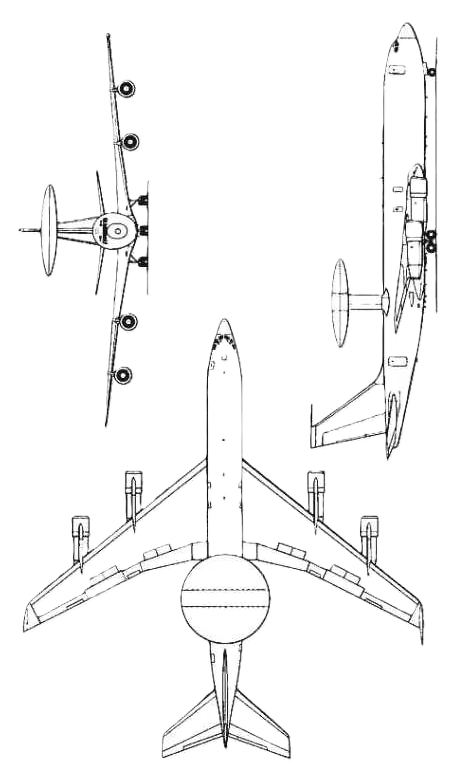
Boeing E-3 Sentry AWACS battlefield management aircraft
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History Boeing Battlefield management aircraft
Boeing E-3 Sentry AWACS
Manufactured 1977–1992
First flight EC-137D: 9 February 1972
E-3: 25 May 197

