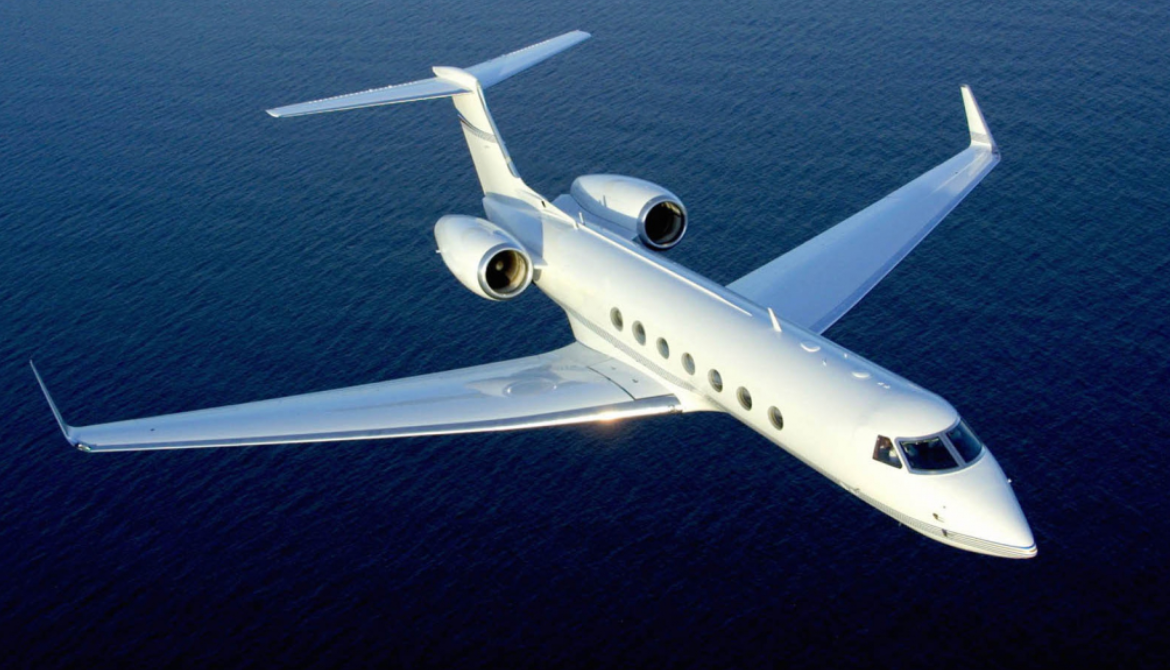
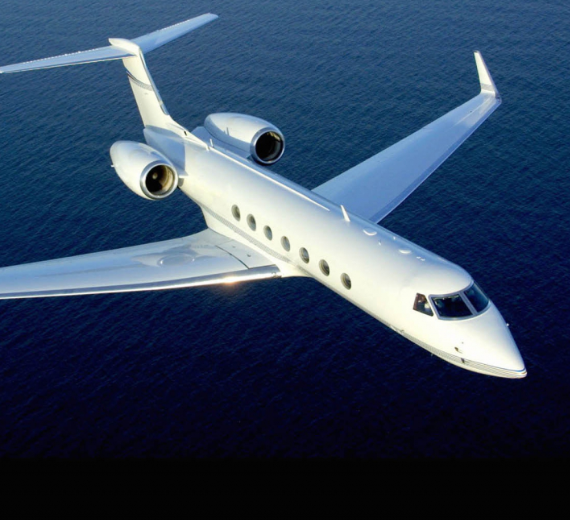
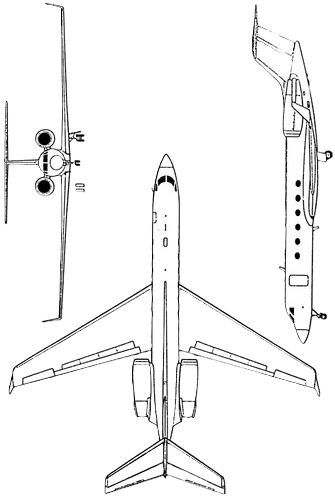
Gulfstream V (Model GV, pronounced "G-five") is a long-range, large business jet aircraft
|
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| National origin | United States | ||||||
| Manufacturer | Gulfstream Aerospace | ||||||
| First flight | November 28, 1995 | ||||||
| Introduction | June 1997 | ||||||
| Status | In service | ||||||
| Primary users | United States Air Force United States Coast Guard United States Navy |
||||||
| Number built | 193 | ||||||
| Developed from | Gulfstream IV | ||||||
| Variants | Gulfstream G550 | ||||||
.
