Northrop Grumman
MQ-8 Fire Scout
 |
|
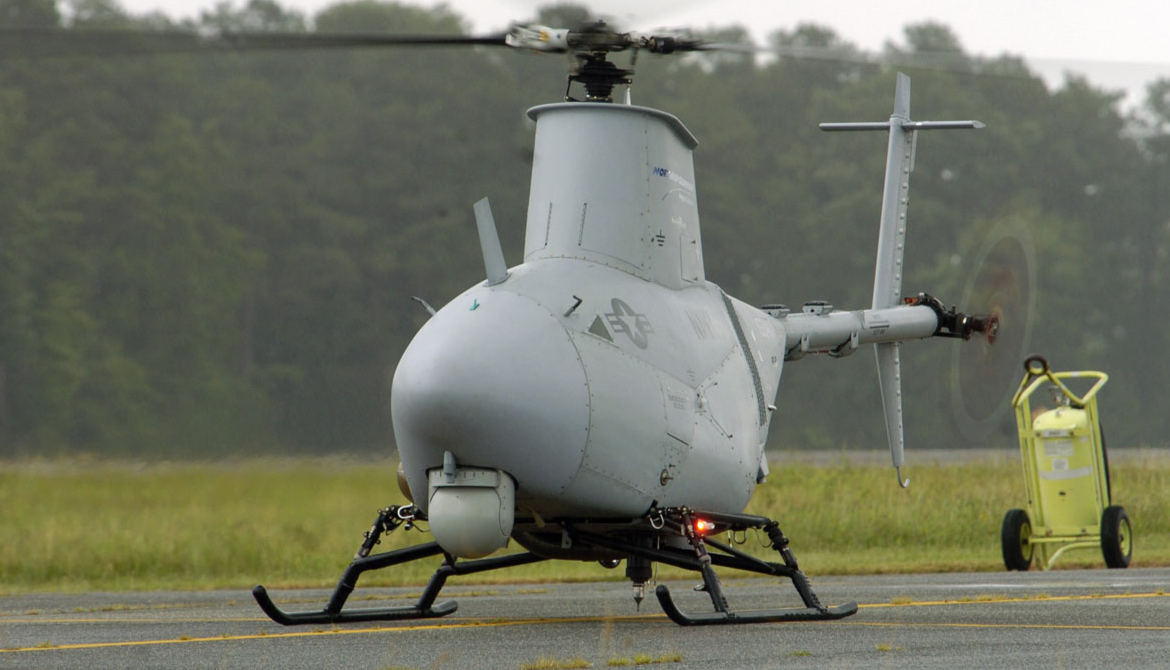
| An MQ-8B Fire Scout completes first biofuel flight at Webster Field, September 2011 | |
| Role | UAV helicopter |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Northrop Grumman |
| First flight | 2000 |
| Introduction | 2009 (MQ-8B) |
| Retired | 2022 |
| Status | Retired (RQ-8A, MQ-8B) |
| Primary user | United States Navy |
| Number built | 30 (MQ-8B) |
| Developed from | Schweizer 330 and 333 |
| Variants | Sikorsky S-434 |
| Developed into | Northrop Grumman MQ-8C Fire Scout |
.
