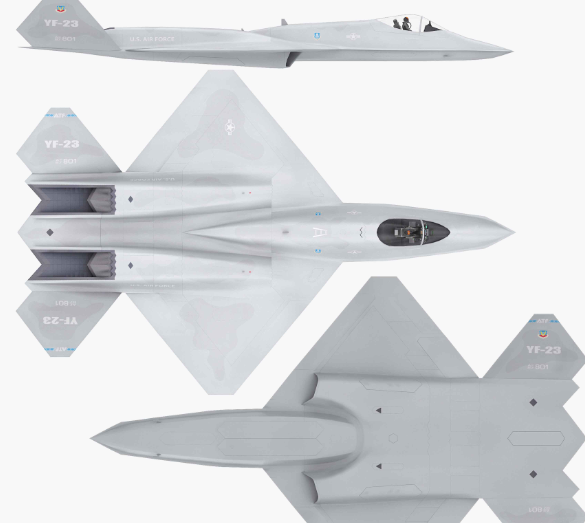

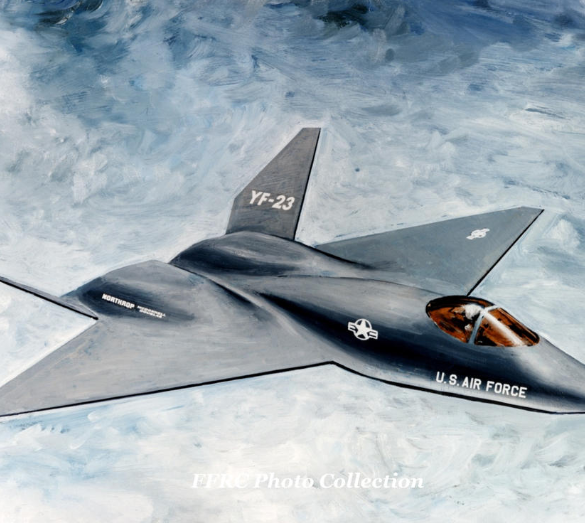
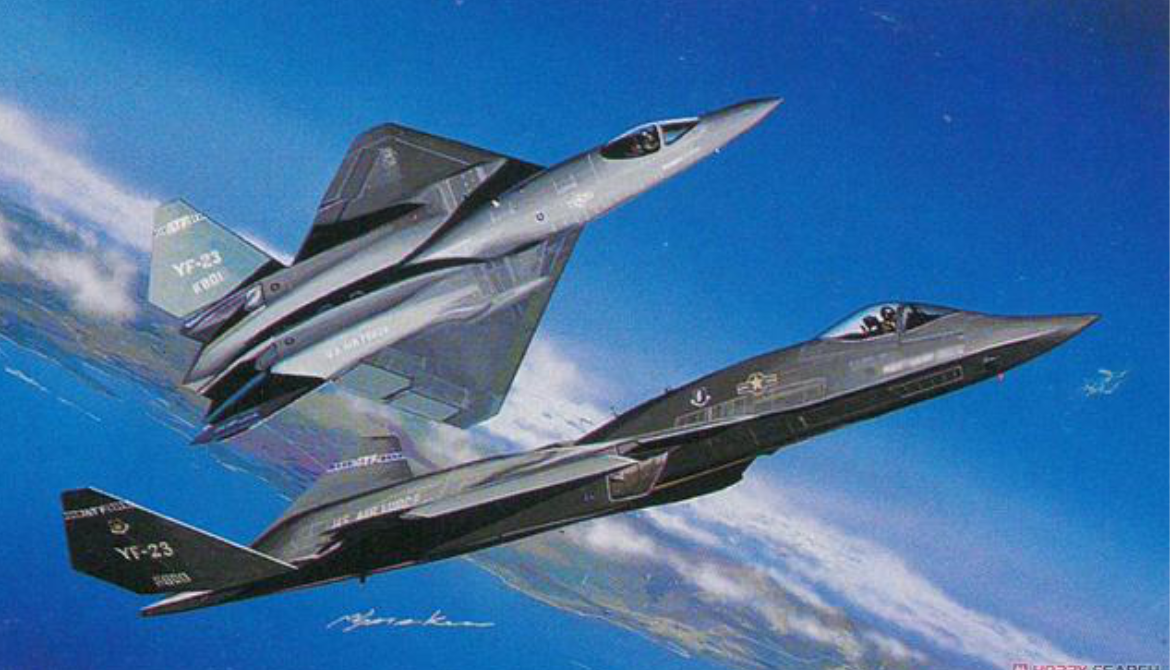
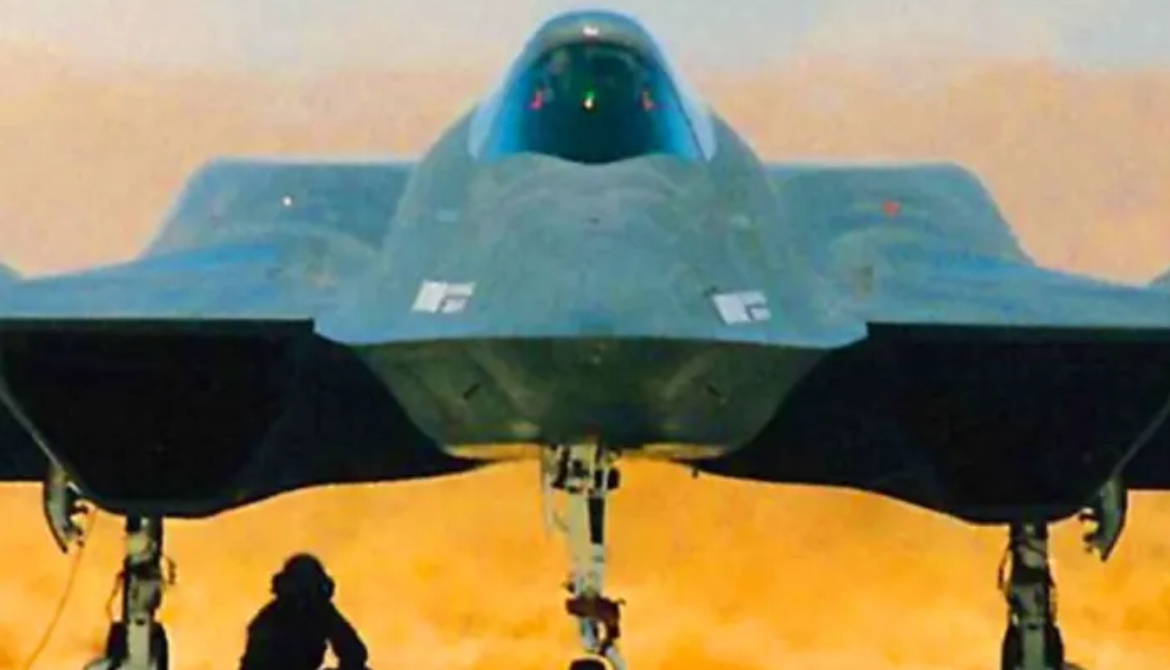
Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23
 |
|
| General information | |
|---|---|
| Type | Stealth fighter technology demonstrator |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | Northrop/McDonnell Douglas |
| Status | Canceled |
| Primary user | United States Air Force |
| Number built | 2 |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1989–1990 |
| First flight | 27 August 1990 |
.
History Northrop
Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23
First flight 27 August 1990 Produced 1989–1990
Design

