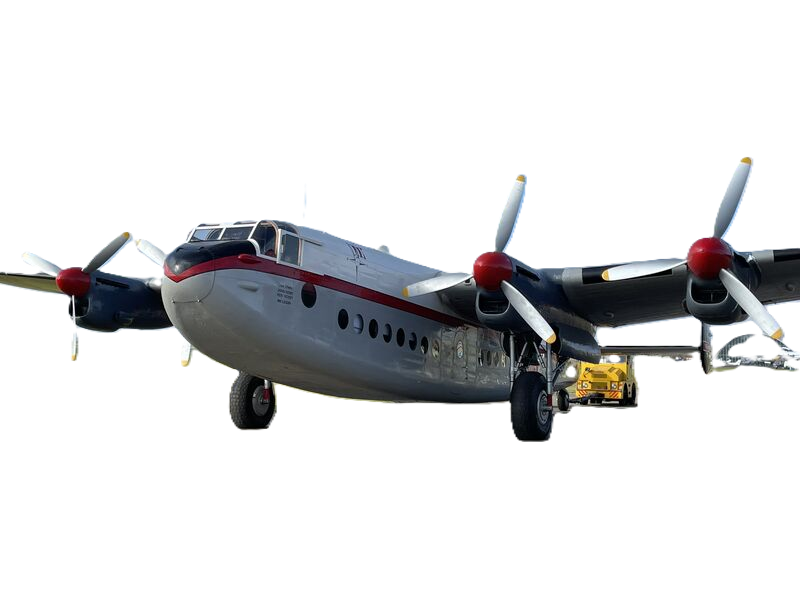
Grumman Aerospace Grumman S-2 Tracker
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Anti-submarine warfare aircraft |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Grumman |
| Status | Active service in Argentine Naval Aviation |
| Primary users | United States Navy (historical)Royal Canadian Navy (historical) Royal Australian Navy (historical) Argentine Navy |
| Number built | 1,284 |
| History | |
| Introduction date | February 1954 |
| First flight | 4 December 1952 |
| Variants | Conair Firecat |
| Developed into | Grumman C-1 Trader Grumman E-1 Tracer |
.
History Grumm![]() an Aerospace
an Aerospace
Grumman S-2 Tracker
(S2F prior to 1962)
Introduction date February 1954 First flight 4 December 1952
Sensors and armament

The Tracker had an internal torpedo bay capable of carrying two lightweight aerial torpedoes or one nuclear depth charge. There were six underwing hard points for rocket pods and conventional depth charges or up to four additional torpedoes. A ventrally-mounted retractable radome for AN/APS-38 radar and a Magnetic Anomaly Detector (MAD) AN/ASQ-8 mounted on an extendable rear mounted boom were also fitted. Early model Trackers had an Electronic Support Measures (ESM) pod mounted dorsally just aft of the front seat overhead hatches and were also fitted with a smoke particle detector or "sniffer" for detecting exhaust particles from diesel-electric submarines running on snorkel. Later S-2s had the sniffer removed and had the ESM antennae moved to four rounded extensions on the wingtips. A 70-million-candlepower searchlight was mounted on the starboard wing. The engine nacelles carried JEZEBEL sonobuoys in the rear (16 in early marks, 32 in the S-2E/G). Early Trackers also carried 60 explosive charges, dispensed ventrally from the rear of the fuselage and used to create sound pulses for semi-active sonar (JULIE) with the AN/AQA-3 and later AQA-4 detection sets, whereas the introduction of active sonobuoys (pingers) and AN/AQA-7 with the S-2G conversion saw these removed. Smoke dispensers were mounted on the port ventral surface of the nacelles in groups of three each.
Operational history

