Mil Helicopter Plant
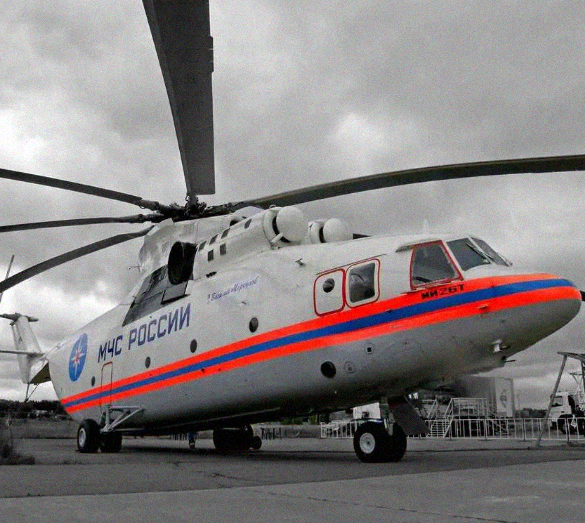
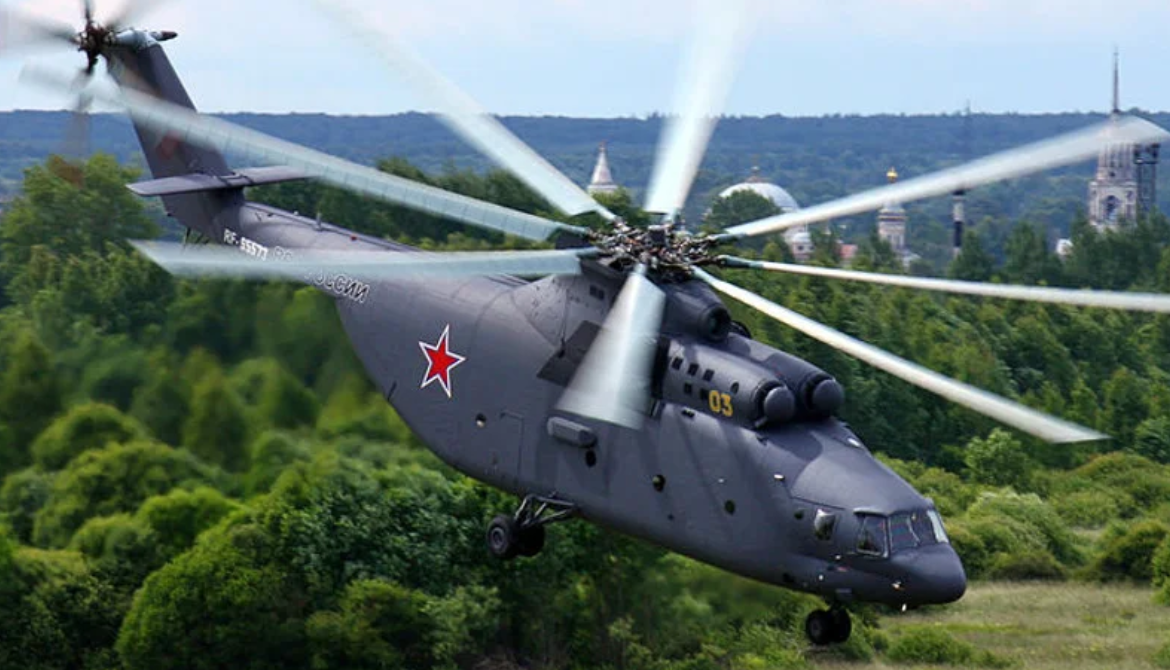
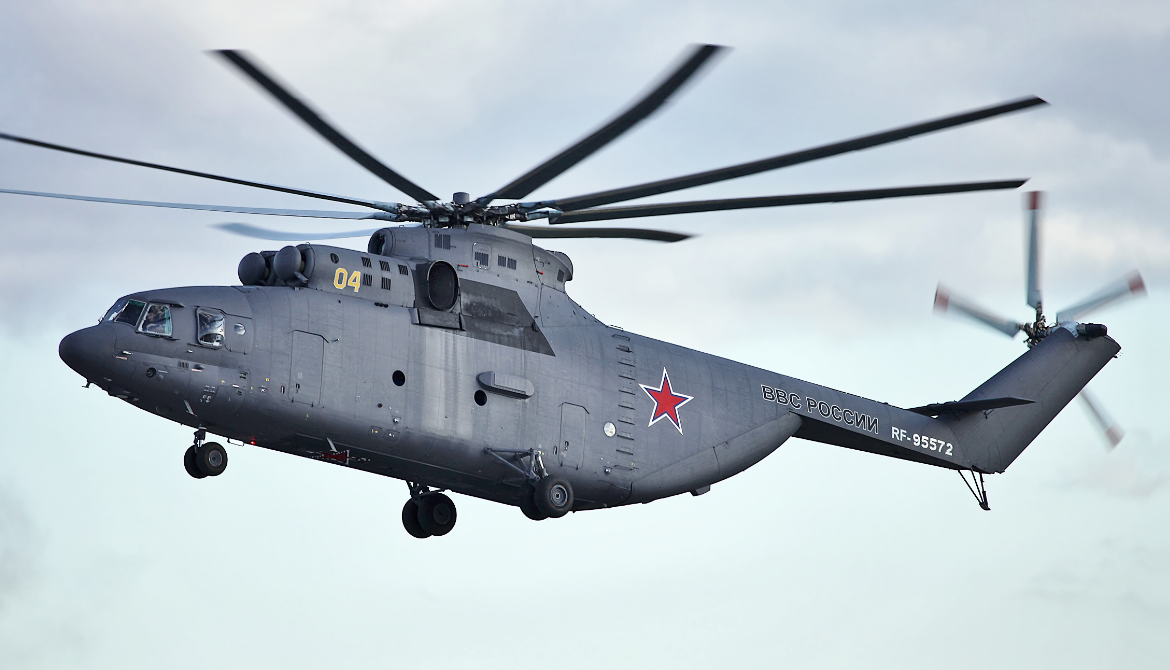
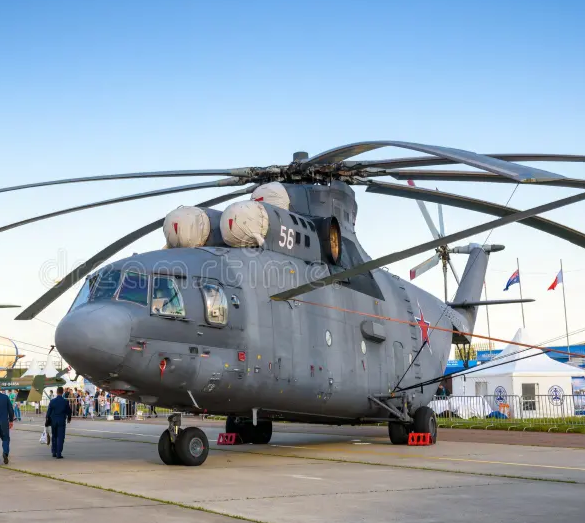
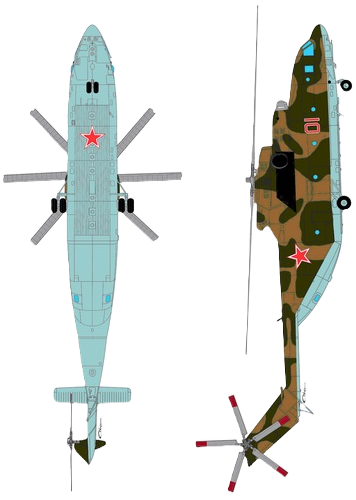
Mil Mi-26, name: Halo
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Heavy lift transport helicopter |
| National origin | Soviet Union/Russia |
| Manufacturer | Rostvertol |
| Designer | Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | Russian Aerospace ForcesIndian Air Force Aeroflot Algerian Air Force |
| Number built | Over 300 as of 2015 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1980–present |
| Introduction date | 1983 |
| First flight | 14 December 1977 |
|
|
|
|
|---|
.
History Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant Mil Mi-26,
NATO reporting name: Halo

