Junkers
Ju 87 "Stuka"
 3 3 |
|
| Type | Dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft |
|---|---|
National origin Nazi Germany
Manufacturer Junkers
Designer Hermann Pohlmann
First flight 17 September 1935
Introduction 1936
Retired 1945
Primary users Luftwaffe
Bulgarian Air Force
Regia Aeronautica / Royal Romanian Air Force
Number built 6,000
.
History Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG JFM
Junkers Ju 87 "Stuka"
First Flight 17 September 1935
Introduction 1936

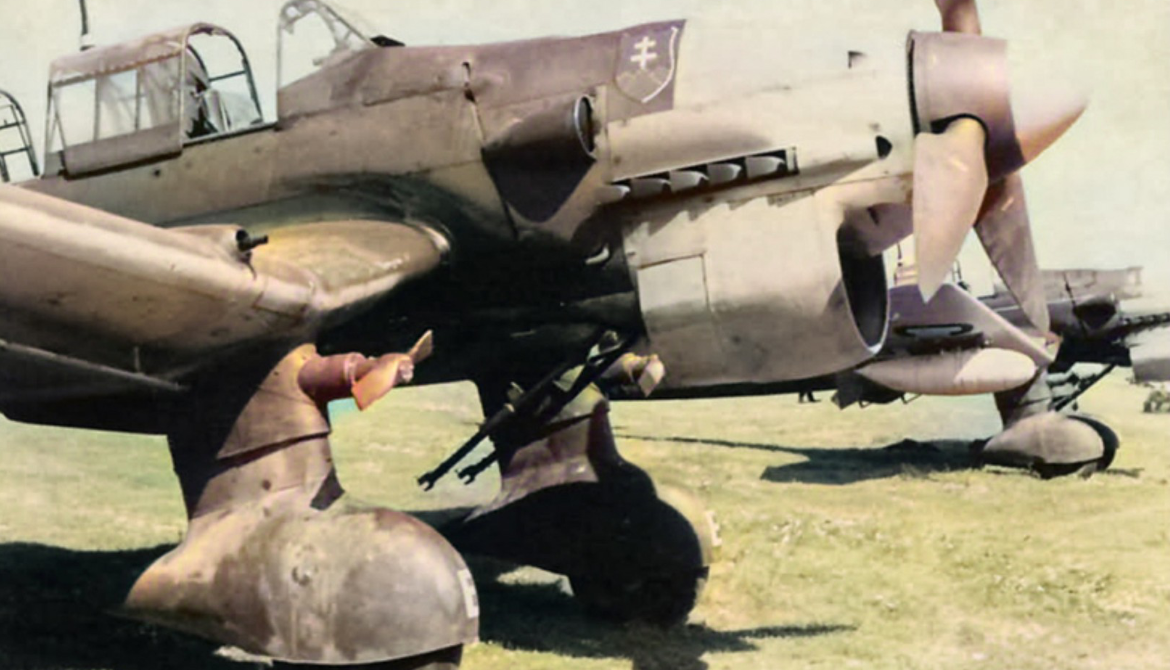
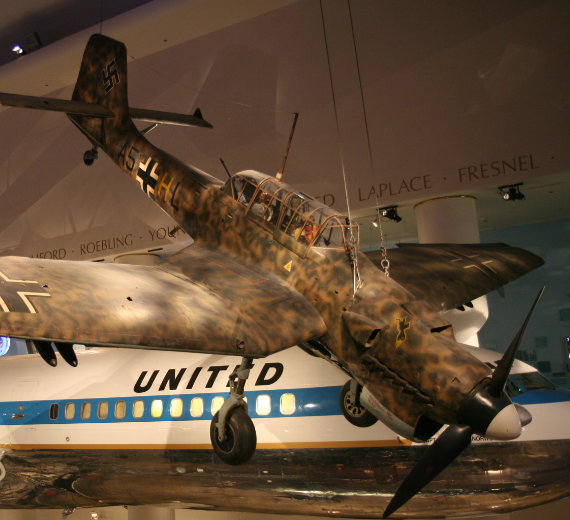
The Junkers Ju 87 or "Stuka" is a German dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft. Designed by Hermann Pohlmann, it first flew in 1935. The Ju 87 made its combat debut in 1937 with the Luftwaffe's Condor Legion during the Spanish Civil War of 1936–1939 and served the Axis in World War II from beginning to end (1939–1945).
