Airbus Group, Inc. EADS HC-144 Ocean Sentry
 |
|
| Role | Search-and-rescue aircraft |
|---|---|
| National origin | Spain |
| Manufacturer | Airbus Military (prime contractor EADS North America) |
| Introduction | 2009 |
| Status | In active service |
| Primary user | United States Coast Guard |
| Number built | 18[1] |
Developed from CASA/IPTN CN-235
.
History Airbus Group, Inc.
EADS HC-144 Ocean Sentry

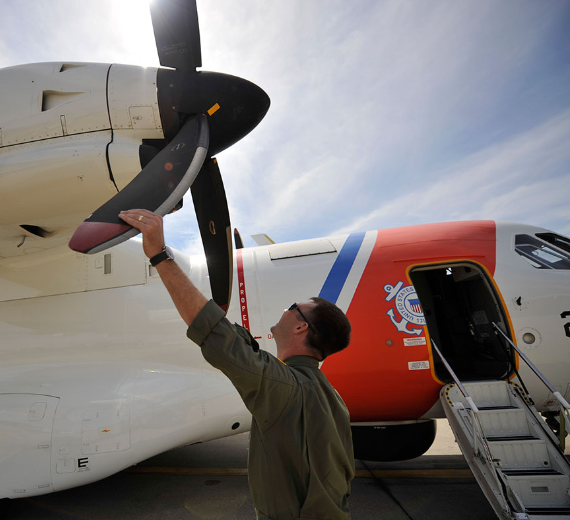
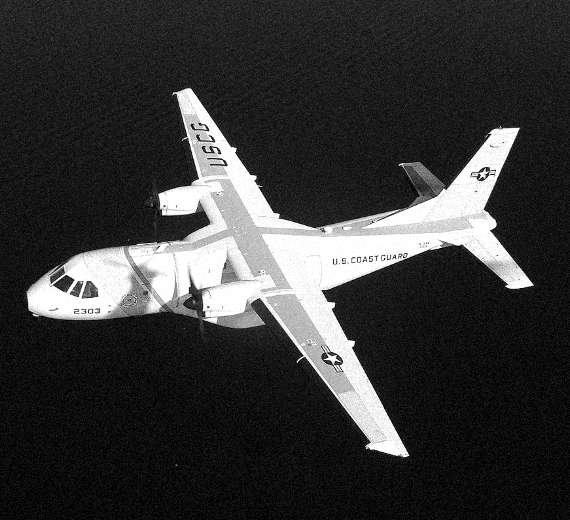
The EADS HC-144 Ocean Sentry is a medium-range, twin-engined turboprop aircraft used by the United States Coast Guard in the search-and-rescue and maritime patrol missions. Based on the Airbus Military CN-235, it was procured as a "Medium Range Surveillance Aircraft." The HC-144 is supplied by Airbus Group, Inc, formerly EADS North America, and is built in Spain by Airbus Military.
Intended to replace the Dassault HU-25 Guardian jet, the HC-144A Ocean Sentry is part of the Coast Guard's Integrated Deepwater System Program of recapitalization and new-asset acquisition. Based on the CN-235-300 MP Persuader, the maritime patrol version of the CN-235 military transport, the HC-144 offers a longer endurance than the HU-25 it is replacing in U.S. Coast Guard service, as well as better performance in the low-level observation role. The HC-144A has an eight-hour endurance, which makes it suited for the command and control and search and rescue roles. Its rear ramp provides for transport of standard cargo pallets. It also features short takeoff and landing capability.
Selection