The Mi-26's unique main gearbox is relatively light at 3,639 kg (8,023 lb) but can absorb 14,700 kilowatts (19,725 shp), which was accomplished using a non-planetary, split-torque design with quill shafts for torque equalization. The Mil Design Bureau designed the VR-26 transmission itself, due to Mil's normal gearbox supplier not being able to design such a gearbox. The gearbox housing is stamped aluminum. A split-torque design is also used in the 5,670 kg (12,500 lb) gearbox assembly on the American three-engine Sikorsky CH-53K King Stallion. As of 2024, the Mi-26 still holds the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale world record for the greatest mass lifted by a helicopter to 2,000 metres (6,562 ft) – 56,768.8 kilograms (125,000 lb) on a flight in 1982. But this record exists only because for the record flights of the Mil V-12, only the maximum payload was recorded, and not the maximum take-off weight, estimated at 105,000 kg
-
Design

An Aeroflot Mi-26 at the 1984 Farnborough Air Show Following the incomplete development of the heavier Mil Mi-12 (prototypes known as Mil V-12) in the early 1970s, work began on a new heavy-lift helicopter, designated as the Izdeliye 90 ("Project 90") and later allocated designation Mi-26. The new design was required to have an empty weight less than half its maximum takeoff weight. The helicopter was designed by Marat Tishchenko, protégé of Mikhail Mil, founder of the OKB-329 design bureau
Variants Military
Operational history

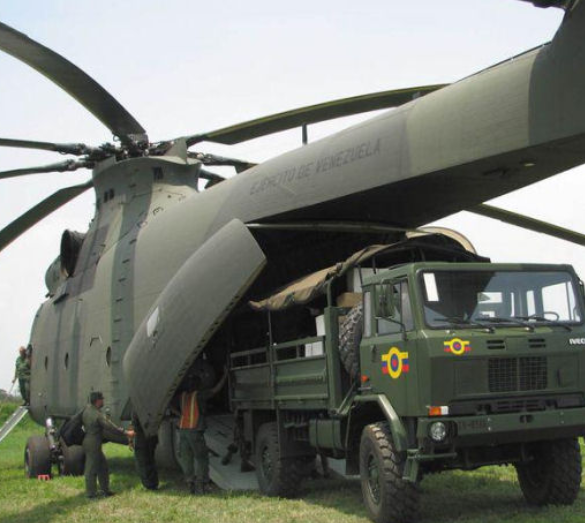
A Mi-26 in a military parade over Caracas, Venezuela Buran programme
The developers of the Buran space vehicle programme considered using Mi-26 helicopters to "bundle" lift components for the Buran spacecraft, but test flights with a mock-up showed this to be risky and impractical.
Variants

A Mi-26TC in firefighting role over Athens 
Latest version Mi-26T2V - V-29
- Prototype version
- Mi-26
- Military cargo/freight transport version. NATO name: 'Halo-A'.
- Mi-26A
- Upgraded military version with a new flight/navigation system. Flown in 1985 but no production
0
KmCeiling
0
KmMAX RANGE
0
Km.hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant Mil Mi-26,
NATO reporting name: Halo


Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant Mil Mi-26,
NATO reporting name: Halo
General characteristics
- Crew: 5 (2 pilots, 1 navigator, 1 flight engineer, 1 flight technician)
- Capacity:
- 90 troops or 60 stretchers
- 20,000 kg (44,000 lb) cargo
- Length: 40.025 m (131 ft 4 in)
- Height: 8.145 m (26 ft 9 in)
- Empty weight: 28,200 kg (62,170 lb)
-
Powerplant
- Powerplant: 2 × ZMKB Progress D-136 turboshaft engines, 8,500 kW (11,400 hp) each
- Main rotor diameter: 32 m (105 ft 0 in)
- Main rotor area: 804.25 m2
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 295 km/h
- Cruise speed: 255 km/h
- Range: 500 km (310 mi, 270 nmi) with 7,700 kg (17,000 lb) cargo
- Ferry range: 1,920 km (with auxiliary tanks)
- Service ceiling: 4,600 m
Links to Youtube & Others
The Mil Mi-26 (Russian: Миль Ми-26, NATO reporting name: Halo) is a Soviet/Russian heavy transport helicopter. Its product code is Izdeliye 90. Operated by both military and civilian operators, it is the largest helicopter to have gone into serial production
Mil Moscow Plant
Mil Mi-26, Halo
The Mi-26S was a disaster response version hastily developed during the containment efforts of the Chernobyl nuclear accident in 1986.
Youtube Link
In October 1999, an Mi-26 was used to transport a 23-tonne (25-short-ton) block of frozen soil encasing a preserved, 23,000-year-old woolly mammoth (Jarkov Mammoth) from the Siberian tundra to a lab in Khatanga, Russia.








.png)


.png)