Bell AH-1Z ZuluCobra
Attack helicopter
 |
|
| An AH-1Z of the USMC | |
| Role | Attack helicopter |
|---|---|
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Bell Helicopter |
| First flight | 8 December 2000 |
| Introduction | 30 September 2010 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | United States Marine Corps Royal Bahraini Air Force Czech Air Force |
| Produced | 2000–present |
| Number built | 195 |
| Developed from | Bell AH-1 SuperCobra |
.
History Bell Textron Inc.
Bell AH-1Z Viper/ZuluCobra attack helicopter
First flight 8 December 2000
Produced 2000–present
Design

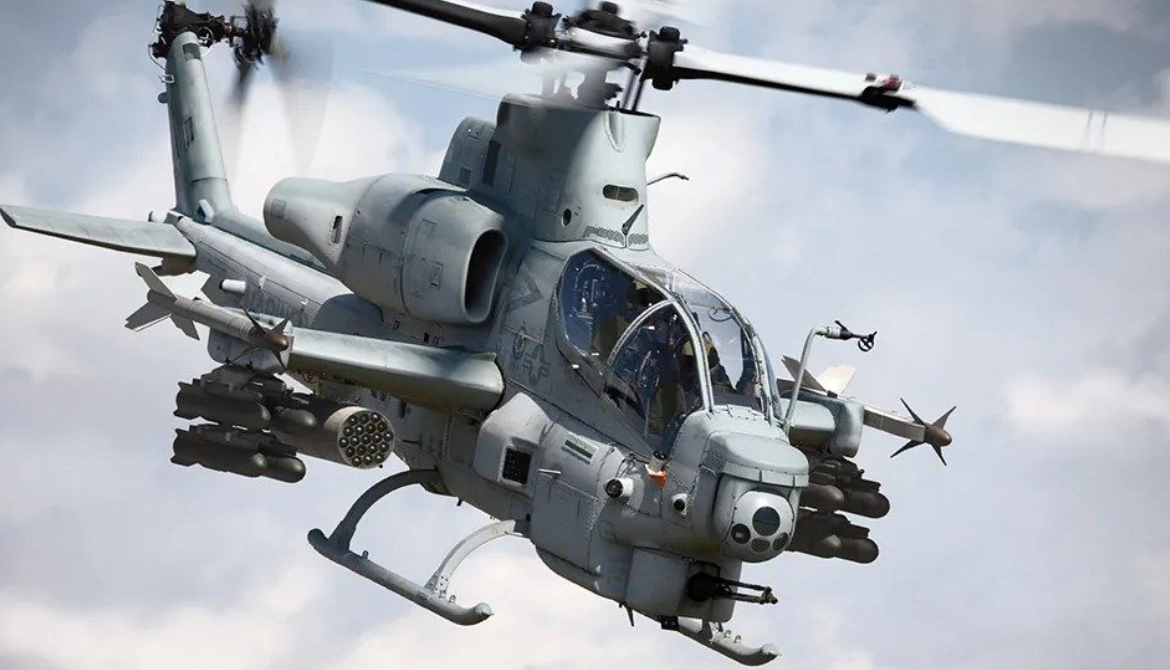
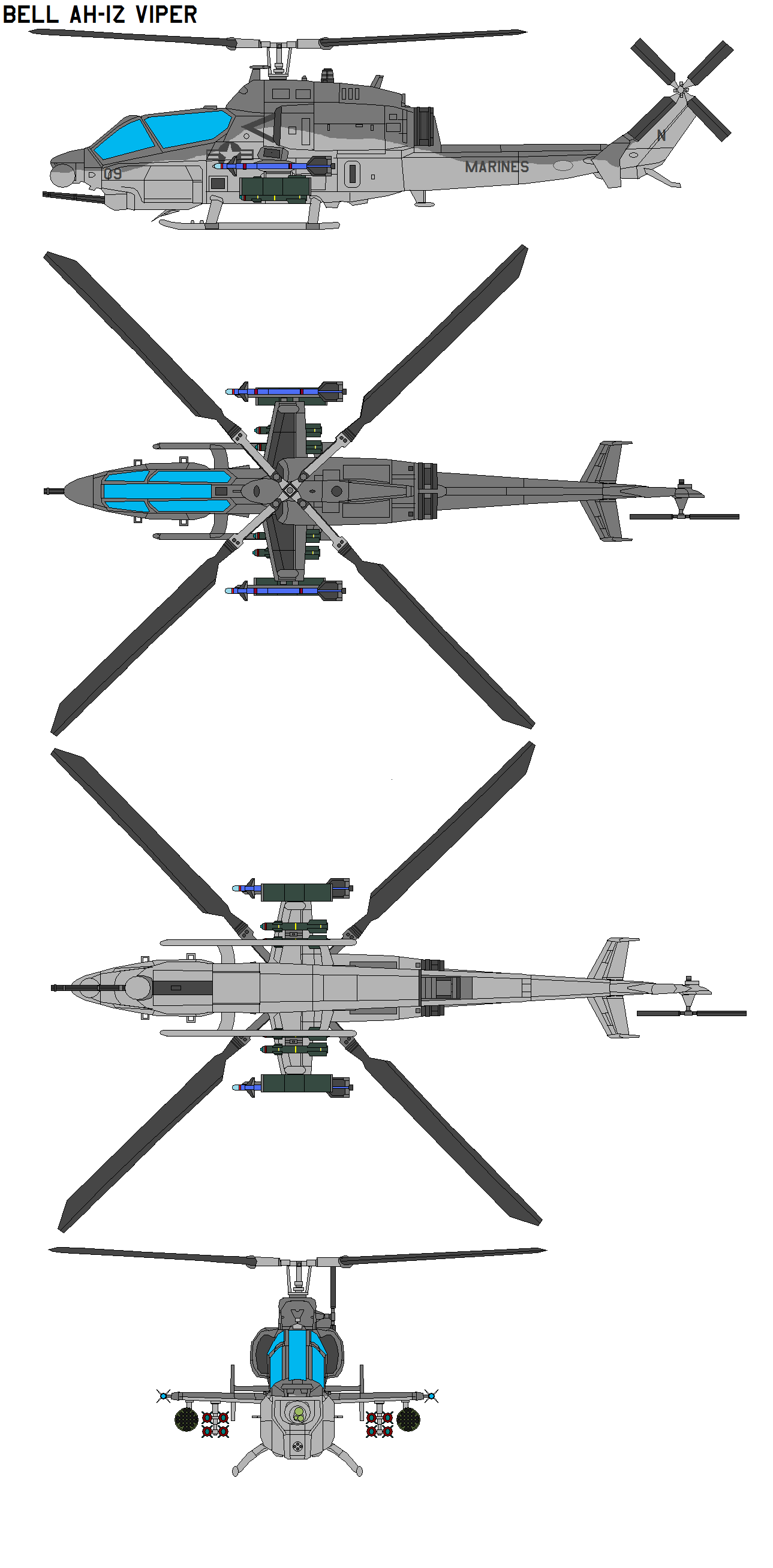
The Bell AH-1Z Viper is an attack helicopter derived from the earlier Bell AH-1 SuperCobra. When contrasted against its predecessor, it incorporates various improvements and advances, including new rotor technology, upgraded military avionics, updated weapons systems, and electro-optical sensors in an integrated weapons platform. Amongst other advantages provided by these changes, it has improved survivability and can locate targets at longer ranges and also attack them using precision weapons The airframe was extensively redesigned to maximise crashworthiness; measures include energy-absorbing landing gear, fuel vapor inerting systems, self-sealing fuel tanks, energy-attenuating crashworthy seating, and a mass retention design approach applied to many major components. Active systems include countermeasure dispensers, radar warning, incoming/on-way missile warning, on-fuselage laser spot warning systems, and the Hover Infrared Suppression System (HIRSS) to protect the engine exhausts.