The Tracker was eventually superseded in U.S. military service by the Lockheed S-3 Viking; the last USN Tracker operational squadron (VS-37 with S-2G models) was disestablished in 1976. The last Navy S-2 was withdrawn from service on 29 August 1976. For many years the TS-2A version of the Tracker was used by U.S. Navy training units, culminating with its use by Training Squadron 27 (VT-27), Training Squadron 28 (VT-28) and Training Squadron 31 (VT-31) for Student Naval Aviator training in the multi-engine pipeline with Training Air Wing FOUR (TRAWING 4) at Naval Air Station Corpus Christi, Texas.
0
KmCeiling
0
mRange
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Grumman S-2 Tracker
(S2F prior to 1962)
Introduction date February 1954 First flight 4 December 1952


Grumman Aerospace Corporation
Grumman S-2 Tracker
(S2F prior to 1962)
Introduction date February 1954
First flight 4 December 1952
General characteristics
- Crew: 4
- Length: 43 ft 6 in (13.26 m)
- Wingspan: 72 ft 7 in (22.12 m)
- Height: 17 ft 6 in (5.33 m)
- Wing area: 485 sq ft (45.1 m2)
-
Powerplant
- Empty weight: 18,315 lb (8,308 kg)
- Gross weight: 23,435 lb (10,630 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: (11,860 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Wright R-1820-82WA 9-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engines, 1,525 hp (1,137 kW) each
Specifications
- Maximum speed: 243 kn (280 mph, 450 km/h) at sea level
- Cruise speed: (150 mph, 240 km/h)
- Range: 1,173 nmi (1,350 mi, 2,172 km)
- Endurance: 9 hours endurance
- Service ceiling: 22,000 ft (6,700 m)
Armament
-
- 4,800 lb (2,200 kg) of payload could be carried in the internal bomb bay and on 6× under-wing hardpoints
- Torpedoes: Mk. 41, Mk. 43, Mk. 34, Mk. 44, or Mk. 46
- Depth charges: Mk. 54 or naval miness
- 4,800 lb (2,200 kg) of payload could be carried in the internal bomb bay and on 6× under-wing hardpoints
-
Links to Youtube & Others
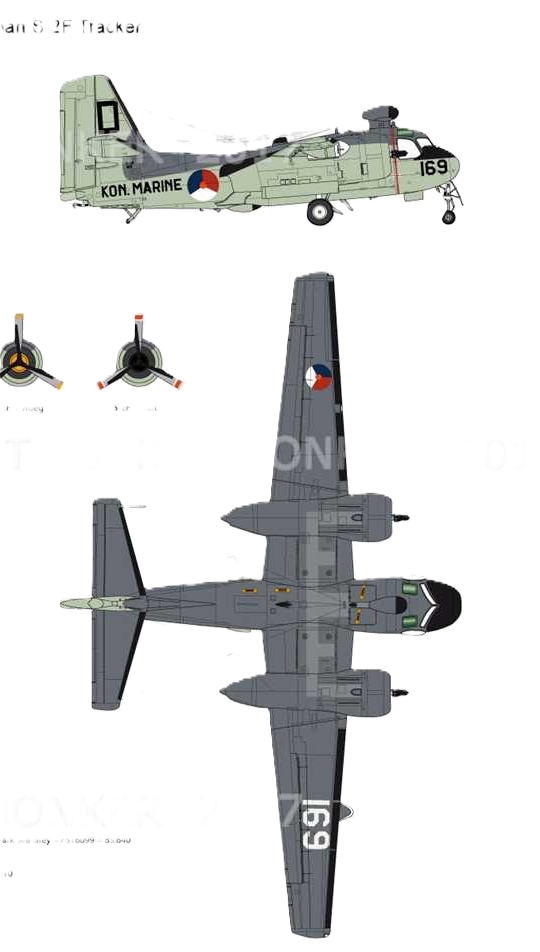
The Netherlands Naval Aviation Service (Marineluchtvaartdienst - MLD), the air arm of the Royal Netherlands Navy, received 28 S-2A (S2F-1) aircraft under MDAP from the US Navy in 1960.
Grumman Aerospace Grumman S-2 Tracker
The Tracker was intended as a replacement for the Grumman AF Guardian,
Youtube Link
A piston-engined S-2 Tracker - believed to be the only flying non-turbo S-2 in the world - performs an aerial firefighting water drop demonstration