de Havilland DH.112 Sea Venom/Aquilon
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
.
History de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited
de Havilland DH.112 Sea Venom/Aquilon
"named Spider Crab"

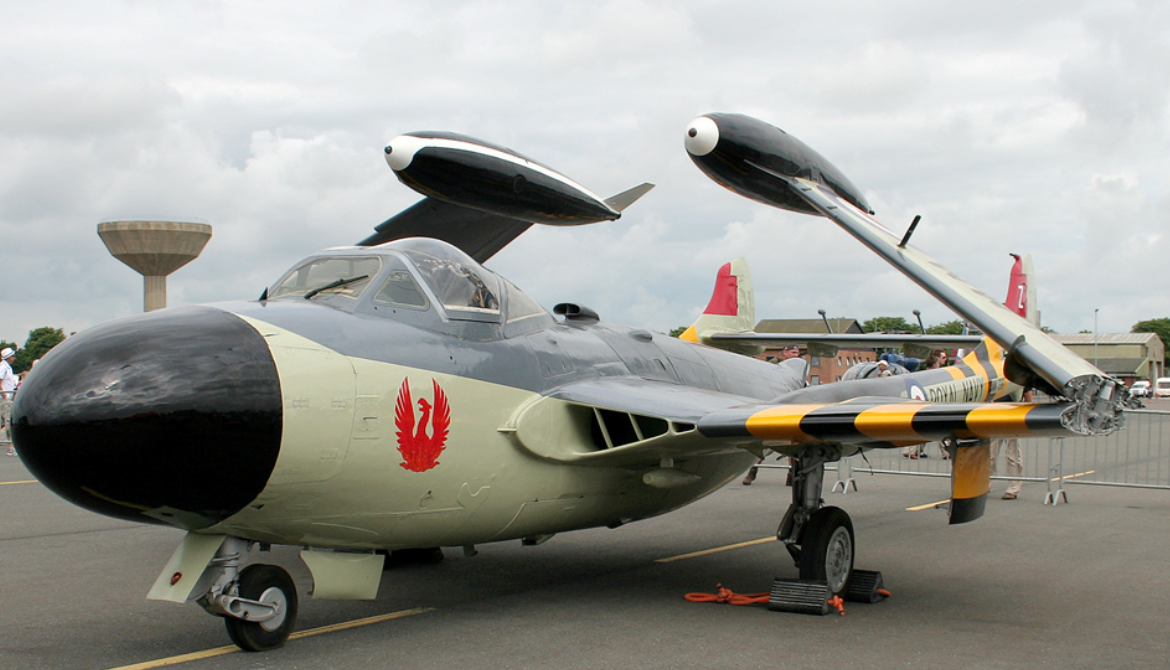
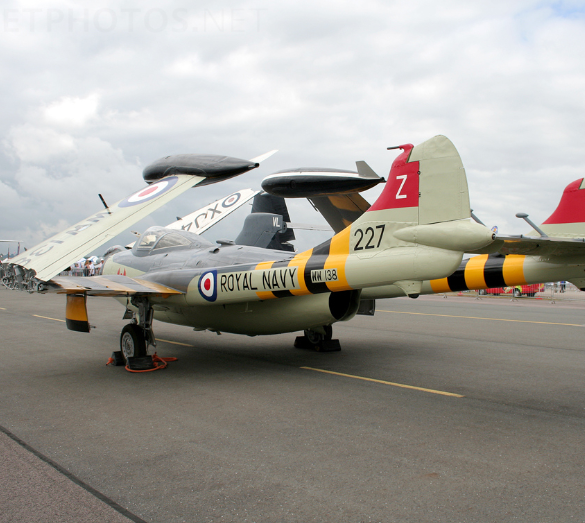
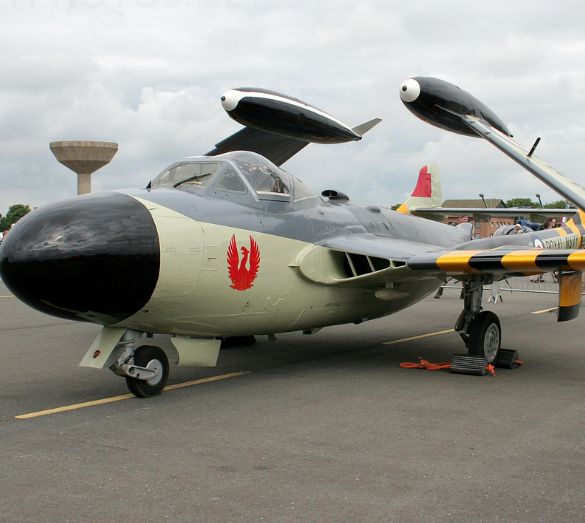
The Sea Venom was the navalised version of the Venom NF.2 two-seat night fighter, and was used as an all-weather interceptor by the Fleet Air Arm (FAA). The necessary modifications for use on the Royal Navy's aircraft carriers included folding wings, a tailhook (which retracted into a characteristic "lip" over the jetpipe) and strengthened, long-stroke undercarriage. The canopy was modified to allow ejection from underwater. The first prototype made its first flight in 1951, and began carrier trials that same year. A further two prototypes were built.[1] The first production Sea Venom took the designation FAW.20 (Fighter, All-Weather). It was powered by a single de Havilland Ghost 103 turbojet engine and its armament was the same as the RAF version. The next variant was the FAW.21, which included the modifications introduced in the Venom NF.2A and NF.3. Some of these modifications included the Ghost 104 engine, a clear-view canopy and American radar. The final Royal Navy variant was the FAW.22 powered by the Ghost 105 engine. A total of 39 of this type were built in 1957–58. Some were later fitted out with the de Havilland Firestreak air-to-air missile.
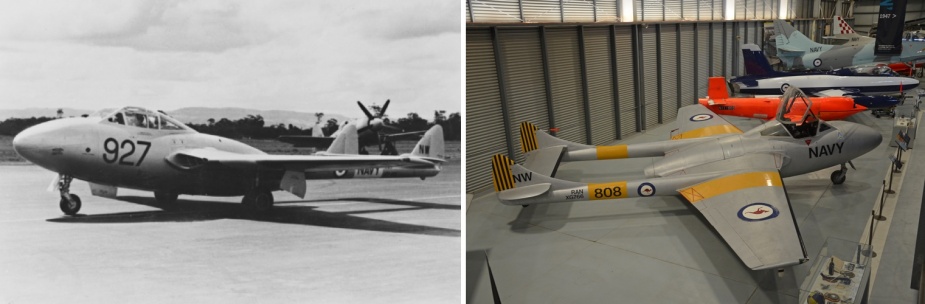 The de Havilland DH.112 Sea Venom is a British postwar carrier-capable jet aircraft developed from the de Havilland Venom. It served with the Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm and with the Royal Australian Navy. The French Navy operated the Aquilon, developed from the Sea Venom FAW.20, built under licence by SNCASE (Sud-Est).
The de Havilland DH.112 Sea Venom is a British postwar carrier-capable jet aircraft developed from the de Havilland Venom. It served with the Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm and with the Royal Australian Navy. The French Navy operated the Aquilon, developed from the Sea Venom FAW.20, built under licence by SNCASE (Sud-Est).
Design

