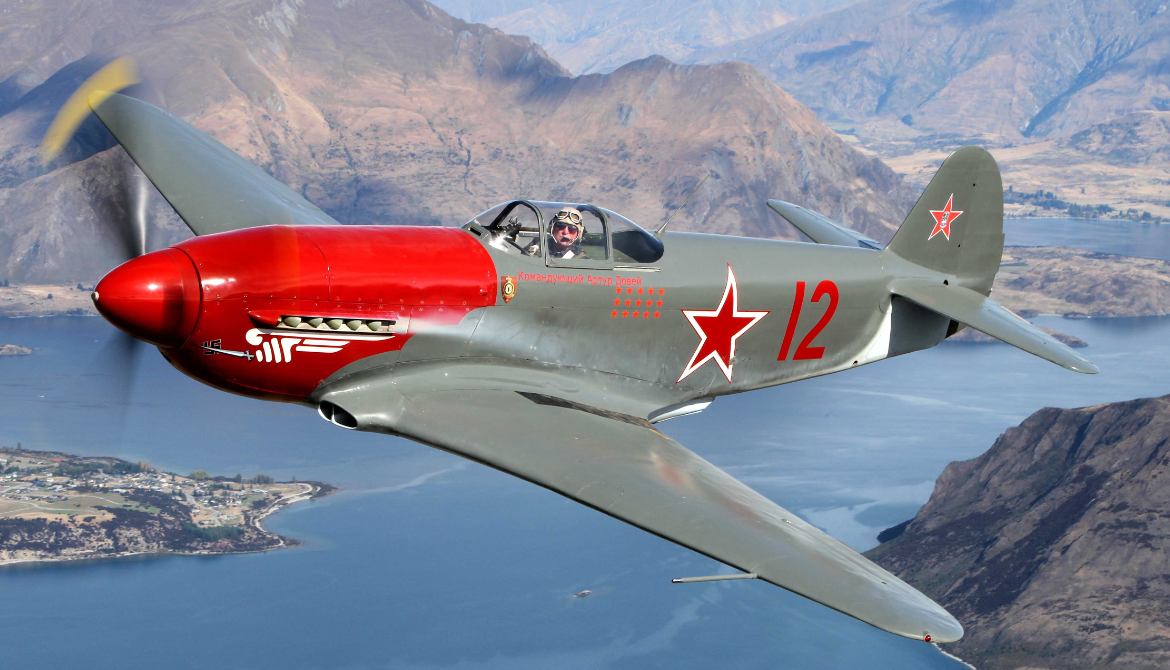
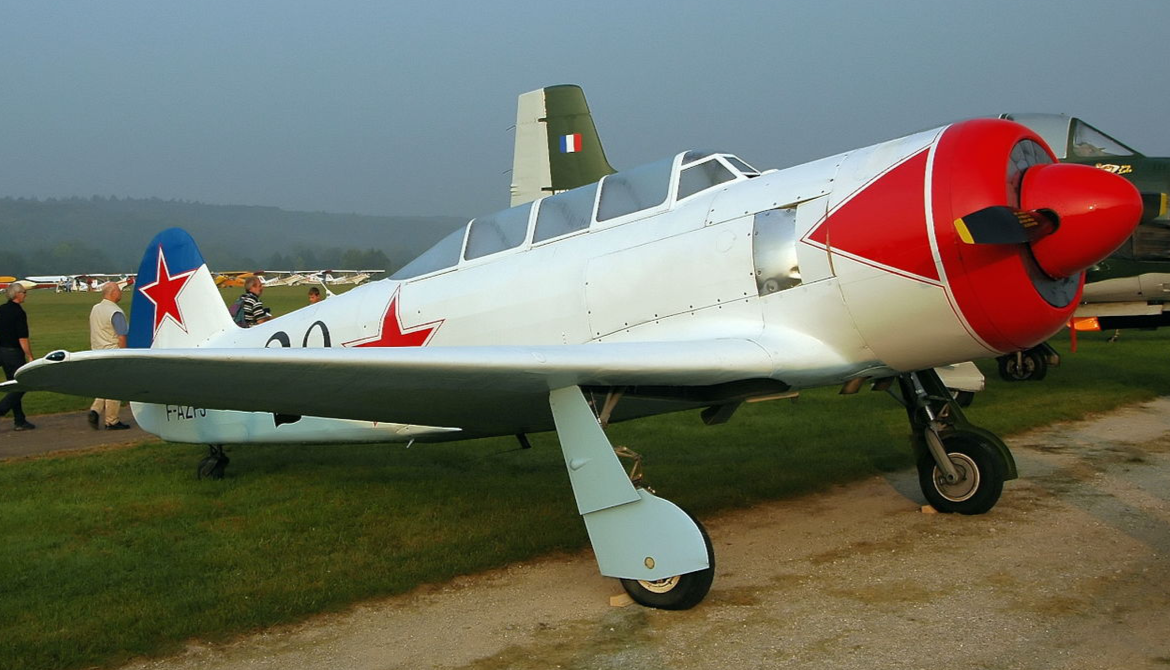
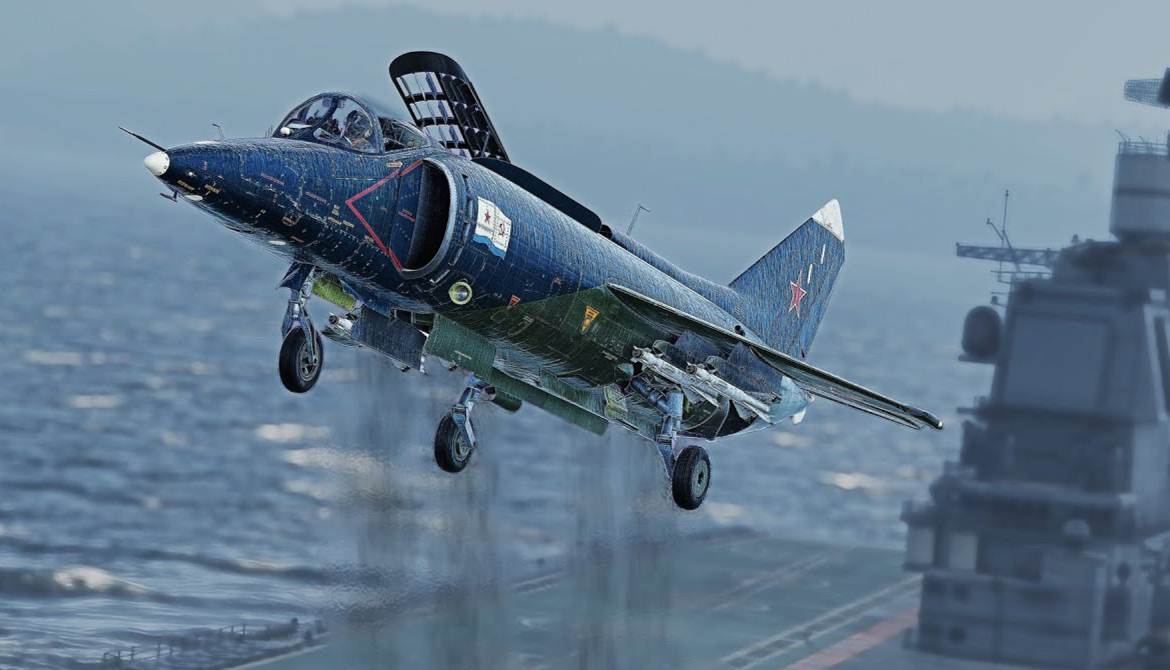
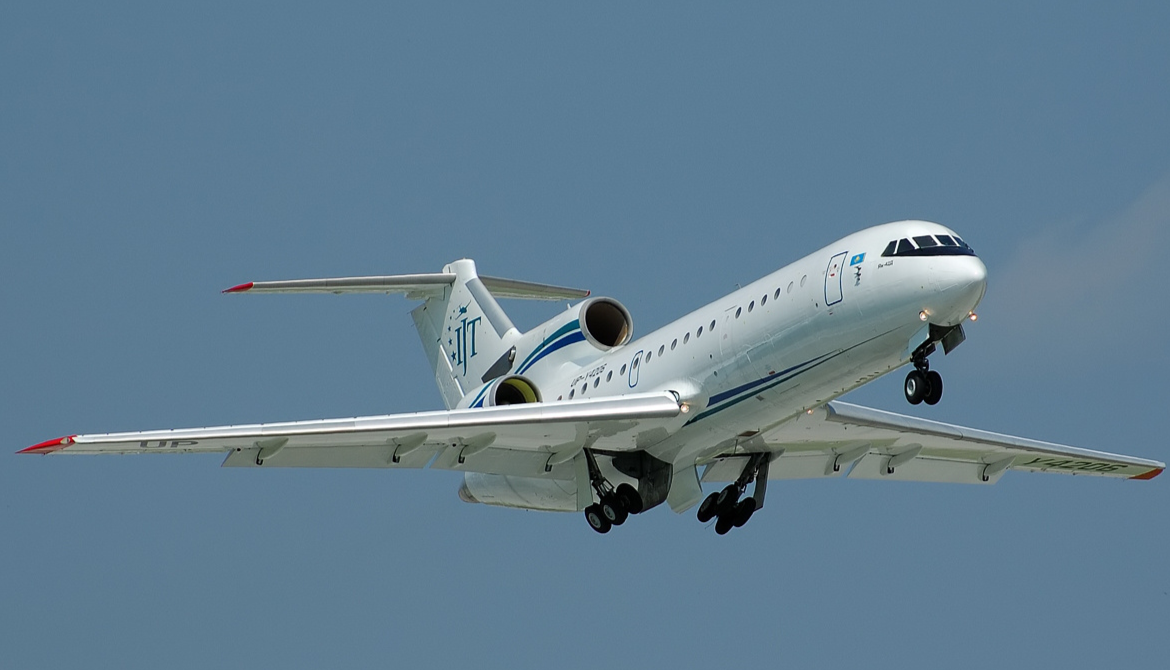