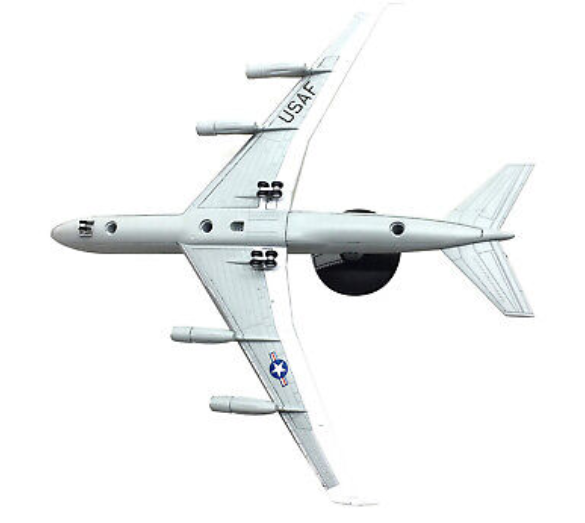
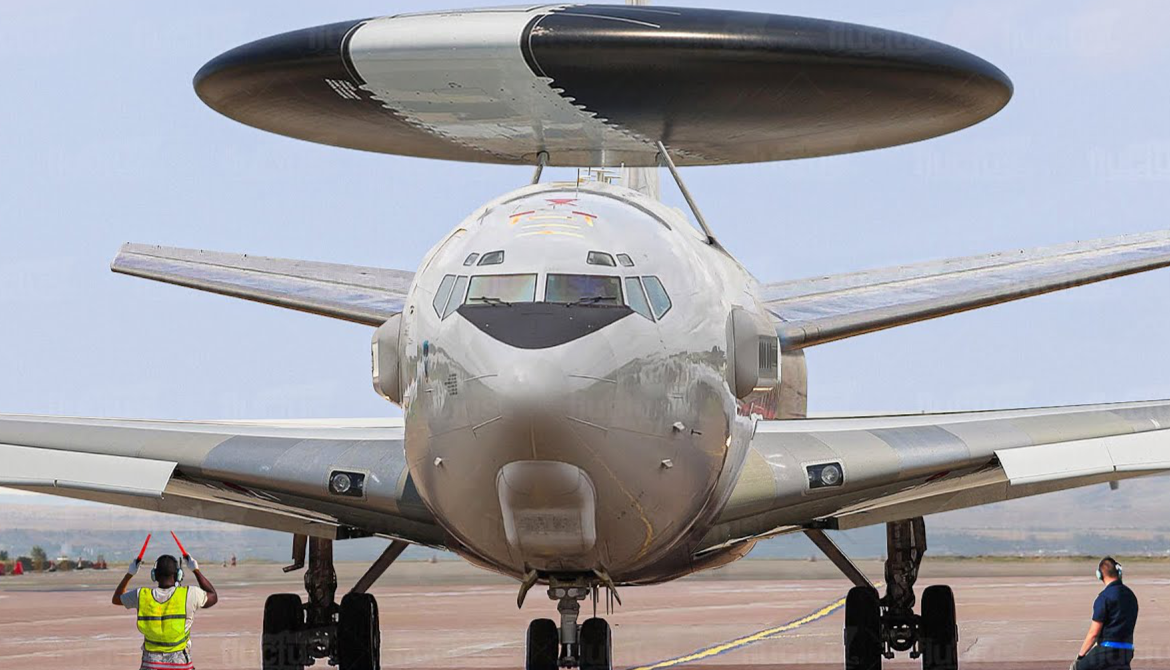
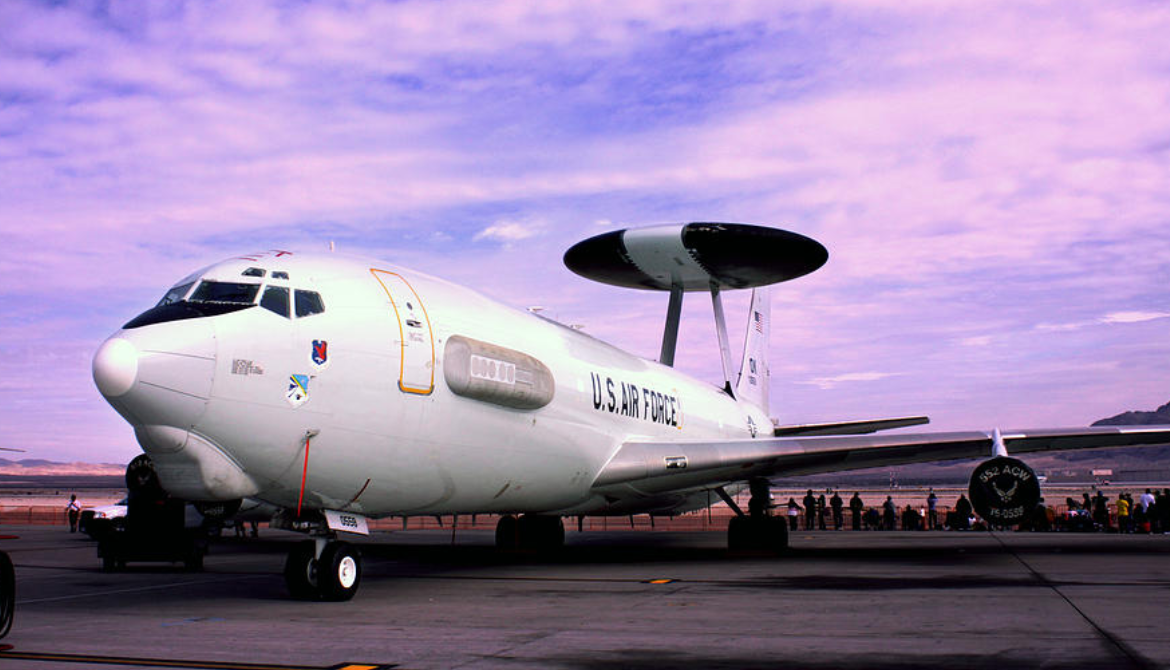
The Boeing E-3 Sentry is an American airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) aircraft developed by Boeing. E-3s are commonly known as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System). Derived from the Boeing 707 airliner, it provides all-weather surveillance, command, control, and communications, and is used by the United States Air Force, NATO, French Air and Space Force, Royal Saudi Air Force and Chilean Air Force. The E-3 has a distinctive rotating radar dome (rotodome) above the fuselage. Production ended in 1992 after 68 aircraft had been built.
In the mid-1960s, the U.S. Air Force (USAF) was seeking an aircraft to replace its piston-engined Lockheed EC-121 Warning Star, which had been in service for over a decade. After issuing preliminary development contracts to three companies, the USAF picked Boeing to construct two airframes to test Westinghouse Electric's and Hughes's competing radars. Both radars used pulse-Doppler technology, with Westinghouse's design emerging as the contract winner. Testing on the first production E-3 began in October 1975.
Design

