Beech Aircraft
T-34C Turbo Mentor
|
|
|
|---|
.
History Beech Aircraft Corporation
Beechcraft T-34C Turbo Mentor
The last Turbo-Mentor rolled
off the production line in 1990.

After a production hiatus of almost 15 years, the T-34C Turbo-Mentor powered by a Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-25 turboprop engine was developed in 1973. The original T-34's modified Bonanza/Debonair-style wing was replaced with a variant of the larger Beech Baron wing, and the original Bonanza/Debonair-style landing gear was replaced with the landing gear from the even-larger Beech Duke.
Design and development
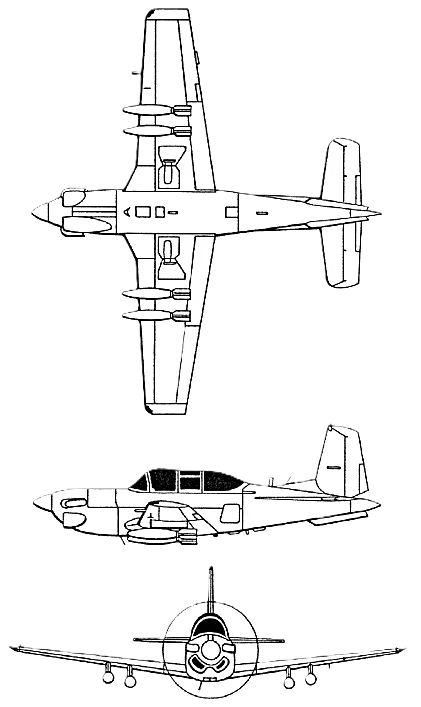
The T-34C Turbomentor is an unpressurized two-seat, tandem cockpit low-wing turboprop trainer whose mission is to train Navy and Marine Corps pilots.
The T-34C is used to provide primary flight training for student pilots. As a secondary mission, approximately 10 percent of the aircraft provide pilot proficiency and other aircraft support services to Commander, Naval Air Force, U.S. Atlantic Fleet; Commander, Naval Air Force, U.S. Pacific Fleet; and Naval Air Systems Command's "satellite sites" operated throughout the continental United States.
The T-34C was procured as a commercial-derivative aircraft certified under an FAA Type Certificate. The T-34C was derived from the civilian Beechcraft Bonanza. Throughout its life, the aircraft has been operated and commercially supported by the Navy using FAA processes, procedures and certifications.
Testing
On 7 May 1944, Beech Test Pilot Vern Carstens Flew The XA-38 On Its Maiden Flight From The Company's Wichita Airfield. The Aircraft Proved Satisfactory In All Respects And Better Than Expected In Some, Including Top Speed.
Photo Gallery
Beech Aircraft Corporation
Beechcraft T-34C Turbo Mentor


Beech Aircraft Corporation
Beechcraft T-35B/C Turbo Mentor
General Info
-
-
-
-
Crew: Two
Length: 28 ft 8½ in (8.75 m)
Wingspan: 33 ft 3⅞ in (10.16 m)
Height: 9 ft 7 in (2.92 m)
-
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
Empty weight: 2,960 lb (1,342 kg)
Max. takeoff weight: 4,300 lb (1,950 kg) (T-34C-1 weapons trainer - 5,500 lb (2,494 kg))
Powerplant: 1 × Model PT6A-25 turbo-prop engine (Pratt & Whitney Aircraft of Canada)
-
Performance
-
Never exceed speed: 515 km per hour
Cruise speed: (396 km/h, 246 mph) max cruise at (5,180 m)
Range: 708 nmi (1,311 km, 814 mi) at 180 knots (333 km/h, 207 mph) and 20,000 ft (6,100 m)
Service ceiling: 30,000 ft (9,145 m)
Armament
-
- None
-
Links to Youtube & Others
World War II
The Beechcraft T-34 Mentor is an American propeller-driven, single-engine, military trainer aircraft derived from the Beechcraft Model 35 Bonanza
Beechcraft Aircraft
Beechcraft T-35 Turbo
The Beechcraft T-34 Mentor is an American propeller-driven, single-engine, military trainer aircraft derived from the Beechcraft Model 35 Bonanza.
Youtube Link
The earlier versions of the T-34, dating from around the late 1940s-1950s, were piston-engined. These were succeeded by the upgraded T-34C Turbo-Mentor, powered by a turboprop engine.









.png)