History Northrop Grumman MQ-8 Fire Scout

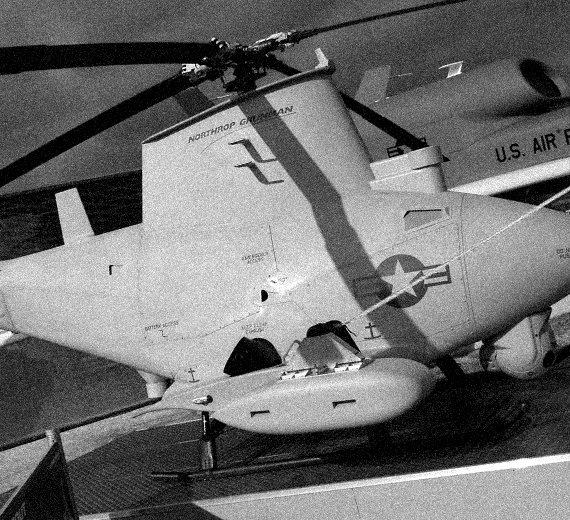
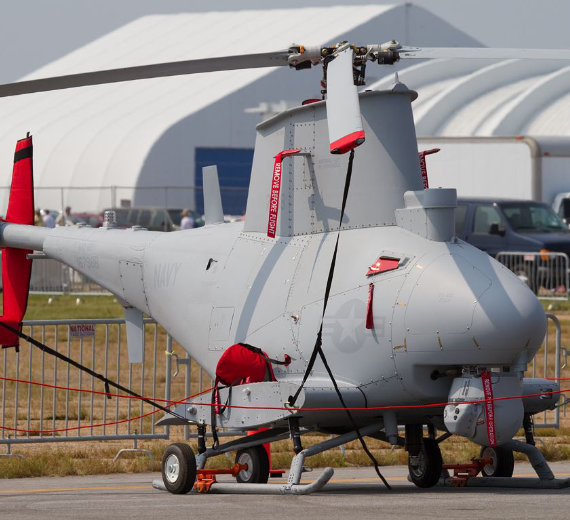
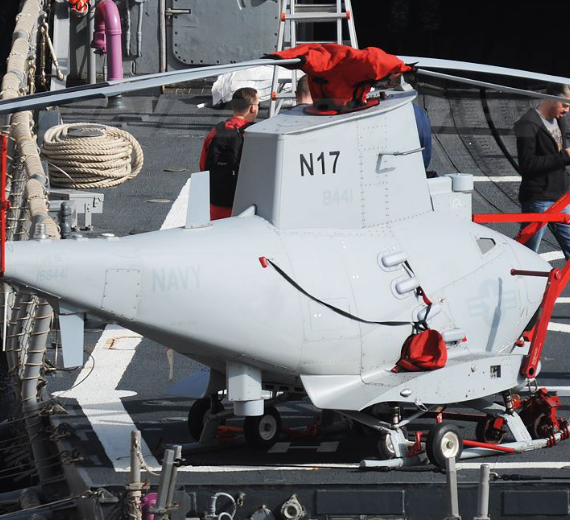
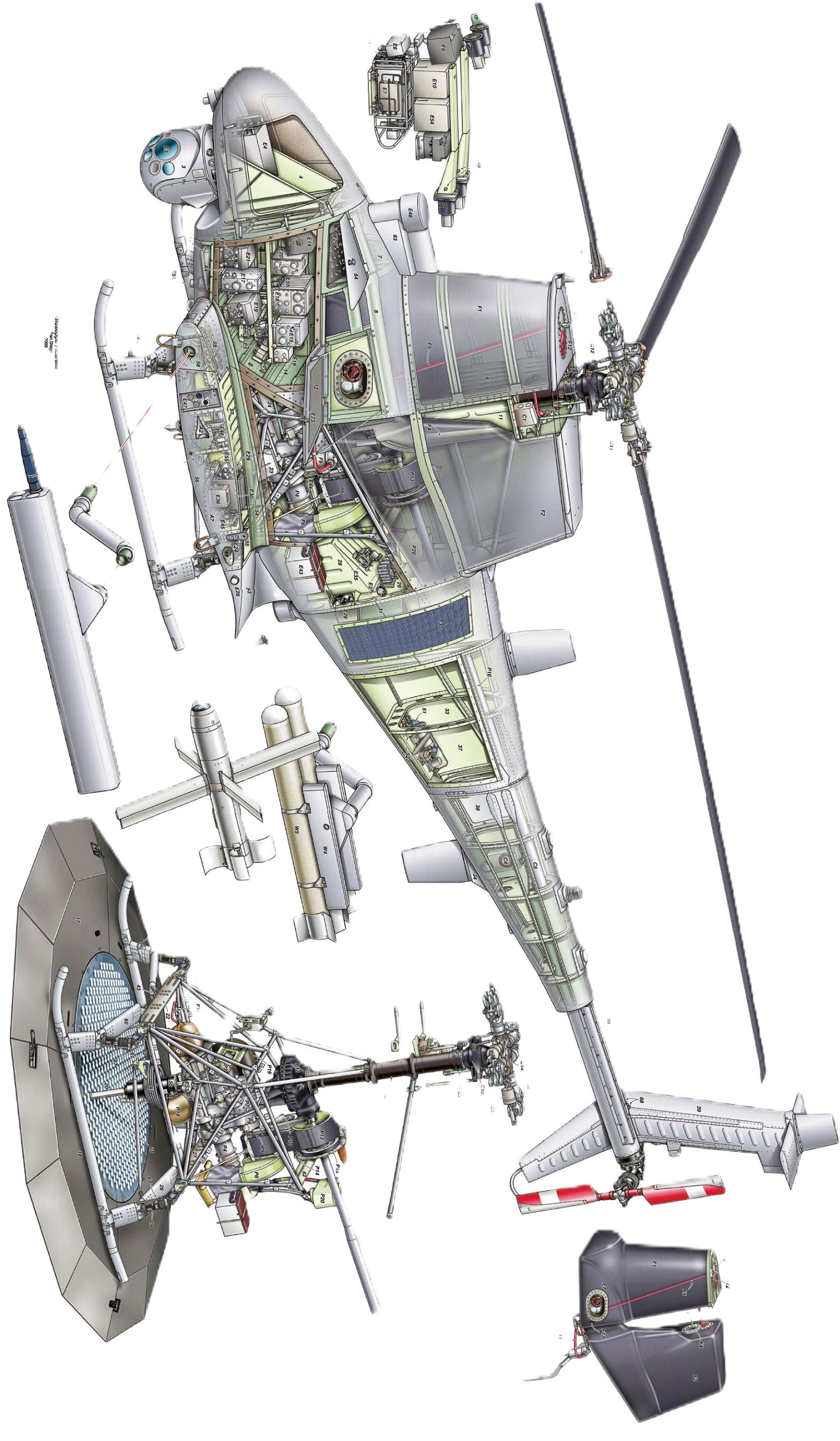
The Northrop Grumman MQ-8 Fire Scout is an unmanned autonomous helicopter developed by Northrop Grumman for use by the United States Armed Forces. The Fire Scout is designed to provide reconnaissance, situational awareness, aerial fire support and precision targeting support for ground, air and sea forces. The initial RQ-8A version was based on the Schweizer 330, while the enhanced MQ-8B was derived from the Schweizer 333. The larger MQ-8C Fire Scout variant is based on the Bell 407.
In February 2018, 23 MQ-8Bs were in service with the U.S. Navy.[4] The MQ-8B was retired from service in October 2022
In January 2006, an RQ-8A Fire Scout landed aboard the amphibious transport ship Nashville while it was steaming off the coast of Maryland near the Patuxent River. This marked the first time an unmanned helicopter has landed autonomously aboard a moving U.S. Navy ship without a pilot controlling the aircraft.[18][19][20] Nashville was maneuvering as fast as 17 mph (27 km/h) in the tests.
Early stages
MQ-8B

Although progress on the project had been regarded as satisfactory, the Navy decided the Fire Scout didn't meet their needs after all, and cut funding for production in December 2001. However, the development program continued, and Northrop Grumman pitched a range of improved configurations to anyone who was interested. As it turned out, the U.S. Army was very interested, awarding a contract for seven improved RQ-8B evaluation machines in late 2003. In 2006, it was redesignated MQ-8B.