Bell Aircraft
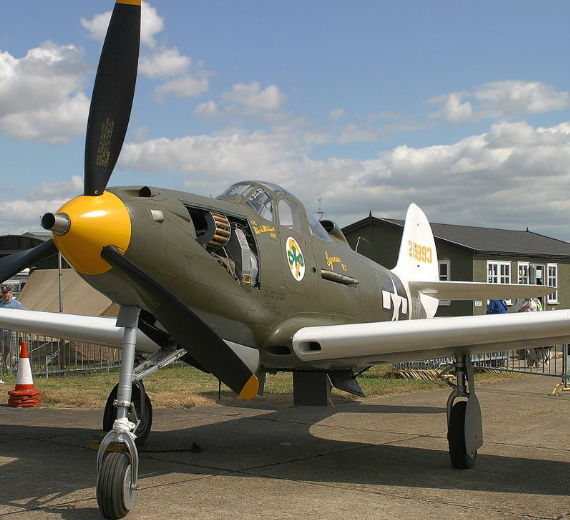
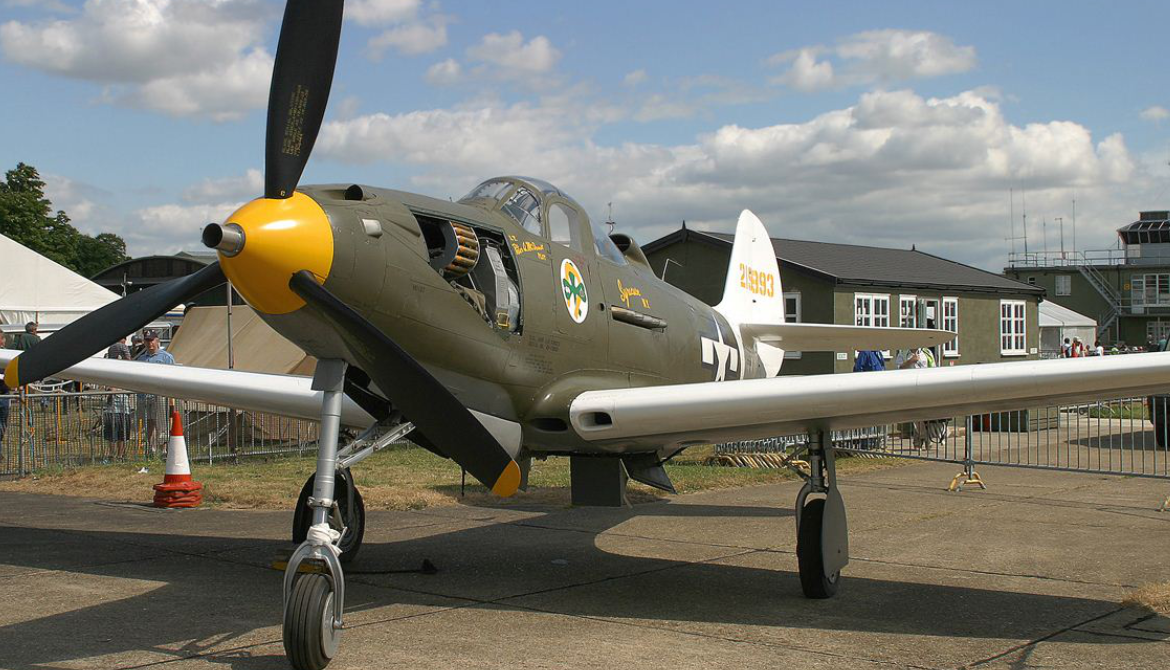
Bell -39A Airacobra
 |
|
| P-39Q Saga Boy II of Lt. Col. Edwin S. Chickering, CO 357th Fighter Group, July 1943 | |
| Role | Fighter |
|---|---|
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Bell Aircraft |
| First flight | 6 April 1938 |
| Introduction | 1941 |
| Status | Retired |
| Primary users | United States Army Air Forces Soviet Air Force Royal Air Force |
| Produced | 1940 – May 1944 |
| Number built | 9,588 |
| Variants | Bell XFL Airabonita Bell P-63 Kingcobra Bell P-76 |
.
