VASO in English, ВАСО Ilyushin Il-76 Candid
 |
|
| A Russian Air Force Il-76MD | |
| Role | Strategic and tactical airlifter |
|---|---|
| National origin | Soviet Union / Russia |
| Design group | Ilyushin |
| Built by | Tashkent Aviation Production Association Aviastar-SP |
| First flight | 25 March 1971 |
| Introduction | June 1974 |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | Soviet Air Forces (historical) Russian Aerospace Forces Ukrainian Air Force Indian Air Force |
| Produced | 1971–present |
| Number built | 969 |
| Variants | Ilyushin Il-78 Beriev A-50 Beriev A-100 KJ-2000 |
.
History Voronezh Aircraft Production Association
Ilyushin Il-76 Candid

The Ilyushin Il-76 (Russian: Илью́шин Ил-76; NATO reporting name: Candid) is a multi-purpose, fixed-wing, four-engine turbofan strategic airlifter designed by the Soviet Union's Ilyushin design bureau as a commercial freighter in 1967, to replace the Antonov An-12. It was developed to deliver heavy machinery to remote, poorly served areas. Military versions of the Il-76 have been widely used in Europe, Asia and Africa, including use as an aerial refueling tanker or command center.
Design and development

Origins
The aircraft was conceived by Ilyushin in 1967 to meet a requirement for a freighter able to carry a payload of 40 tonnes (88,000 lb) over a range of 5,000 kilometres (2,700 nmi; 3,100 mi) in less than six hours, able to operate from short[] and unprepared airstrips, and capable of coping with the worst weather conditions likely to be experienced in Siberia and the Soviet Union's Arctic regions. It was intended to replace the Antonov An-12. Another project design for a double-decked 250-passenger airliner was cancelled. The Il-76 first flew in March 1971.
Production of Il-76s was allocated to the Tashkent Aviation Production Association in Tashkent, Uzbekistan, then a republic of the Soviet Union. Some 860 of the basic transport variants were manufactured. In the 1990s,
Further development
From 2004 onwards, a number of aircraft in commercial service were modernized to the Il-76TD-90VD version; this involved the adoption of the newly developed PS-90 engine to comply with European noise limitations. In 2005, the People's Republic of China placed an order for 34 new Il-76MDs and four Il-78 tankers. In June 2013, Russian military export agency Rosoboronexport announced an order by China for 12 Il-76MD aircraft.

The Il-76 has also been modified into an airborne refuelling tanker, designated the Il-78, around 50 aircraft having been produced. A variant of the Il-76 also serves as a firefighting waterbomber. Its airframe was used as a base for the Beriev A-50 'Mainstay' AEW&C (airborne early warning and control) aircraft; around 25 aircraft were made. Another application for the type was found in Antarctic support flights and for conducting simulated weightlessness training for cosmonauts (akin to the "Vomit Comet" used by NASA). Beriev and NPO Almaz also developed an airborne laser flying laboratory designated A-60, of which two were built, much of this project's details remaining classified.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
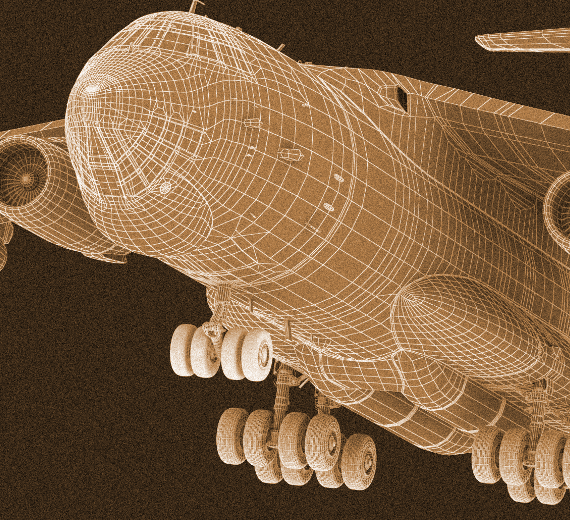
Photo Gallery
Voronezh Aircraft Production Association
Ilyushin Il-76 Candid


Voronezh Aircraft Production Association
Ilyushin Il-76 Candid
General Info
-
-
-
- Crew: 3
- Length: 17.65 m (57 ft 11 in)
- Wingspan: 21.45 m (70 ft 4 in)
- Height: 6.7 m (22 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 60 m2 (650 sq ft)
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
-
- Empty weight: 12,890 kg
- Gross weight: 18,400 kg
- Max takeoff weight: 21,200 kg
- Powerplant: 2 × Klimov VK-1A centrifugal-flow turbojet engines, 26.5 kN (6,000 lbf) thrust each
-
-
Performance
-
- Maximum speed:902 km at 4,500m
- Cruise speed: 770 km/h (480 mph, 420 kn) at 10,000 m (33,000 ft)
- Range: 2,180 km
- Service ceiling: 12,300 m (40,400 ft)
Related development
-
- Guns: 4 × Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 cannons (2 in nose and 2 in tail barbette)
- Bombs: 3,000 kg (6,600 lb) of bombs in internal bay (1,000 kg (2,200 lb) normal)
.
Links to Youtube & Others
In February 2017, it was announced that Russia's United Aircraft Corporation had signed a contract with its subsidiary Ilyushin Aviation Complex for the development of a new version of Ilyushin Il-96-400 wide-body passenger airliner to compete with the Boeing 777-9 and Airbus A350-1000.
IIyushin II-76 Candid
By January 2020, the first test-flight airframe was in final assembly and the wing and fuselage were joined, to be finished at the end of 2020 before a first flight in 2021
Youtube Link
Projected double-deck version of Il-96 for 550-600 passengers and powered by Kuznetsov NK-93 propfan engines. Following flight tests in 2007 the engines were removed and the aircraft was not developed further.








.png)