Sea Venom
- DH.112 Sea Venom NF.20
- Prototype Sea Venom, based on Venom NF.2.,three-built.
- FAW.20
- Initial production aircraft, based on Venom NF.2A. 4,850 lbf (21.6 kN) Ghost 103 turbojet engine, AI Mk 10 (US SCR 720) radar. 50 built.
- FAW.21
- Improved version, equivalent to Venom NF.3. 4,950 lbf (22.1 kN) Ghost 104 engine, AI Mk 21 (US APS-57) radar, strengthened long-stroke undercarriage.167 built.
- ECM.21
- Six FAW.21s modified from 1957 for ECM purposes. No armament.
- FAW.22
- More powerful (5,300 lbf (23.6 kN)) Ghost 105 engine, giving improved high-altitude performance. 39 new built.
- ECM.22
- Equivalent of ECM.21, based on FAW.22
- FAW.53
- Australian designation for the Sea Venom FAW.21. 39 built.[
SNCASE Aquilon

SNCASE (Sud-Est) license-built 101 Sea Venom FAW.20 as the Aquilon for the French Navy.,
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited
de Havilland DH.112 Sea Venom/Aquilon
"the Spider crab"


de Havilland Aircraft Company Limited
de Havilland DH.112 Sea Venom
General Info
-
-
-
- Crew: 2
- Length: 36 ft 7 in (11.15 m)
- Wingspan: 42 ft 11 in (13.08 m)
- Height: 8 ft 6.25 in (2.5972 m)
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Gross weight: 15,400 lb (6,985 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 15,800 lb (7,167 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × de Havilland Ghost 105 centrifugal-flow turbojet engine, 5,300 lbf (24 kN) thrust
-
Performance
-
- Maximum speed: 576 mph (927 km/h, 501 kn) at sea level
-
-
-
- 555 mph (482 kn; 893 km/h) at 30,000 ft (9,100 m)
-
-
- Range: 705 mi (1,135 km, 613 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 39,500 ft (12,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 5,750 ft/min (29 m/s)
Armament
-
-
- Guns: 4 × 20 mm (0.787 in) Hispano Mk.V cannon, 150 rpg
- Rockets: 8 × "60lb" RP-3 unguided rockets
- Bombs: 2 × 1,000 lb (454 kg) bombs
-
Links to Youtube & Others
Although in operational use, the Vulcan typically carried various nuclear armaments, the type also had a secondary conventional role. While performing conventional combat missions, the Vulcan could carry up to 21 1,000 lb (454 kg) bombs inside its bomb bay.
de Havilland
DH.112 Sea Venom
The Vulcan's only combat missions took place towards the end of the type's service in 1982. During the Falklands War.
Youtube Link
The missions performed by the Vulcan became known as the Black Buck raids, each aircraft had to fly 3,889 mi (6,259 km) from Ascension Island to reach Stanley on the Falklands. Victor tankers conducted the necessary air-to-air refuelling.














.svg.png)