Design

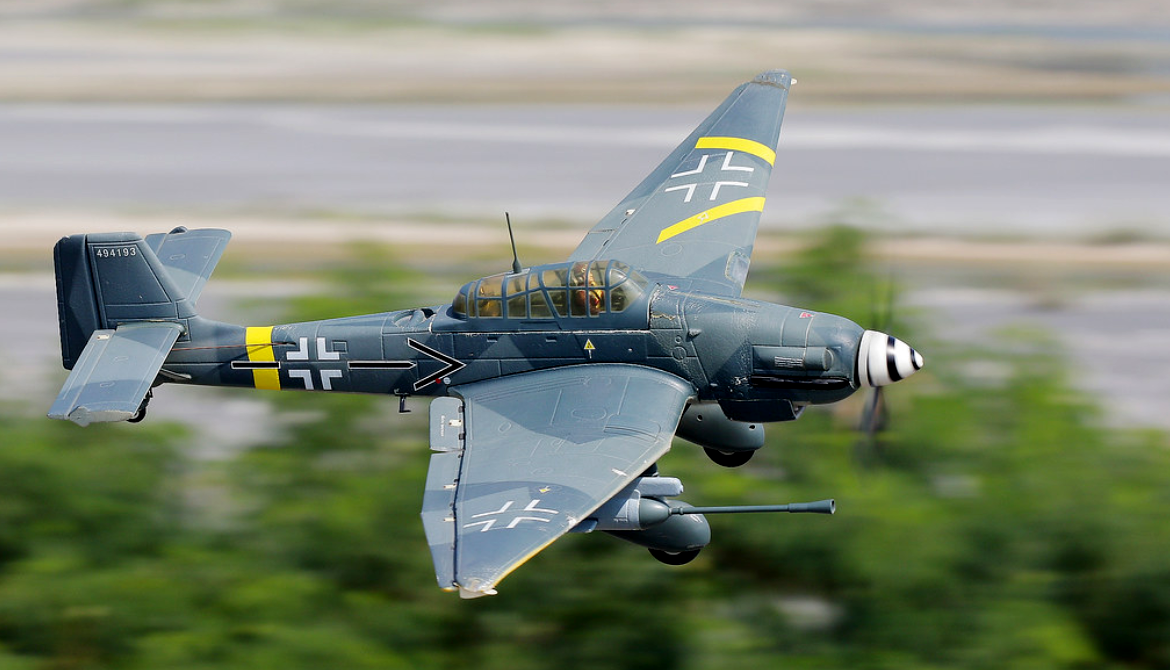
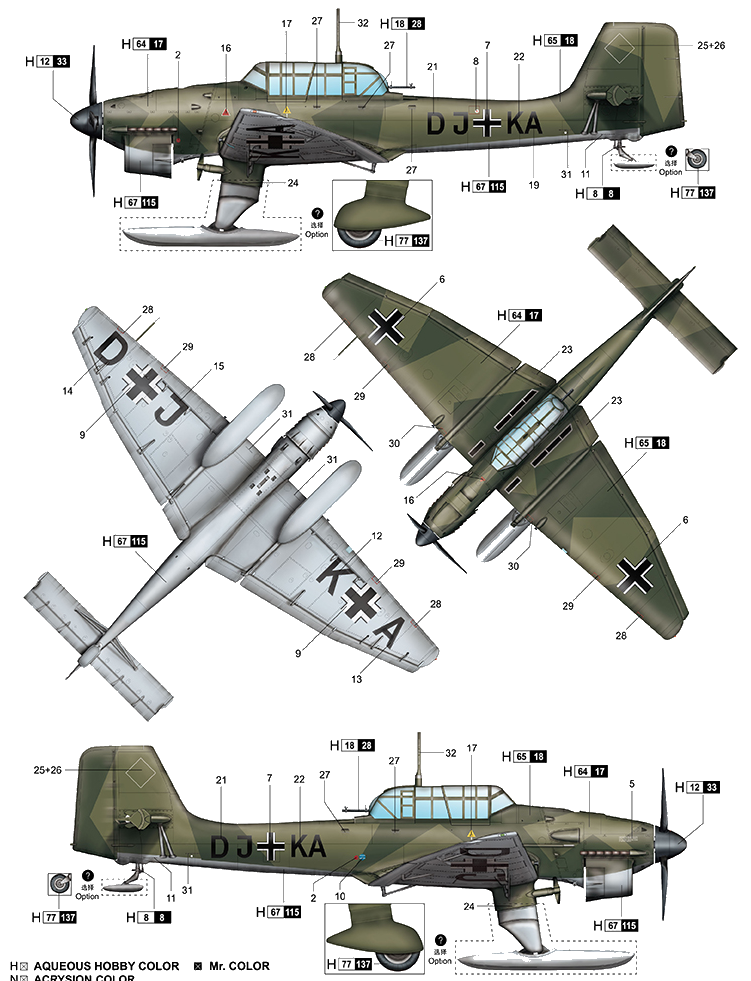
The wing was the most unusual feature. It consisted of a single centre section and two outer sections installed using four universal joints. The centre section had a large negative dihedral (anhedral) and the outer surfaces a positive dihedral. This created the inverted gull, or "cranked", wing pattern along the leading edge. The shape of the wing improved the pilot's ground visibility and also allowed a shorter undercarriage height. The centre section protruded by only 3 m (9 ft 10 in) on either side.
The offensive armament was two 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 17 machine guns fitted one in each wing outboard of undercarriage, operated by a mechanical pneumatics system from the pilot's control column. The rear gunner/radio operator operated one 7.92 mm (.312 in) MG 15 machine gun for defensive purposes.
