Avro Int. Aerospace
AVRO 504 Biplane
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Trainer, fighter, bomber |
| Manufacturer | Avro |
| Primary users | Royal Flying CorpsRoyal Naval Air Service |
| Number built | 11,303 including Japanese, Soviet and other foreign production |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1913–1932 |
| Introduction date | 1913 |
| First flight | 18 September 1913 |
| Retired | 1934 |
.
History Avro International Aerospace
AVRO 504 Biplane
Manufactured 1913–1932
Introduction date 1913, First flight 18 September 1913

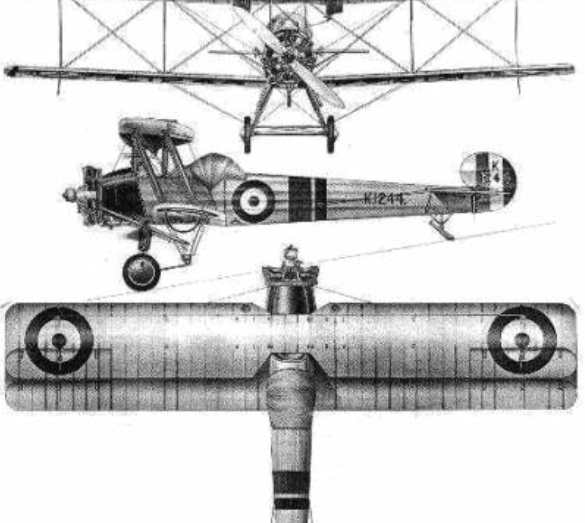
The Avro 504 is a single-engine biplane bomber made by the Avro aircraft company and under licence by others. Production during World War I totalled 8,970 and continued for almost 20 years, making it the most-produced aircraft of any kind that served in any military capacity during the First World War. More than 10,000 were built from 1913 until production ended in 1932.
Design and development

First flown from Brooklands by Fred "Freddie" Raynham on 18 September 1913,powered by an 80 hp (60 kW) Gnome Lambda seven-cylinder rotary engine, the Avro 504 was a development of the earlier Avro 500, designed for training and private flying. It was a two-bay all-wooden biplane with a square-section fuselage..
Operational history


Small numbers of early aircraft were purchased by the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS) prior to the start of the First World War, and were taken to France when the war started. One of the RFC aircraft was the first British aircraft to be shot down by the Germans, on 22 August 1914. The pilot was 2nd Lt. Vincent Waterfall and his navigator Lt Charles George Gordon Bayly (both of 5 Sqn RFC)[9][10] The RNAS used four 504s to form a special flight to bomb the Zeppelin works at Friedrichshafen on the shores of Lake Constance. Three set out from Belfort in north-eastern France on 21 November 1914, carrying four 20 lb (9 kg) bombs each. While one aircraft was shot down, the raid was successful, with several direct hits on the airship sheds and the destruction of the hydrogen generating plant.[.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Avro International Aerospace
AVRO 504 Biplane
Manufactured 1913–1932 Introduction date 1913 First flight 18 September 1913


Avro Int. Aerospace
AVRO 504K Biplane Introduction date 1913
First flight 18 September 1913
General Info
-
-
-
- Crew: 2
- Length: 29 ft 5 in (8.97 m)
- Wingspan: 36 ft 0 in (10.97 m)
- Height: 10 ft 5 in (3.18 m)
- Wing area: 330 sq ft (31 m2)
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
- Empty weight: 1,231 lb (558 kg)
- Gross weight: 1,829 lb (830 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 25.5 imp gal (31 US gal; 116 L) fuel; 6 imp gal (7 US gal; 27 L) castor oil
- Powerplant: 1 × Le Rhône 9J 9-cylinder air-cooled rotary piston engine, 110 hp (82 kW)
- Propellers: 2-bladed Avro fixed-pitch wooden propeller, 9 ft 0 in (2.74 m) diameter 8 ft 8 in (2.6 m) pitch
-
Performance
-
- Maximum speed: 95 mph (153 km/h, 83 kn) at sea level
-
-
-
- 87 mph (76 kn; 140 km/h) at 8,000 ft (2,400 m)
-
-
- Cruise speed: 74 mph (119 km/h, 64 kn) at 75% power at 8,000 ft (2,400 m)
-
-
-
- 71 mph (62 kn; 114 km/h) at 75% power at 10,000 ft (3,000 m)
-
-
- Range: 250 mi (400 km, 220 nmi)
- Endurance:
-
- 2 hours at sea level at maximum speed
- Service ceiling: (4,900 m)
Related development
-
-
1 fixed .303 Lewis atop upper wing (single-seat night fighter variants)
-
Links to Youtube & Others
The Avro 504J and 504K were the primary training aircraft used during the First World War, built in greater numbers than any other British aircraft of the period.
Avro Int.
Avro 504 Biplane
Engine choices for the 504K included the 100 hp Gnome Monosoupape, the 80 or 110 hp Le Rhone, and the 130 hp Clerget, amongst others.
Youtube Link
From mid-1915 onward, the Avro 504 was withdrawn from operations in France and it became the standard training aircraft for the Royal Flying Corps.













.svg.png)