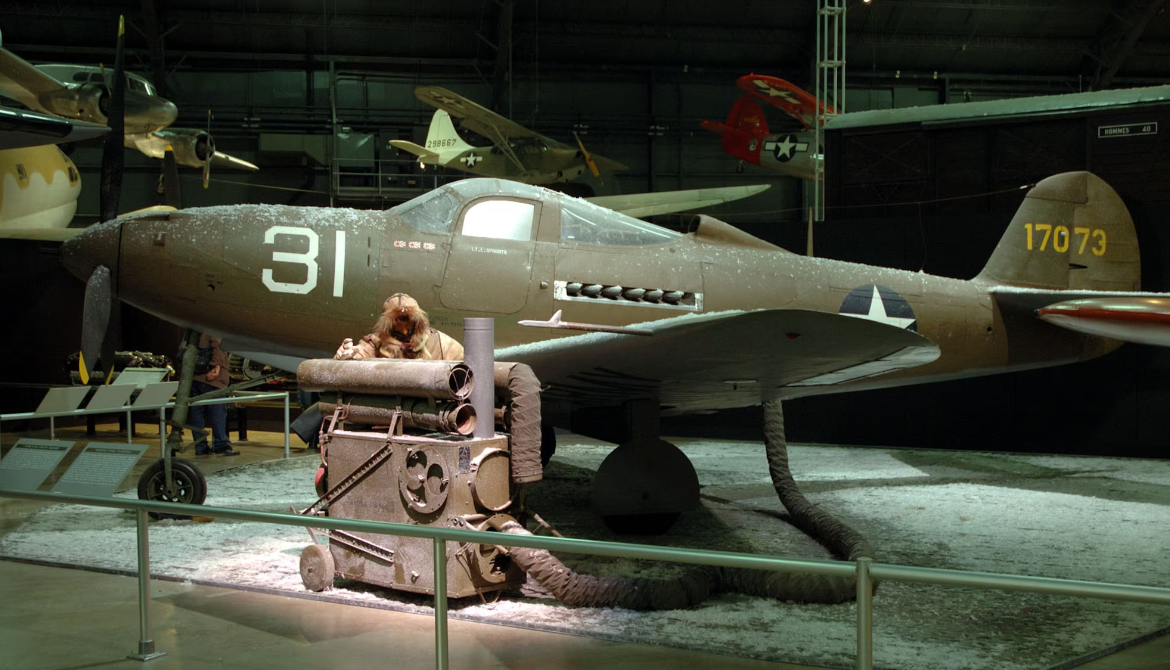
History Bell Textron Inc.
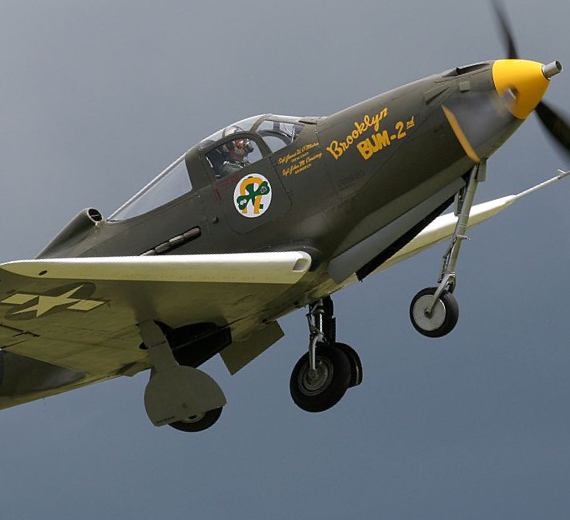
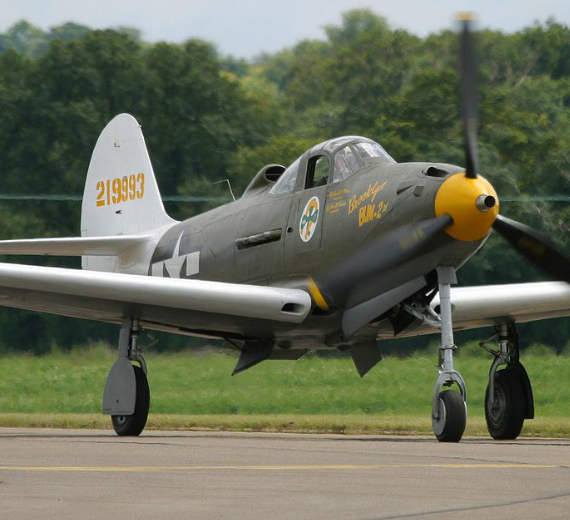
Bell P-39A Airacobra Fighter WW2 "Kobrushka"
Design and development
Circular Proposal X-609
In February 1937, Lieutenant Benjamin S. Kelsey, Project Officer for Fighters at the United States Army Air Corps (USAAC), and Captain Gordon P. Saville, fighter tactics instructor at the Air Corps Tactical School, issued a specification for a new fighter via Circular Proposal X-609. It was a request for a single-engine high-altitude "interceptor" having "the tactical mission of interception and attack of hostile aircraft at high altitude". Despite being called an interceptor, the proposed aircraft's role was simply an extension of the traditional pursuit (fighter) role, using a heavier and more powerful aircraft at higher altitude. Specifications called for at least 1,000 lb (450 kg) of heavy armament including a cannon, a liquid-cooled Allison engine with a General Electric turbo-supercharger, tricycle landing gear, a level airspeed of at least 360 mph (580 km/h) at altitude, and a climb to 20,000 ft (6,100 m) within six minutes. This was the most demanding set of fighter specifications the USAAC had presented to that date. Although Bell's limited fighter design work had previously resulted in the unusual Bell YFM-1 Airacuda, the Model 12 proposal adopted an equally original configuration with an Allison V-12 engine mounted in the middle of the fuselage, just behind the cockpit, and a propeller driven by a shaft passing beneath the pilot's feet under the cockpit floor.
