- Gross weight: 145,500 lb (65,998 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 165,000 lb (74,843 kg)
- Landing weight: 136,739 lb (62,024 kg) with maximum cargo
- Fuel capacity: 66,000 lb (29,937 kg)
- Powerplant: 4 × Allison T40-A-10 turboprop engines, 5,332 shp (3,976 kW) each
- Propellers: 6-bladed Aeroproducts, 15 ft (4.6 m) diameter contra-rotating fully-feathering reversible propellers
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 299 kn (344 mph, 554 km/h) at 21,000 ft (6,401 m) at MTOW
-
-
-
- 308 kn (354 mph; 570 km/h) at 23,000 ft (7,010 m) at normal gross weight
-
-
- Cruise speed: 300 kn (350 mph, 560 km/h) average at 29,000–34,200 ft (8,839–10,424 m)
- Stall speed: 98 kn (113 mph, 181 km/h) at MTOW power off
-
-
-
- 89.4 kn (102.9 mph; 165.6 km/h) at 136,739 lb (62,024 kg) power off
- 87.5 kn (100.7 mph; 162.1 km/h) at 136,739 lb (62,024 kg) with approach power
-
-
- Range: 2,420 nmi (2,780 mi, 4,480 km)
- Combat range: 1,240 nmi (1,430 mi, 2,300 km)
- Service ceiling: 30,300 ft (9,200 m) at MTOW
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The program was halted after thirteen aircraft were built, the reason being the unreliability of the Allison T-40 turboprops. The crash of one of the two XP5Y-1 aircraft was judged due to catastrophic engine failure; when little progress was being made with the engine problems, the Navy halted the program.
Convair R3Y Tradewind
R3Y-2 Tradewind refuels a record four fighters in flight, 1956

Youtube Link
The Navy decided not to proceed with the patrol boat version, instead directing that the design should be developed into a passenger and cargo aircraft.