0
ftCeiling
0
nmiMAX RANGE
0
MphAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23
First flight 27 August 1990 Produced 1989–1990


Northrop/Grumman Airplanes
Northrop YF-23 Black Widow
First flight 27 August 1990 Produced 1989–1990
General characteristics
Crew: 1
Length: 67 ft 5 in (20.55 m)Wingspan: 43 ft 7 in (13.28 m)Height: 13 ft 11 in (4.24 m)
Wing area: 900 sq ft (84 m2)
Empty weight: 29,000 lb (13,154 kg)
Powerplant
Gross weight: 51,320 lb (23,278 kg)
Max takeoff weight: (28,123 kg)
Powerplant: 2 × Pratt & Whitney YF119 or General Electric YF120 afterburning turbofan engines, 35,000 lbf (160 kN) with afterburner
Specifications
Maximum speed: Mach 2.2 (1,450 mph, 2,335 km/h) at high altitude
Supercruise: Mach 1.72 at altitude
Range: (2,789 mi, 4,489 km)
Combat range: 651–695 nmi (749–800 mi, 1,206–1,287 km)
Service ceiling: 65,000 ft (20,000 m)
Wing loading: 57 lb/sq ft (280 kg/m2)
Thrust/weight: 1.36
Armament
None as tested but provisions made for:
1 × 20 mm (0.79 in) M61 Vulcan cannon
4 × AIM-120 AMRAAM or AIM-7 Sparrow medium-range air-to-air missiles
2 × AIM-9 Sidewinder short-range air-to-air missiles and more Wiki Link
Links to Youtube & Others
American reconnaissance satellites first spotted the advanced Soviet Su-27 and MiG-29 fighter prototypes in 1978, which caused concern in the U.S. Both Soviet models were expected to reduce the maneuverability advantage of contemporary US fighter aircraft.
Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23
The Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23 is an American single-seat, twin-engine, supersonic stealth fighter aircraft technology demonstrator designed for the United States Air Force.

Youtube Link
The Northrop/McDonnell Douglas YF-23, is an American single-seat, twin-engine stealth fighter aircraft technology demonstrator designed for the United States Air Force.








.png)
.png)