The E-3 Sentry's airframe is a modified Boeing 707-320B Advanced model. Modifications include a rotating radar dome (rotodome), uprated hydraulics from 241 to 345 bar (3500–5000 psi) to drive the rotodome, single-point ground refueling, air refueling, and a bail-out tunnel or chute. A second bail-out chute was deleted to cut mounting costs.
USAF and NATO E-3s have an unrefueled range of 7,400 km (4,600 mi) or 8 hours of flying.[] The newer E-3 versions bought by France, Saudi Arabia, and the UK are equipped with newer CFM56-2 turbofan engines, and these can fly for about 11 hours or more than 9,250 km (5,750 mi). The Sentry's range and on-station time can be increased through air-to-air refueling and the crews can work in shifts by the use of an on-board crew rest and meals area. The aircraft are equipped with one toilet in the rear, and a urinal behind the cockpit. Saudi E-3s were delivered with an additional toilet in the rear.
Avionics
The unpressurized rotodome is 30 ft (9.1 m) in diameter, 6 ft (1.8 m) thick at the center, and is held 11 ft (3.4 m) above the fuselage by 2 struts. It is tilted down at the front to reduce its aerodynamic drag, which lessens its detrimental effect on take-offs and endurance. This tilt is corrected electronically by both the radar and secondary surveillance radar antenna phase shifters. The rotodome uses bleed air, outside cooling doors, and fluorocarbon-based cold plate cooling to maintain the electronic and mechanical equipment temperatures. The hydraulically rotated antenna system permits the AN/APY-1 [uk] and AN/APY-2 passive electronically scanned array radar system[citation needed] to provide surveillance from the Earth's surface up into the stratosphere, over land or water.

Photo Gallery
Boeing Battlefield management aircraft
Boeing E-3 Sentry AWACS
Manufactured 1977–1992
First flight EC-137D: 9 February 1972 E-3: 25 May 197


Boeing E-3C Sentry
Battlefield management aircraft
Manufactured 1977–1992
First flight EC-137D: 9 February 1972 E-3: 25 May 197
General Info 1
-
-
- Crew: Flight crew: 4 (aircraft commander, pilot, navigator, flight engineer)
-
-
-
- Mission crew: 13–19
-
-
- Length: 152 ft 11 in (46.61 m)
- Wingspan: 145 ft 9 in (44.42 m)
- Height: 41 ft 4 in (12.60 m)
- Wing area: 3,050 sq ft (283 m2)
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 185,000 lb (83,915 kg)
- Gross weight: 344,000 lb (156,036 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 347,000 lb (157,397 kg)
- Powerplant: 4 × Pratt and Whitney TF33-PW-100A turbofan, 21,500 lbf (96 kN) thrust each
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 461 kn (531 mph, 854 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 310 kn (360 mph, 580 km/h) optimum
- Range: 4,000 nmi (4,600 mi, 7,400 km)
- Endurance: more than 8 hours without refuelling (about 11 hours with CFM56 engine)
- Service ceiling: 29,000 ft (8,800 m) minimum
General Info 4
-
-
-
Avionics
- AN/APS-133 colour weather radar
- Westinghouse Corporation AN/APY-1 or AN/APY-2 passive electronically scanned array radar system
-
-
Links to Youtube & Others
NATO intends to extend the operational status of its AWACS until 2035 by significantly upgrading fourteen aircraft in the Final Lifetime Extension Program (FLEP) between 2019 and 2026.Upgrades include the expansion of data capacity, expansion of bandwidth for satellite communications, new encryption equipment, new HAVE QUICK radios, upgraded mission computing software and new operator consoles.
Boeing E-3 Sentry AWACS
In February 1987 the UK and France ordered E-3 aircraft in a joint project which saw deliveries start in 1991.
Youtube Link
The first USAF E-3 was delivered in March 1977, and during the next seven years, a total of 34 aircraft were manufactured.











.png)