Republic Aviation
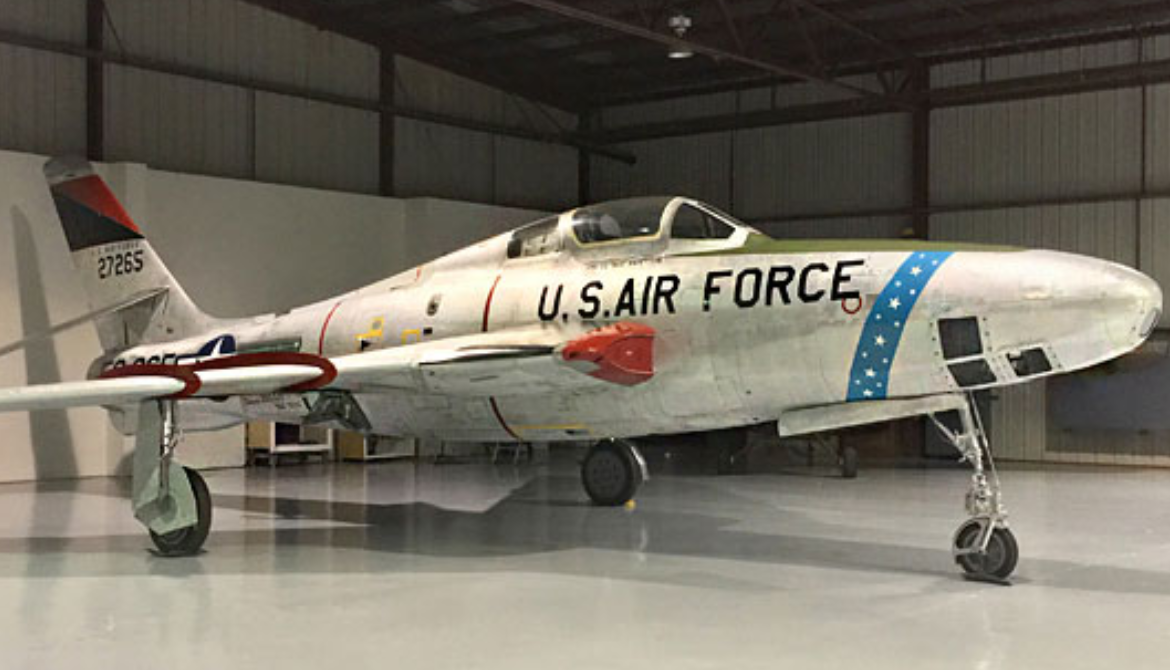
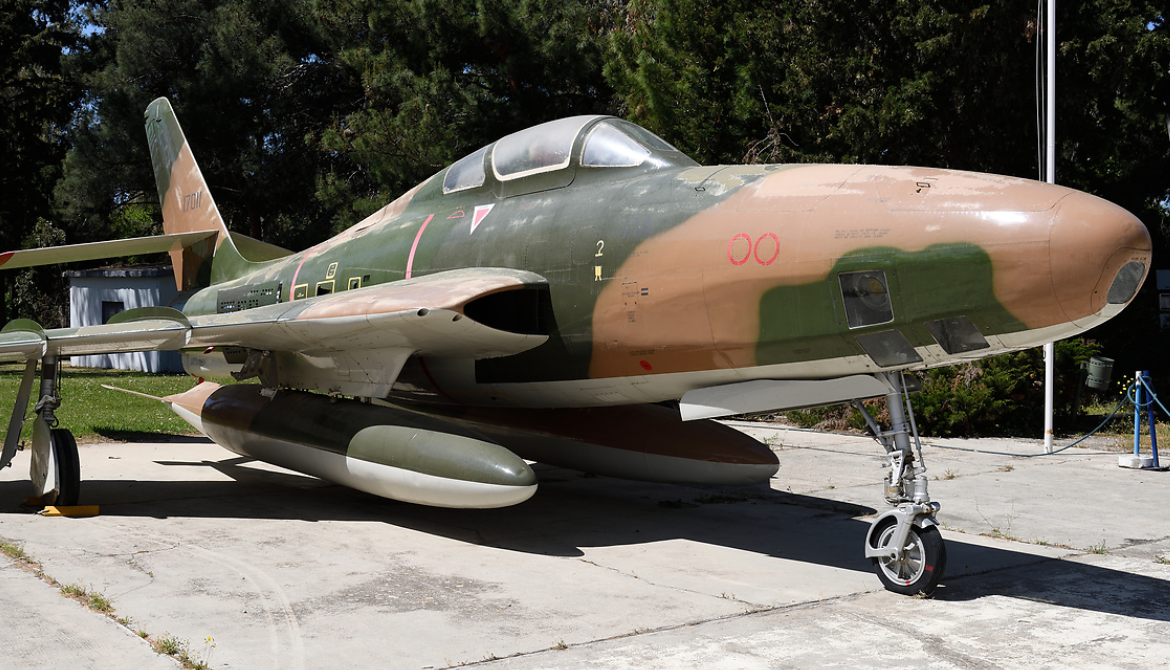
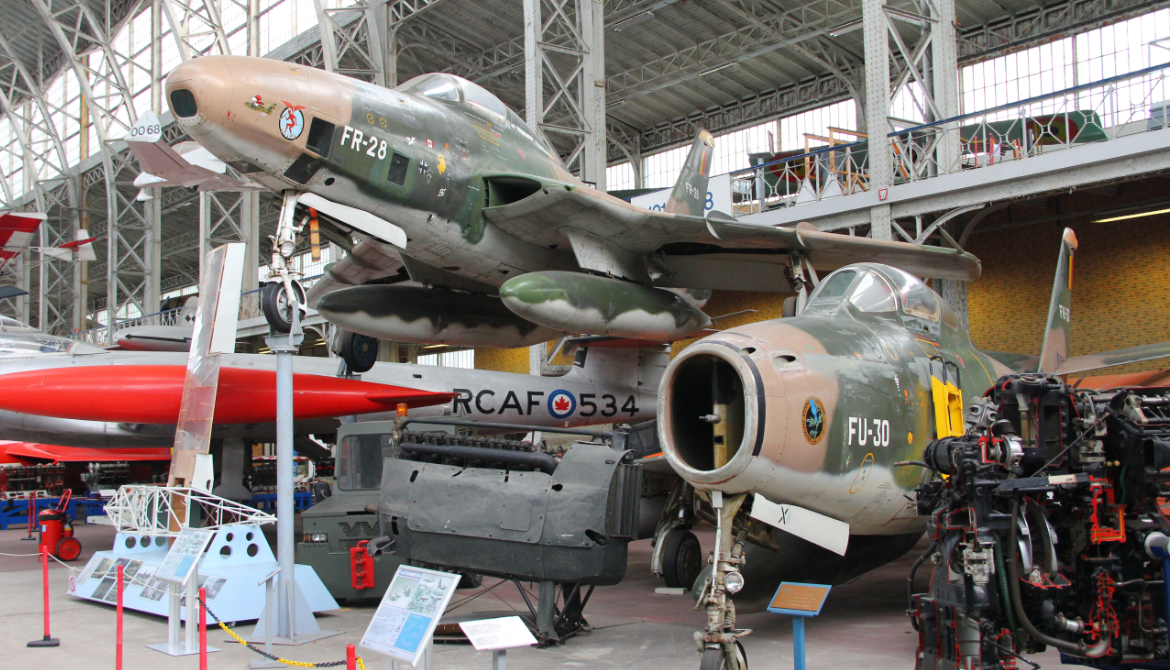
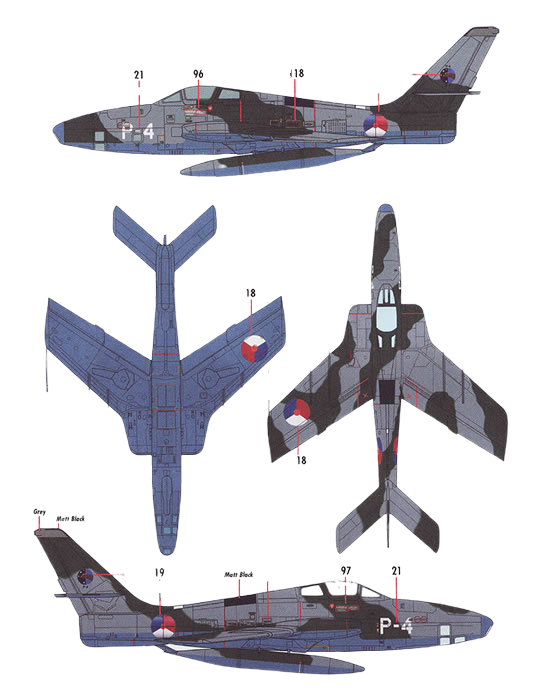
RF-84F Thunderflash
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Fighter-bomber Reconnaissance aircraft |
Manufacturer Republic Aviation
First flight 28 February 1950
Introduction November 1954
Retired 1972 (USAF)
1991 (Greece)
Primary user United States Air Force
Number built 3,428
Developed into Republic F-84F Thunderstreak
Republic XF-84H Thunderscreech
Republic XF-91 Thunderceptor
.
History Republic Aviation Corporation.
RF-84F Thunderflash
First Flight 28 February 1950
Introduction November 1954

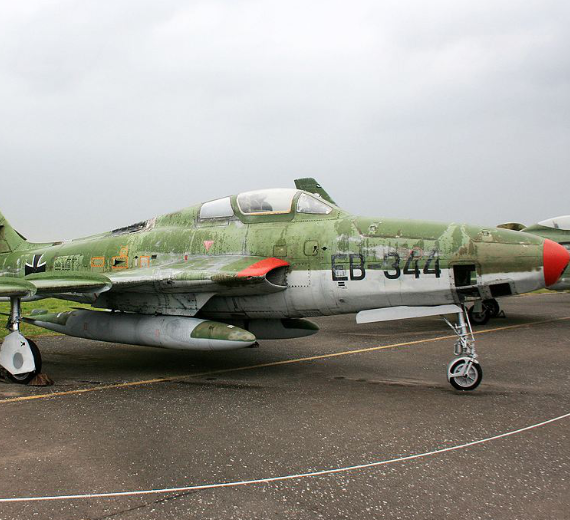