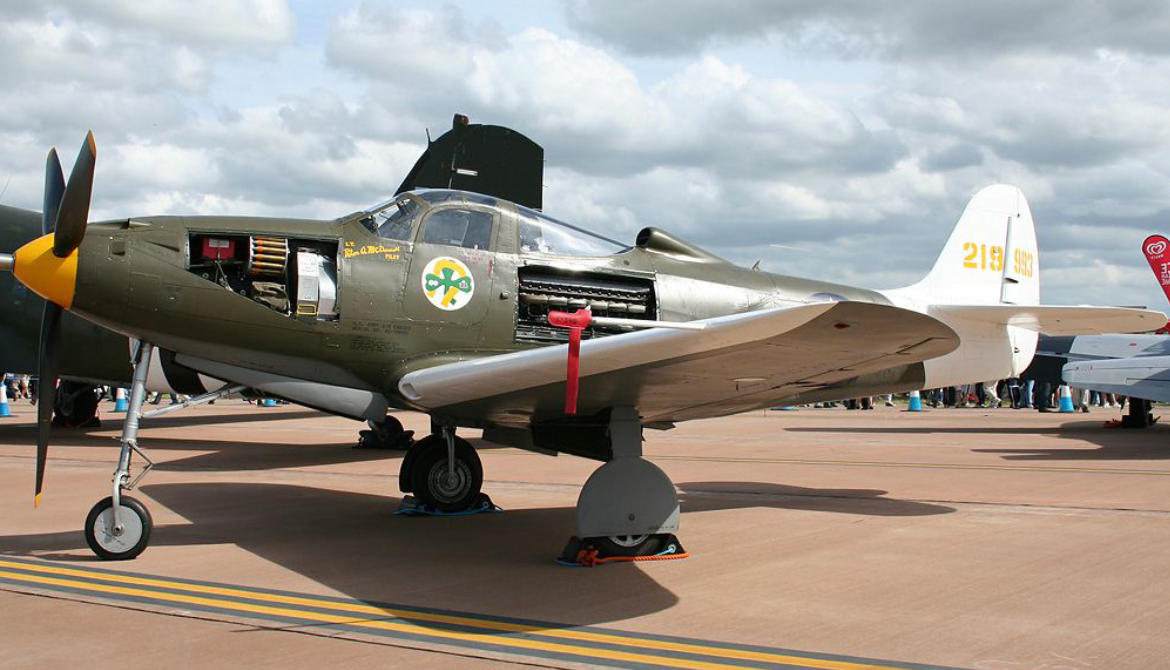
 The weapons bay of the P-39.
The weapons bay of the P-39.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmMAX RANGE
0
Km/HAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Bell P-39A Airacobra Fighter WW2


Bell Textron Inc.
Bell P-39A Airacobra Fighter WW2
General Info
- Crew: One
- Length: 30 ft 2 in (9.19 m)
- Wingspan: 34 ft 0 in (10.36 m)
- Height: 12 ft 5 in (3.78 m)
- Wing area: 213 sq ft (19.8 m2)
- Empty weight: 6,516 lb (2,956 kg)
- Gross weight: 7,570 lb (3,434 kg)
-
-
Powerplant
- Max takeoff weight: 8,400 lb (3,810 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Allison V-1710-85 V-12 liquid-cooled piston engine, 1,200 hp (890 kW) at 9,000 ft (2,743 m) (emergency power)
- Propellers: 3-bladed constant-speed propeller
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 389 mph (626 km/h, 338 kn)
- Stall speed: 95 mph (153 km/h, 83 kn) power off, flaps and undercarriage down
- Never exceed speed: 525 mph (845 km/h, 456 kn)
- Range: 525 mi (845 km, 456 nmi) on internal fuel
- Service ceiling: (11,000 m)
-
-
Armament
- Guns:
-
- 1 × 37 mm M4 cannon firing through the propeller hub
- 2 × .50 caliber synchronized Browning M2 machine guns, nose-mounted
- 2 × .50 caliber Browning M2 machine guns one each wing
- Bombs: Up to 500 lb (230 kg) of bombs under wings and belly
-
-
Links to Youtube & Others
The UH-60 entered service with the U.S. Army's 101st Combat Aviation Brigade of the 101st Airborne Division in June 1979.[92] The U.S. military first used the UH-60 in combat during the invasion of Grenada in 1983.
Bell P-39A Airacobra Fighter WW2
Eliminate threats at unimaginable range. With anti-armor and air-to-air missiles, the Bell AH-1Z
Youtube Link
Eliminate threats at unimaginable range. With anti-armor and air-to-air missiles, the Bell AH-1Z















.svg.png)