Operational history

United States
During May 2005, it was announced that the AH-1Z had completed its first round of sea-based flight trials. On 15 October 2005, the USMC, through the Naval Air Systems Command, accepted delivery of the first AH-1Z production standard helicopter. Both the AH-1Z and UH-1Y completed their developmental testing during early 2006. During the first quarter of 2006, initial examples of the type were transferred to the Operational Test Unit at the NAS Patuxent River to undergo operational evaluation (OPEVAL) testing. In February 2008, both the AH-1Z and UH-1Y began the second and final portion of OPEVAL testing. On 30 September 2010, the USMC declared that the AH-1Z had attained combat readiness0
KmCeiling
0
KmMAX RANGE
0
Km/HAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
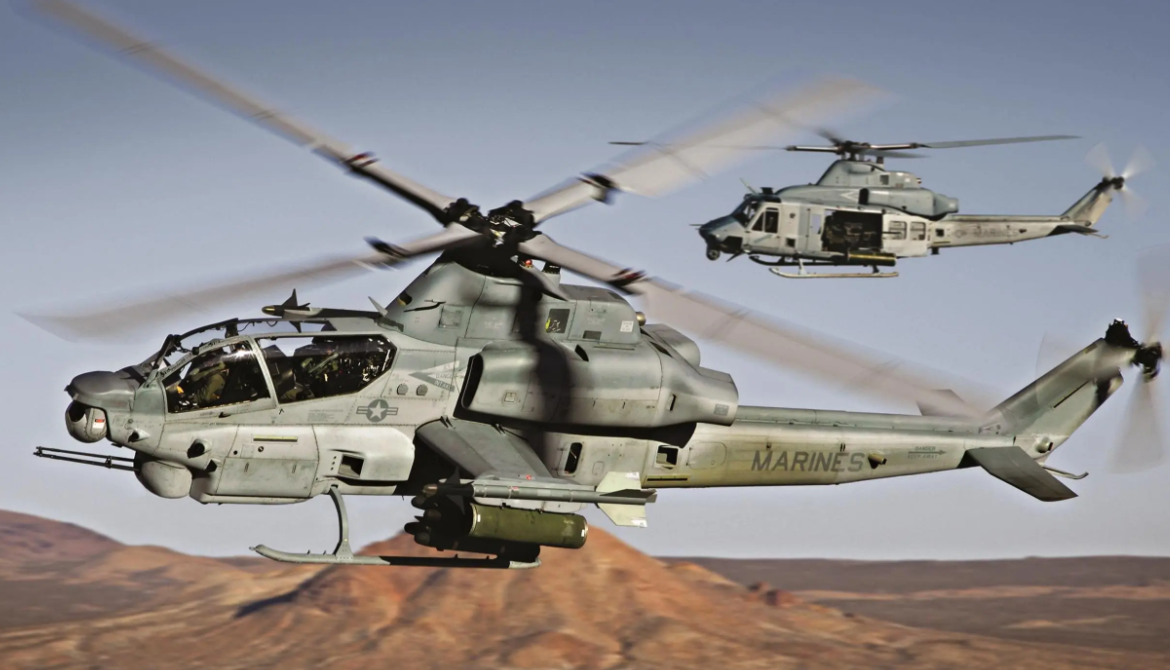
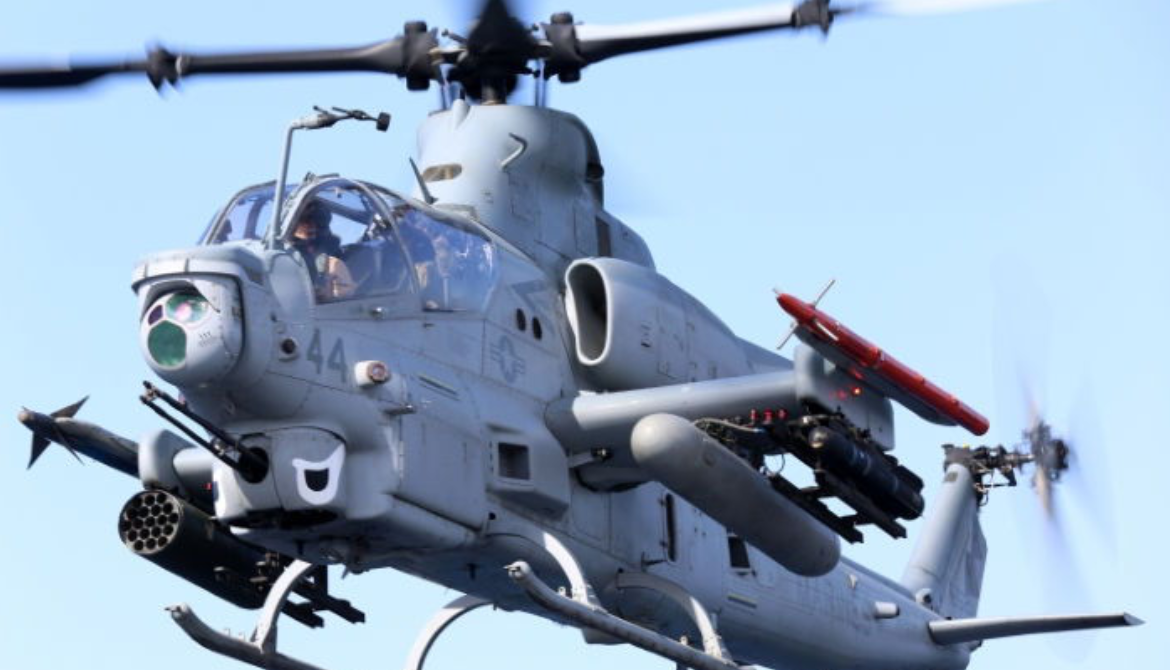
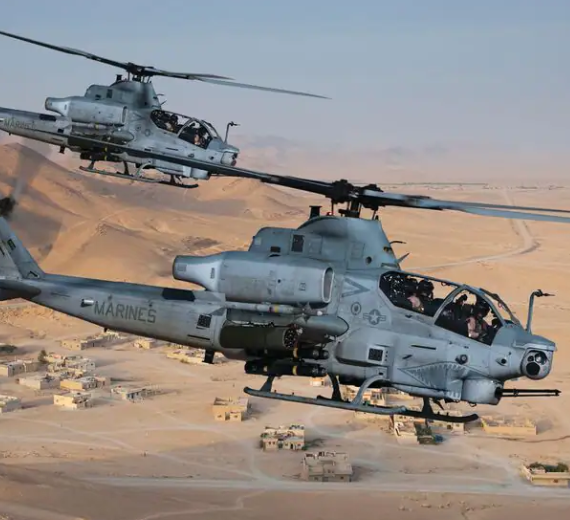
Photo Gallery
Bell AH-1Z Viper/ZuluCobra.


Bell Textron Inc.
Bell AH-1G Viper or ZuluCobra
General Info
- Crew: Two: pilot and co-pilot/gunner (CPG)
- Length: 58 ft 3 in (17.75 m)
- Height: 14 ft 4 in (4.37 m)
- Empty weight: 12,300 lb (5,579 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 18,500 lb
-
-
Powerplant
- Powerplant: 2 × General Electric T700-GE-401C turboshaft, 1,800 shp (1,300 kW) each