Republic USA, a reconnaissance version of the F-84F Thunderstreak with a different nose and side air intakes.
In late 1949, the American Republic factory began designing the F-84F. The RF-84 was a reconnaissance version with a different nose due to the camera installation in the nose, and intakes were placed on the sides of the fuselage. Developed in 1951, the first prototype flew in 1952.
In the third YF-84F prototype, the nose air intake was omitted as a test to accommodate a new radar system. This took up considerably more space. The aircraft was equipped with air intakes in the wing root and a closed nose. However, this resulted in some loss of thrust, further reducing performance. This was reason enough to abandon this project. Because the USAF's now-aged RF-80 was due for replacement, the aircraft was later used as a prototype for photo-reconnaissance. The first pre-production model, the YRF-84F (51-1828), was completed in February 1952. Differences from the third YF-84 included enlarged air intakes. The nose was widened to accommodate the cameras, and four .50 caliber machine guns were mounted in the wing root. A total of six cameras could be carried.
Variants

The Republic XF-84H Thunderscreech prototype 
One of the YF-84J prototypes - YF-84F
- Two swept-wing prototypes of the F-84F, initially designated YF-96.
- F-84F Thunderstreak
- Swept wing version with Wright J65 engine. Tactical Air Command aircraft were equipped with Low-Altitude Bombing System (LABS) for delivering nuclear bombs. 2,711 built, 1,301 went to NATO under Mutual Defense Assistance Program (MDAP).