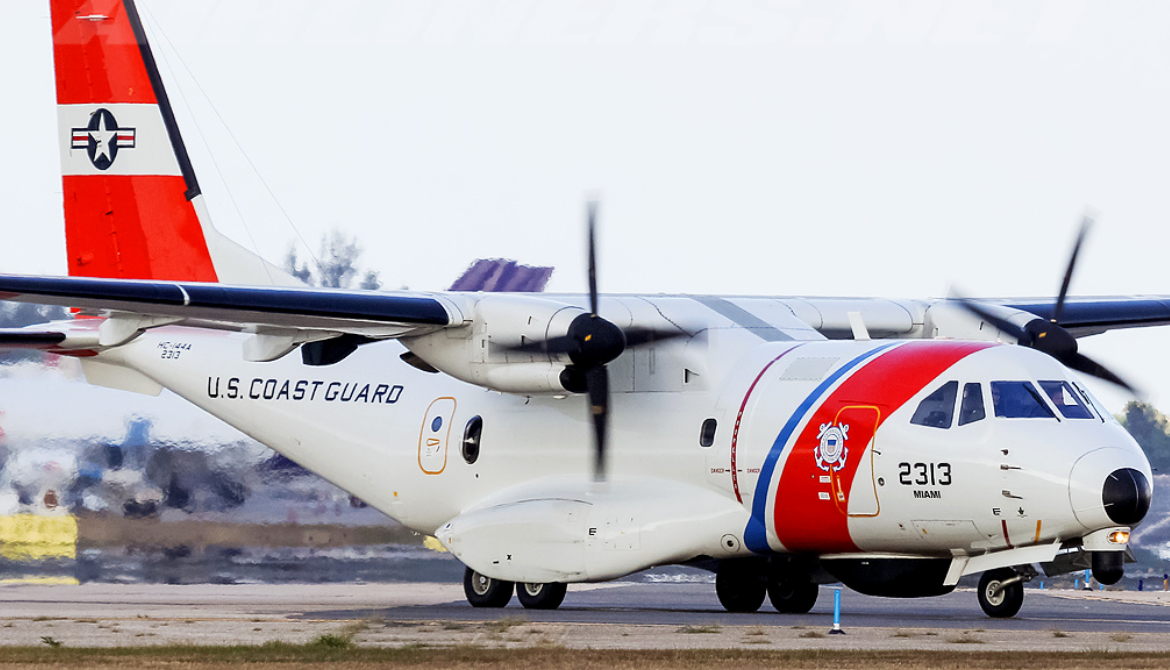
The first HC-144 was delivered to the U.S. Coast Guard in December 2006. Initial Operational Capability (IOC) was achieved in April 2009; thirteen Ocean Sentry aircraft were operational with the Coast Guard in January 2011. A total of 36 aircraft were planned to be procured, with twelve Mission System Pallets being swapped between the operational aircraft.
The HC-144A has been involved in several missions during its career, including involvement in the Marquis Cooper search-and-rescue mission, the response to the 2010 Haiti earthquake, environmental missions monitoring the Deepwater Horizon oil spill, transporting endangered marine animals for rehabilitation, and being involved with Hurricane Sandy relief efforts. In June 2014, the Coast Guard's fleet of 17 HC-144s reached 50,000 flight hours, five years after achieving IOC. The Ocean Sentry is flown more hours per airframe in a year than any other Coast Guard aircraft
0
HrEndurance
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Airbus Group, Inc.
EADS HC-144 Ocean Sentry


Airbus Group, Inc.
EADS HC-144 Ocean Sentry
General characteristics
- Crew: six
- Length: 70 ft 3 in (21.41 m)
- Wingspan: 84 ft 8 in (25.81 m)
- Height: 26 ft 10 in (8.18 m)
- Wing area: 636 sq ft (59.1 m2)
Powerplant
- Empty weight: 21,605 lb (9,800 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (16,502 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × General Electric CT7 turboprop, 1,870 shp (1,390 kW) each
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 272 mph (437 km/h, 236 kn)
- Range: 1,801 mi (2,898 km, 1,565 nmi)
- Endurance: 8.7 hours
Related development
-
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Links to Youtube & Others
The "Camel" may be regarded as the prototype of the Consolidated response to the USAAS's 1924 requirement for a new primary trainer. In the early summer of 1924.
Airbus Group, Inc.
EADS HC-144 Ocean Sentry
The HC-144A uses electronic systems on the Mission System Pallet roll-on, roll-off electronics suite from Lockheed Martin,
Youtube Link
The first HC-144 was delivered to the U.S. Coast Guard in December 2006. Initial Operational Capability (IOC) was achieved in April 2009; thirteen Ocean Sentry aircraft were operational with the Coast Guard in January 2011.