History Gulfstream V (Model GV, pronounced "G-five")
is a long-range,large business jet aircraft
First flight November 28, 1995

The Gulfstream V (Model GV, pronounced "G-five") is a long-range, large business jet aircraft produced by Gulfstream Aerospace, derived from the previous Gulfstream IV. It flies up to Mach 0.885 (508 kn; 940 km/h), up to 51,000 feet (16,000 m) and has a 6,500 nmi (12,000 km) range. It typically accommodates four crew and 14 passengers. It first flew on November 28, 1995, and entered service in June 1997. It is used by the US military under the designation C-37A. It is followed by an improved version, the Gulfstream 550 (Model GV-SP).
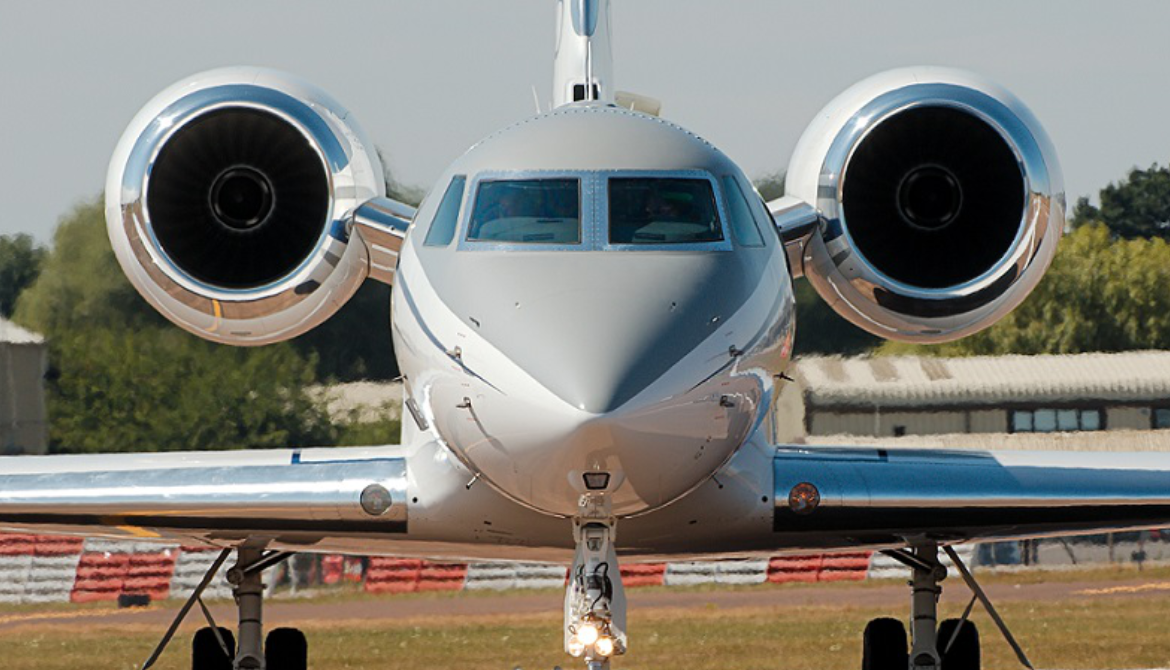
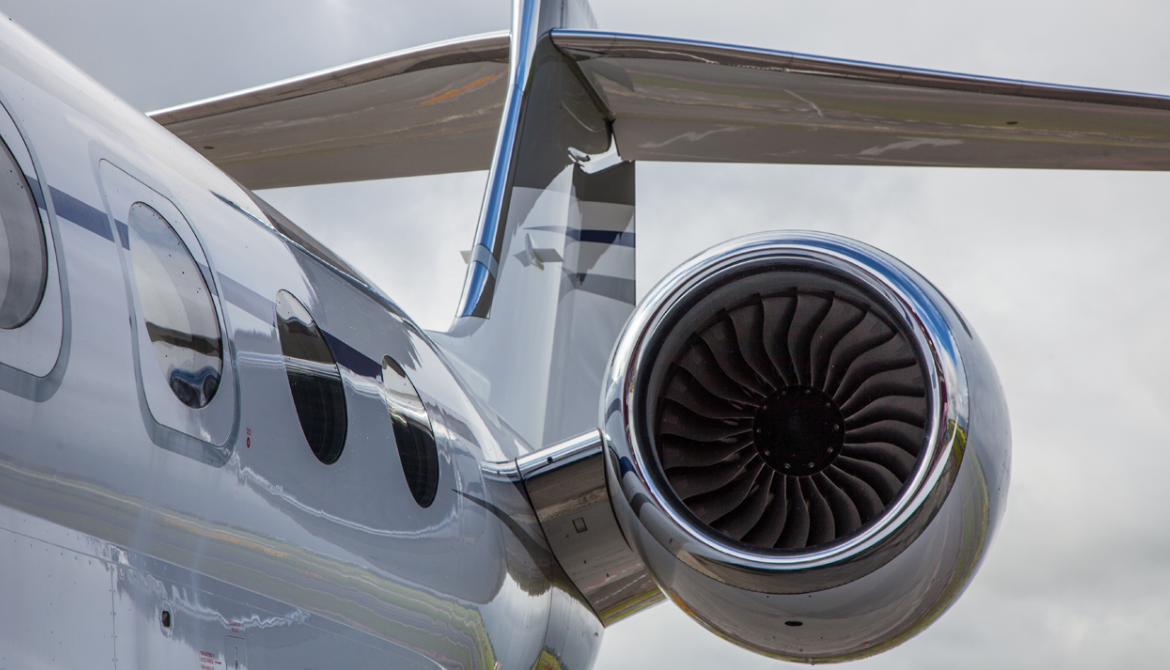
Compared to the Gulfstream IV, the engines are changed from Rolls-Royce Tay to Rolls-Royce BR700-710A1-10 with increased thrust, higher bypass ratio, and Full Authority Digital Engine Controls (FADEC). Operating ceiling is increased from 45,000 to 51,000 ft (14,000 to 16,000 m). It has thrust reversers and composite flight control surfaces. The horizontal tail area is 30% larger, wingspan is increased from 74.6 to 93.5 ft (22.7 to 28.5 m), the fuselage is lengthened by 5 ft (1.5 m) forward of the main entry door, and by 2 ft (0.6 m) aft of the wing. Maximum takeoff and landing weights are increased by 15%.
Variants

- G-V
- Production aircraft powered by two BMW-Rolls-Royce 700-710A1-10 engines.
- C-37A
- United States military designation for the G-V aircraft.[7]
- C-20C
- Modified C-20B with enhanced, secure communications. Used to support senior-level personnel and to provide backup for Air Force One.Only 3 delivered to the Air Force in 1985 as the Reagan administration’s massive investment in “continuity of government” operations upgraded the government’s command-and-control systems.Their tail numbers were 50049, 50050 and 60403.One of three aircraft long tasked with evacuating the president in an emergency and preserving the so-called National Command Authorities,the officials with authority to launch nuclear weapons.The C-20Cs had slightly older dial-and-gauge cockpits to help protect the plane from the electromagnetic pulse that would accompany a nearby nuclear explosion.The gear aboard is top-notch, with special satellite communications networks and special classified defensive measures that would protect the plane during an attack.