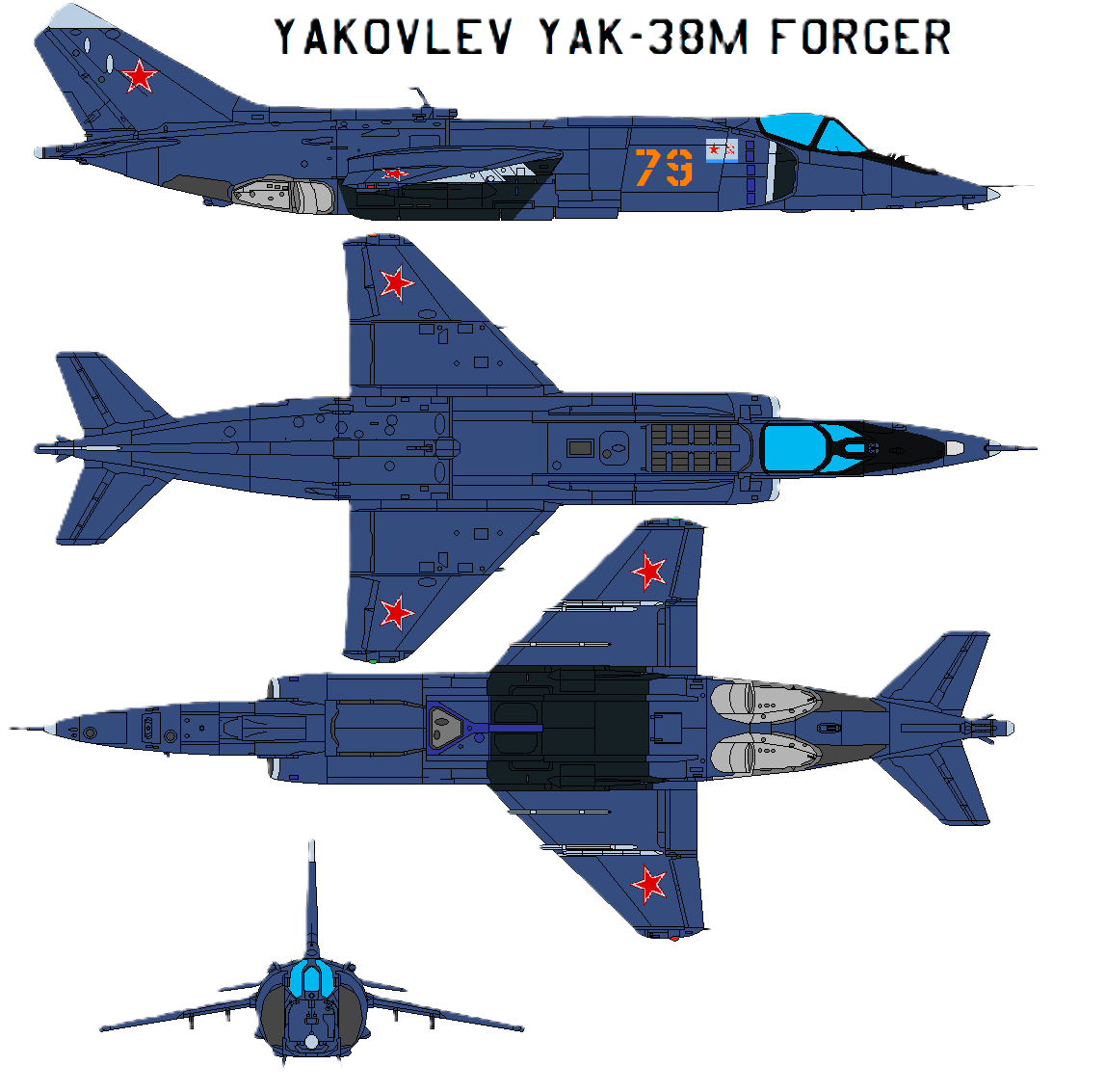
.
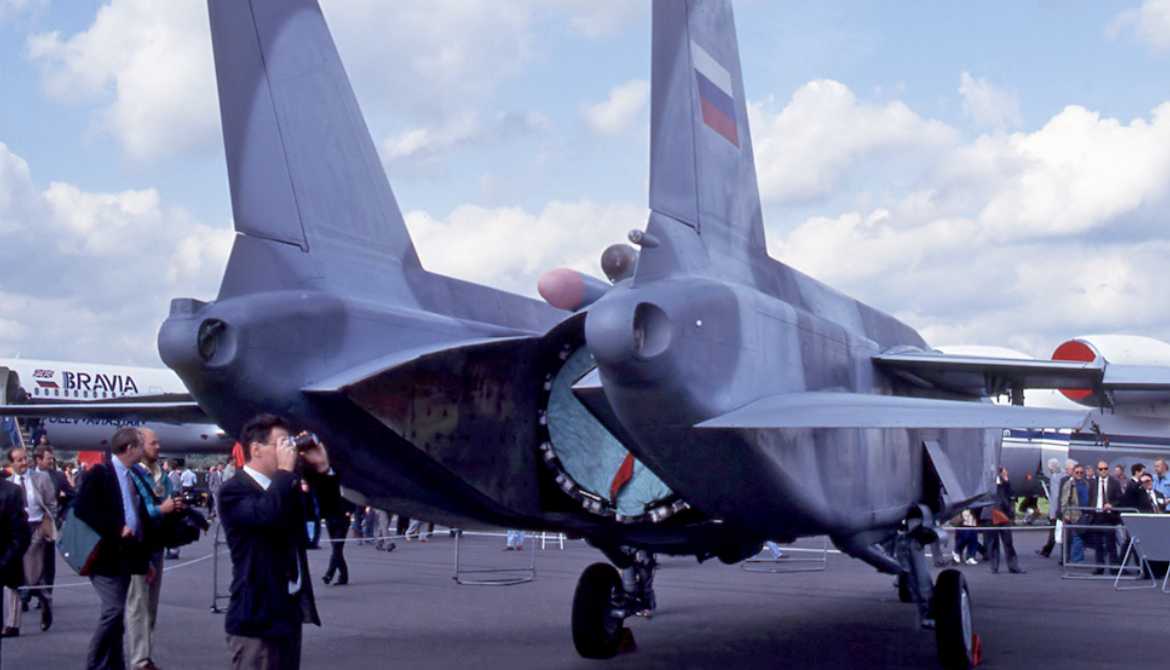
About The JSC A.S. Yakovlev Design Bureau (Russian: ОАО Опытно-конструкторское бюро им. А.С. Яковлева).
Amazing The JSC A.S. Yakovlev Design Bureau (Russian: ОАО Опытно-конструкторское бюро им. А.С. Яковлева) is a Russian aircraft designer and manufacturer (design office prefix Yak). Its head office is in Aeroport District, Northern Administrative Okrug, Moscow.