- Main rotor diameter: 48 ft (15 m)
- Main rotor area: 1,808 sq ft (168.0 m2) 4-bladed main and tail rotors
Specifications
- Cruise speed: 160 kn (180 mph, 300 km/h)
- Never exceed speed: 222 kn (255 mph, 411 km/h)
- Range: 370 nmi (430 mi, 690 km)
- Combat range: 125 nmi (144 mi, 232 km) with 2,500 lb (1,100 kg) payload
- Service ceiling: 20,000 ft (6,100 m) +
- Rate of climb: 2,790 ft/min (14.2 m/s)
-
-
Armament
- Guns:
-
- 1 × 20 mm (0.787 in) M197 three-barreled rotary cannon in the A/A49E-7 turret (750 round ammo capacity)
-
Hardpoints: 6 total pylon stations on stub wings with a capacity of 5,764 lb (2,615 kg) maximum, with provisions to carry combinations of:
-
Rockets:
-
Missiles:
- AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles – one mounted on each wing tip station (two total)
-
Rockets:
Links to Youtube & Others
The UH-60 entered service with the U.S. Army's 101st Combat Aviation Brigade of the 101st Airborne Division in June 1979.[92] The U.S. military first used the UH-60 in combat during the invasion of Grenada in 1983.
Bell AH-1G Viper
attack helicopter
Eliminate threats at unimaginable range. With anti-armor and air-to-air missiles, the Bell AH-1Z
Youtube Link
Eliminate threats at unimaginable range. With anti-armor and air-to-air missiles, the Bell AH-1Z














.svg.png)