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Gulfstream V (Model GV, pronounced "G-five") is a long-range, large business jet aircraft
First flight November 28, 1995


Gulfstream V (Model GV, pronounced "G-five")
is a long-range, large business jet aircraft
First flight November 28, 1995
General Info
-
-
-
- Crew: 2
- Capacity: 15–19
- Length: 96.4 ft (29.4 m)
- Wingspan: 93.45 ft (28.48 m)
- Height: 26.85 ft (8.18 m)
- Wing area: 1,137 sq ft (105.6 m2)
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Max takeoff weight: 41,050 kg)
- Maximum Landing Weight :34,200 kg)
- Maximum Zero Fuel Weight : 24,700 kg)
- Maximum Fuel Load : (18,700 kg)
- Maximum Payload : (3,800 kg)
- Payload w/ Max Fuel : (1,500 kg)
- Cabin Length : 43.92 feet (13.39 m)
- Cabin floor Width : (1.60 m)
- Cabin Height : 6.17 feet (1.88 m)
- Powerplant: 2 × Rolls-Royce BR710A1-10 turbofan, 14,750 lbf (65.6 kN) thrust each
-
-
Performance
-
- Maximum speed: Mach 0.88
- Range: 7,500 mi (12,000 km, 6,500 nmi) , long range cruise with 4 crew, 8 passengers
- Endurance: 14hr 28min
- Service ceiling: 51,000 ft (16,000 m)
- Cruise speed : Mach 0.83 (882 km/h)
- Normal cruise range : 5,500 nautical miles (10,186 km), with 5 crew, 12 passengers
- Climb rate : per minute (21.28 m/s)
- Ceiling : 51,000 feet (16,000 m)
Related development
Links to Youtube & Others
In 1986, Boeing bought the company in a bid to improve production at DHC's Downsview Airport plants, as well as better position itself to compete for a new Air Canada order for large intercontinental airliners.
Gulfstream V (Model GV, pronounced "G-five")
Bombardier aimed to produce the Q400 more economically. A deal with its machinists union in June 2017
Youtube Link
The Dash 8 is a turboprop airliner designed by De Havilland Canada. It shares engines and avionics with many other airplane types.