The engine and propeller had automatic controls, and an auto-trimmer made the aircraft tail-heavy as the pilot rolled over into his dive, lining up red lines at 60°, 75° or 80° on the cockpit side window with the horizon and aiming at the target with the sight of the fixed gun. The heavy bomb was swung down clear of the propeller on crutches prior to release.
Diving procedure
Variants
Ju 87 A

The second prototype had a redesigned single vertical stabiliser and a 610 PS (601.7 hp; 448.7 kW) Jumo 210 A engine installed, and later the Jumo 210Da. The first A series variant, the A-0, was of all-metal construction, with an enclosed cockpit under a "greenhouse" well-framed canopy; bearing twin radio masts on its aft sections, diagonally mounted to either side of the airframe's planform centreline and unique to the -A version. To ease the difficulty of mass production, the leading edge of the wing was straightened out and the ailerons' two aerofoil sections had smooth leading and trailing edges. The pilot could adjust the elevator and rudder trim tabs in flight, and the tail was connected to the landing flaps, which were positioned in two parts between the ailerons and fuselage. The A-0 also had a flatter engine cowling, which gave the pilot a much better field of vision. In order for the engine cowling to be flattened, the engine was set down nearly 0.25 m (9.8 in). The fuselage was also lowered along with the gunner's position, allowing the gunner a better field of fire
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
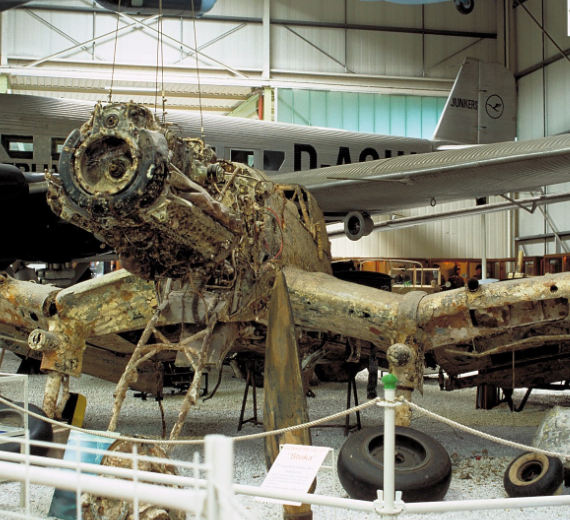
Photo Gallery
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG JFM
Junkers Ju 87 "Stuka"


Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG JFM
Junkers Ju 87 "Stuka"
General Info
-
-
- Crew: 2
- Length: 11.10 m (36 ft 5 in)
- Wingspan: 13.805 m (45 ft 3.5 in)
- Height: 4.01 m (13 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 31.900 m2 (343.37 sq ft)
-
Powerplant
-
- Empty weight: 2,712 kg (5,980 lb)
- Empty equipped weight: 2,760 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 4,336 kg
- Powerplant: 1 × Junkers Jumo 211Da V-12 inverted liquid-cooled piston engine, 890 kW (1,200 hp) for take-off
-
-
- 820 kW (1,100 hp) at 1,500 m
-
- Propellers: 3-bladed Junkers constant-speed propeller
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 339.6 km/h (211.0 mph, 183.4 kn) at sea level
-
-
- 383 km/h (238 mph; 207 kn) at 4,087 m (13,410 ft)
-
- Cruise speed: 209 km/h (130 mph, 113 kn) at 4,572 m (15,000 ft)
- Range: 595.5 km (370.0 mi, 321.5 nmi) with 500 kg (1,102 lb) bomb
-
-
- 789 km (490 mi; 426 nmi) without bomb load
-
- Rate of climb: 2.3 m/s (450 ft/min)
- Time to altitude: 1,000 m (3,281 ft) in 2 minutes
-
-
- 2,000 m (6,562 ft) in 4 minutes 18 seconds
- 3,716 m (12,190 ft) in 12 minutes
-
Armament
-
- Guns: 2× 7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 17 machine gun forward, 1× 7.92 mm (0.31 in) MG 15 machine gun to rear
- Bombs: 1× 250 kg (550 lb) bomb beneath the fuselage and 4× 50 kg (110 lb) under-wing.
Links to Youtube & Others
The aircraft is easily recognisable by its inverted gull wings and fixed spatted undercarriage. Upon the leading edges of its faired main gear legs were mounted ram-air sirens known as Jericho trumpets, which became a propaganda symbol of German air power and of the so-called Blitzkrieg victories of 1939–1942.
Junkers GmbH
Ju 87 "Stuka"
The Junkers Ju 87 or "Stuka" is a German dive bomber and ground-attack aircraft. Designed by Hermann Pohlmann, it first flew in 1935.
Youtube Link
The Ju 87's principal designer, Hermann Pohlmann, held the opinion that any dive-bomber design needed to be simple and robust.