- GRF-84F
- 25 RF-84Fs were converted to be carried, and launched from the bomb bay of a GRB-36F bomber as part of the FICON project. The aircraft were later redesignated RF-84K.
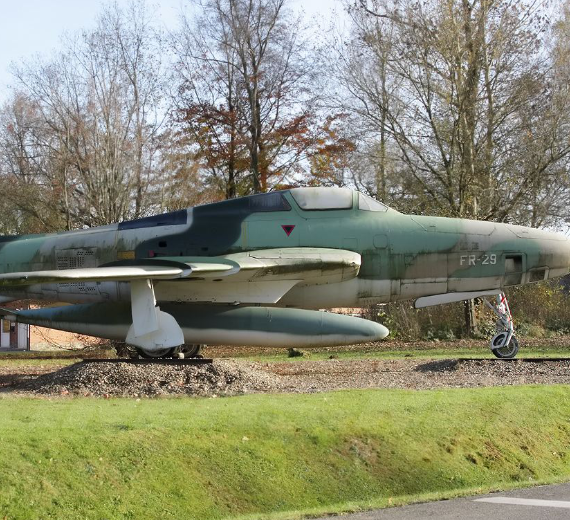
- RF-84F Thunderflash
- Reconnaissance version of the F-84F with intakes relocated to the wing-roots, 715 built.
- RF-84K Thunderflash (FICON)
- RF-84F with a retractable probe for hookup with carrier GRB-36Ds and tailplanes with marked anhedral, 25 redesignated from RF-84F.
- XF-84H
- Two F-84Fs were converted into experimental aircraft. Each was fitted with an Allison XT40-A-1 turboprop engine of 5,850 shaft horsepower (4,365 kW) driving a supersonic propeller. Ground crews dubbed the XF-84H the Thunderscreech due to its extreme noise output.[1]
- YF-84J
- Two F-84Fs were converted into YF-84J prototypes with enlarged nose intakes and a deepened fuselages for the General Electric J73 engine; the YF-84J reached Mach 1.09 in level flight on 7 April 1954. The project was cancelled due to the excessive cost of converting existent F-84Fs.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
MachAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Republic Aviation Corporation.
RF-84F Thunderflash


Republic Aviation Corporation. Originally known as the Seversky Aircraft Company
RF-84F Thunderflash
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 1
- Length: 38 ft 1 in (11.61 m)
- Wingspan: 36 ft 5 in (11.10 m)
- Height: 12 ft 7 in (3.84 m)
- Wing area: 260 sq ft (24 m2)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: (5,033 kg)
- Gross weight: (8,457 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (10,671 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 450 US gal (1,700 L) internal fuel
- Powerplant: 1 × Allison J35-A-29 turbojet engine, 5,600 lbf (25 kN) thrust
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: (1,001 km/h, 541 kn) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 483 mph (777 km/h, 420 kn) at 35,000 ft (11,000 m)
- Range: (1,080 km, (internal fuel)
- Ferry range: 2,000 mi (3,200 km, 1,700 nmi) with external tanks
- Service ceiling: (12,300 m)
Armament
-
- Guns: 6 × .50 in (12.7 mm) M3 Browning machine guns, 300 rounds per gun
- Rockets: Up to 32 5-inch rockets
- Bombs: 4,000 lb (1,800 kg) bombs, including 1 × Mark 7 nuclear bom
Links to Youtube & Others
The Bf 108A first flew in 1934, followed by the Bf 108B in 1935. The Bf 108B used the substantially larger, 12.67 litre displacement Argus As 10 air-cooled inverted V8 engine. The nickname Taifun (German for "typhoon") was given to her own aircraft by Elly Beinhorn, a well-known German pilot, and was generally adopted
Republic
RF-84F Thunderflash
Development of the type continue and in 1935 the Bf 108B appeared with the fin and rudder having undergone modifications.
Youtube Link
Conceived as a competitive aircraft the Bf 108 would take part in the 1936 Berlin Olympics.