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
MachAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Northrop Grumman MQ-8 Fire Scout


McDonnell Douglas aircraft
Northrop Grumman MQ-8 Fire Scout
General Info
-
- Crew: 0 (on-board)
- Capacity: 600 lb (272 kg)
- Length: 23 ft 11.4 in (7.3 m)
- Wingspan: 27 ft 6 in (8.4 m)
- Height: 9 ft 8.5 in (2.9 m)
Powerplant
- Empty weight: (940.3 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (1,430 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Rolls-Royce 250 , 420 hp (313 kW)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 213 km/h)
- Cruise speed: (130 mph, 200 km/h)
- Combat range: 110 nmi (126.6 mi, 203.7 km) with 5+ hours on station
- Endurance: 8 hours (typical), 5 hours fully loaded
- Service ceiling: 20,000 ft (6,100 m)
Links to Youtube & Others
With vehicle endurance greater than five hours, a VTUAV system will be capable of twelve continuous hours of operations providing coverage 110 nautical miles from the launch site.
Northrop
MQ-8 Firescout
The program is currently completing EMD (engineering, manufacturing, development), and should begin low rate initial production in FY 07
Youtube Link
The air vehicle component of the VTUAV system was designated the MQ-8B to reflect the Fire Scout’s evolution toward an increased, multi-functional role.