Consolidated / Convair
Consolidated B-24 Liberator
Role
Heavy bomber
Anti-submarine warfare
Maritime patrol aircraft
Manufacturer Consolidated Aircraft
First flight 29 December 1939
Introduction 1941
Retired 1968 (Indian Air Force)
Primary users United States Army Air Forces
United States Navy
Royal Air Force
Royal Australian Air Force
Produced 1940–1945
Number built 18,18
Variants Consolidated PB4Y-2 Privateer
Consolidated C-87 Liberator Express
Consolidated LiberatorI
Developed into
Consolidated R2Y
Consolidated B-32 Dominator
.
History Consolidated / Convair
Consolidated B-24 Liberator
"The Flying Coffin"
First flight 29 December 1939, Produced 1940–1945

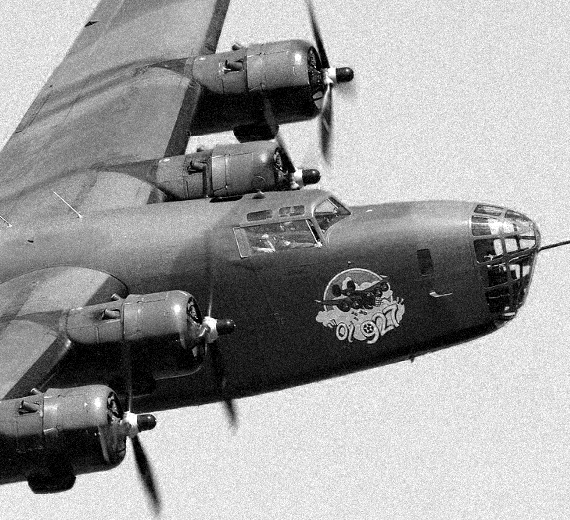
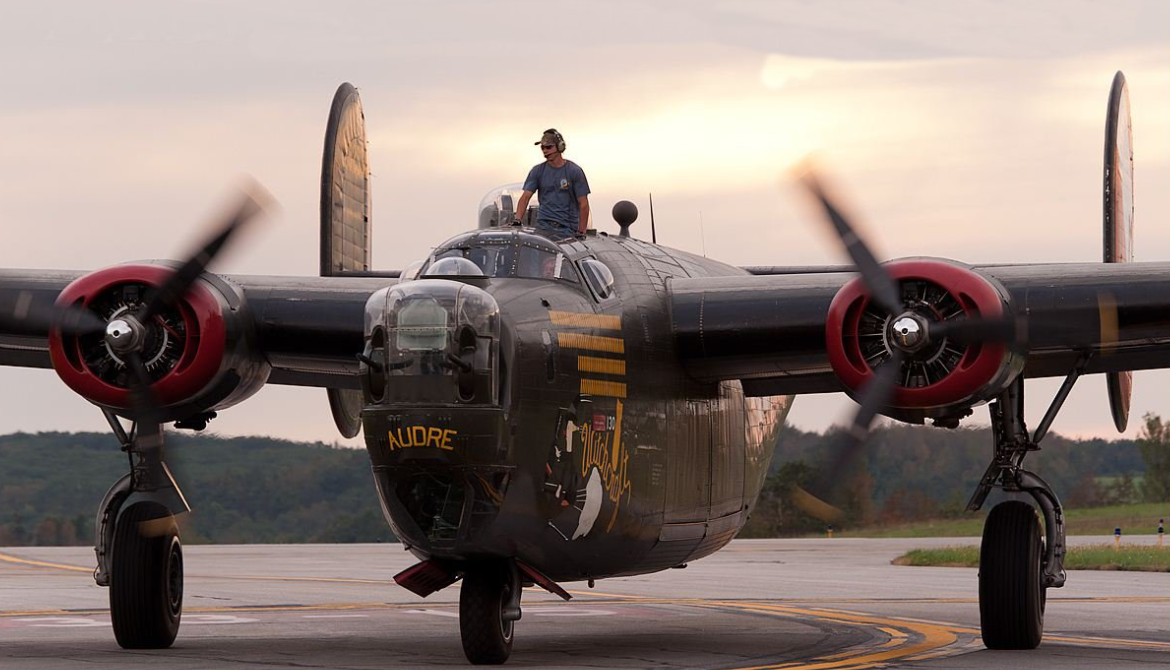
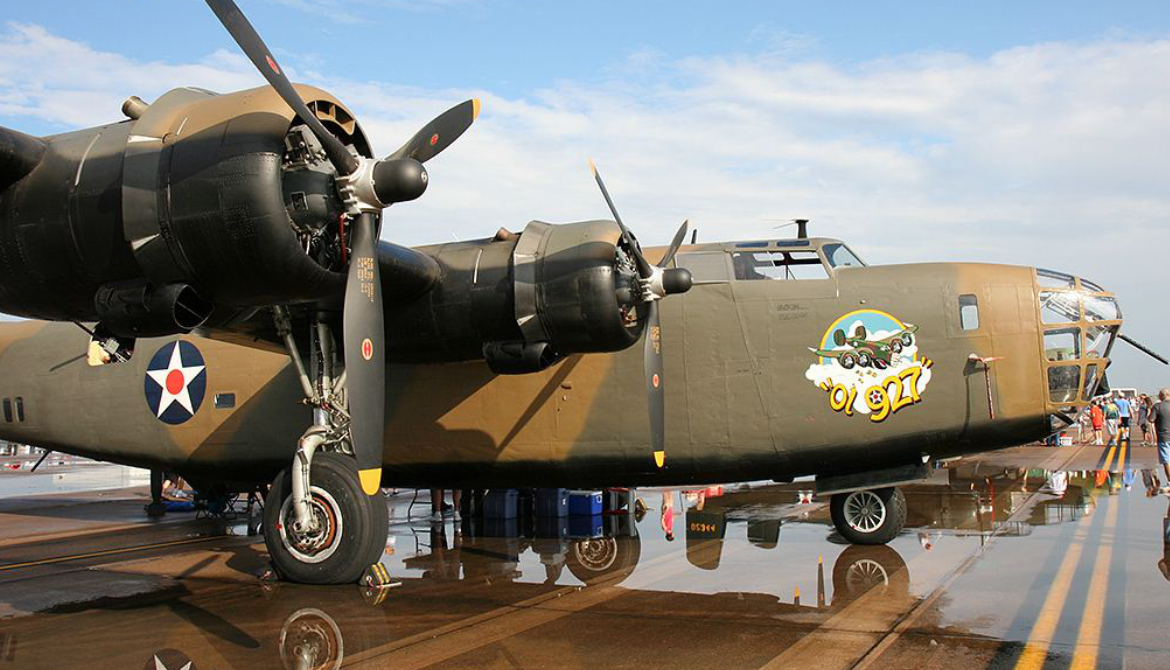
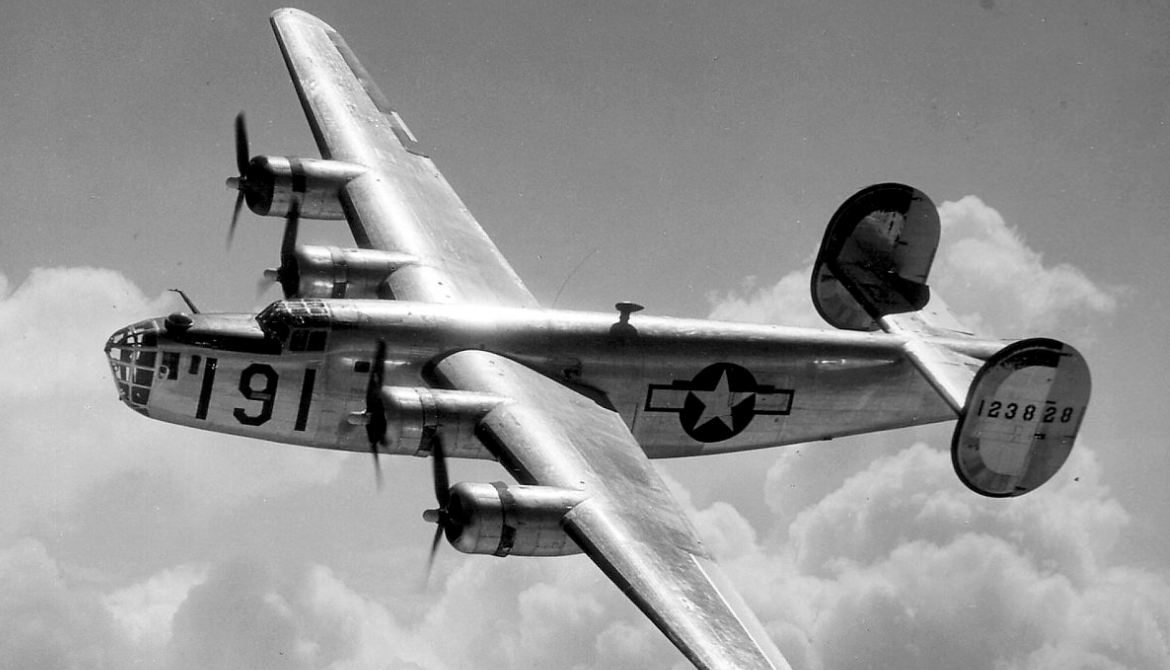
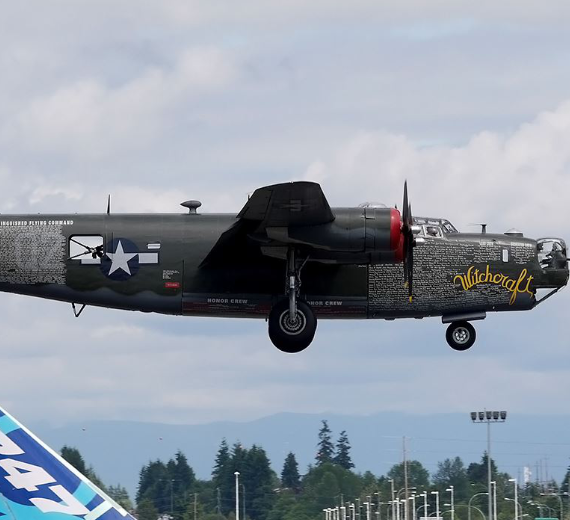
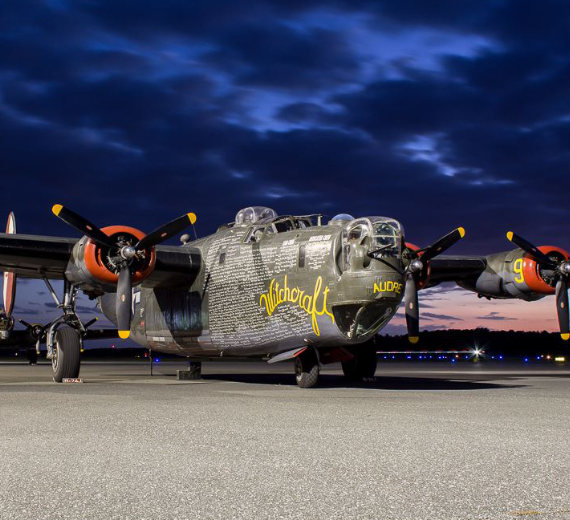
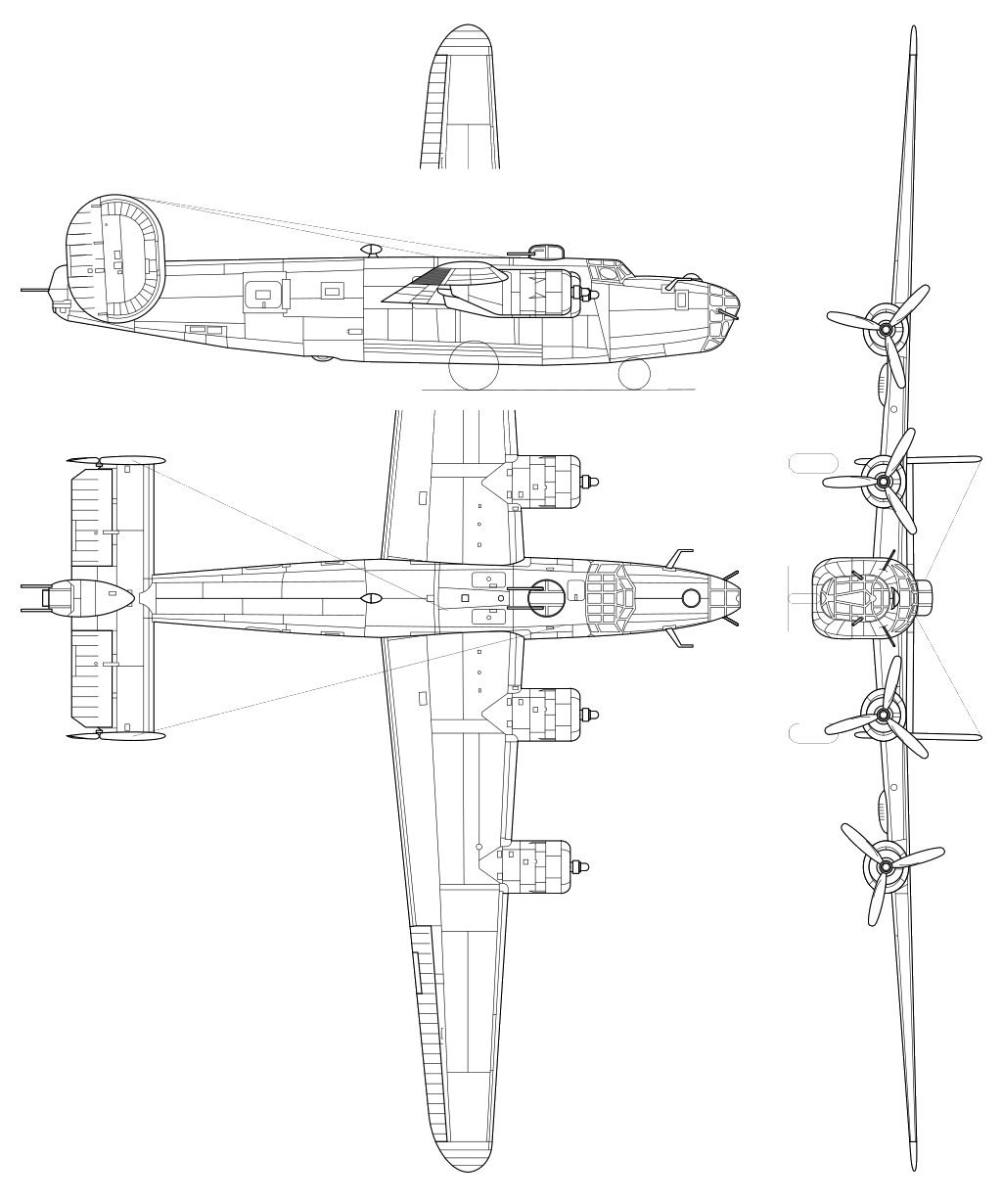
The Consolidated B-24 Liberator is an American heavy bomber, designed by Consolidated Aircraft of San Diego, California. It was known within the company as the Model 32, and some initial production aircraft were laid down as export models designated as various LB-30s, in the Land Bomber design category.
The B-24 was used extensively in World War II where it served in every branch of the American armed forces, as well as several Allied air forces and navies. It saw use in every theater of operations. Along with the B-17, the B-24 was the mainstay of the US strategic bombing campaign in the Western European theater. Due to its range, it proved useful in bombing operations in the Pacific, including the bombing of Japan. Long-range anti-submarine Liberators played an instrumental role in closing the Mid-Atlantic gap in the Battle of the Atlantic. The C-87 transport derivative served as a longer range, higher capacity counterpart to the Douglas C-47 Skytrain
.Design and development

Initial specifications
The Liberator originated from a United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) request in 1938 for Consolidated to produce the Boeing B-17 under license. After company executives including President Reuben Fleet visited the Boeing factory in Seattle, Washington, Consolidated decided instead to submit a more modern design of its own.
The new Model 32 combined designer David R. Davis's wing, a high-efficiency airfoil design created by unorthodox means, with the twin tail design from the Consolidated Model 31 flying boat, together on a new fuselage. This new fuselage was intentionally designed around twin bomb bays, each one being the same size and capacity of the B-17 bomb bays.
In January 1939, the USAAC, under Specification C-212, formally invited Consolidated to submit a design study for a bomber with longer range, higher speed and greater ceiling than the B-17. The specification was written such that the Model 32 would automatically be the winning design. The program was run under the umbrella group, "Project A", an Air Corps requirement for an intercontinental bomber that had been conceived in the mid-1930s. Although the B-24 did not meet Project A goals, it was a step in that direction. Project A led to the development of the Boeing B-29 and Consolidated's own B-32 and B-36.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Consolidated / Convair / Vultee
Consolidated B-24 Liberator
"The Flying Coffin"
First flight 29 December 1939, Produced 1940–1945


Consolidated Convair Vultee
Consolidated B-24 Liberator
Consolidated B-24 Liberator
"The Flying Coffin"
First flight 29 December 1939, Produced 1940–1945
General characteristics
- Crew: 11 (pilot, co-pilot, navigator, bombardier, radio operator, nose turret, top turret, 2 waist gunners, ball turret, tail gunner)
- Length: 67 ft 2 in (20.47 m)
- Wingspan: 110 ft (34 m)
- Height: 17 ft 7.5 in (5.372 m)
- Wing area: 1,048 sq ft (97.4 m2)
Powerplant
- Empty weight: (16,556 kg)
- Gross weight: (24,948 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (29,484 kg) plus
- Fuel capacity: 2,344 US gal (1,952 imp gal; 8,870 L) normal capacity; 3,614 US gal (3,009 imp gal; 13,680 L) with long-range tanks in the bomb bay; Oil capacity 131.6 US gal (109.6 imp gal; 498 L) in four self-sealing nacelle hopper tanks
- Powerplant: 4 × Pratt & Whitney R-1830-35 Twin Wasp, R-1830-41 or R-1830-65 14-cylinder two-row air-cooled turbo-supercharged radial piston engines, 1,200 hp (890 kW) each
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 297 mph (478 km/h, 258 kn) at 25,000 ft (7,600 m)
- Cruise speed: 215 mph (346 km/h,
- Stall speed: 95 mph (153 km/h,
- Range: 1,540 mi (2,480 km, 1,340 nmi) at 237 mph (206 kn; 381 km/h) and 25,000 ft (7,600 m) with normal fuel and maximum internal bomb load
- Ferry range: 3,700 mi (6,000 km,
- Service ceiling: 28,000 ft (8,500 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,025 ft/min (5.21 m/s)
Armament
- Guns: 10 × .50 caliber (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine guns in 4 turrets and two waist positions
- Bombs:
- Short range (400 mi [640 km]): 8,000 pounds (3,600 kg)
- Long range (800 mi [1,300 km]): 5,000 pounds (2,300 kg)
- Very long range (1,200 mi [1,900 km]): 2,700 pounds (1,200 kg)
.
Links to Youtube & Others
The Liberator originated from a United States Army Air Corps (USAAC) request in 1938 for Consolidated to produce the Boeing B-17 under license.
Consolidated
B-24 Liberator
The B-24 was employed in operations in every combat theater during World War II.
Youtube Link
The B-24D on display flew combat missions from North Africa in 1943-1944 with the 512th Bomb Squadron