JSC A.S. Yakovlev
Yak-38 ("Forger")
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
.
History JSC A.S. Yakovlev Design Bureau
Yakovlev Yak-15
( NATO reporting name: Feather),USAF/DOD designation Type 2

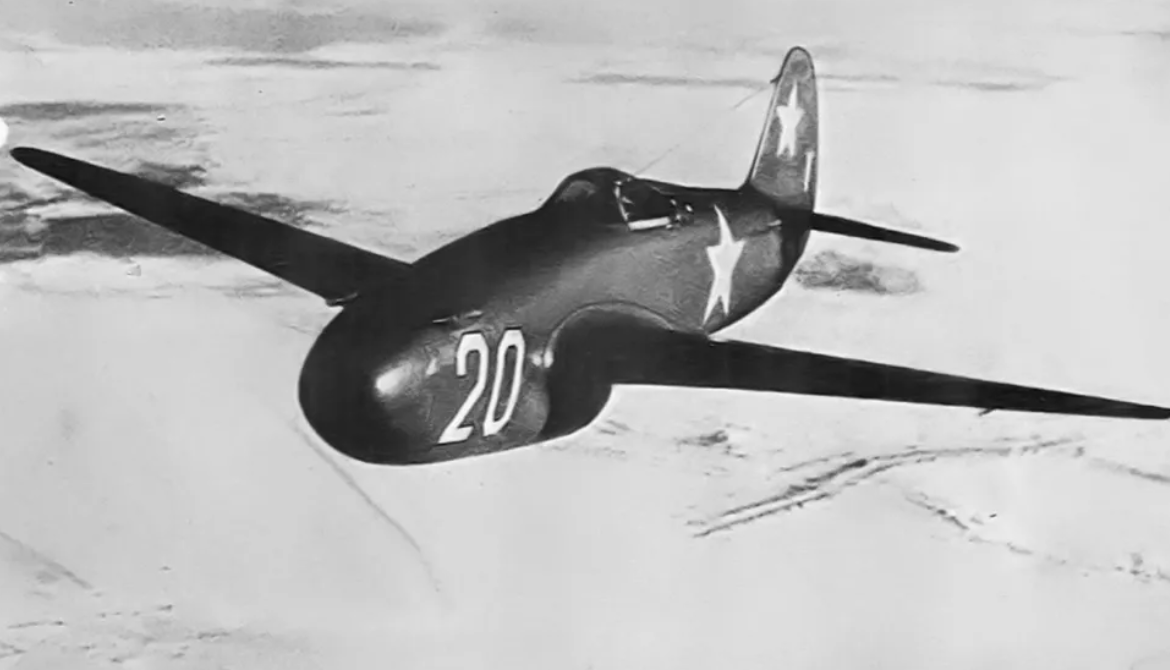
The Yakovlev Yak-15 (Russian: Яковлев Як-15; NATO reporting name: Feather, USAF/DOD designation Type 2) was a first-generation Soviet turbojet fighter developed by the Yakovlev design bureau (OKB) immediately after World War II. The main fuselage was that of Yakovlev Yak-3 piston-engine fighter modified to mount a reverse-engineered German Junkers Jumo 004 engine. The Yak-15 and the Swedish Saab 21R were the only two jets to be successfully converted from piston-power to enter production. 280 aircraft were built in 1947. Although nominally a fighter, it was mainly used to qualify piston-engine-experienced pilots to fly jets.
Design and development

Survivors
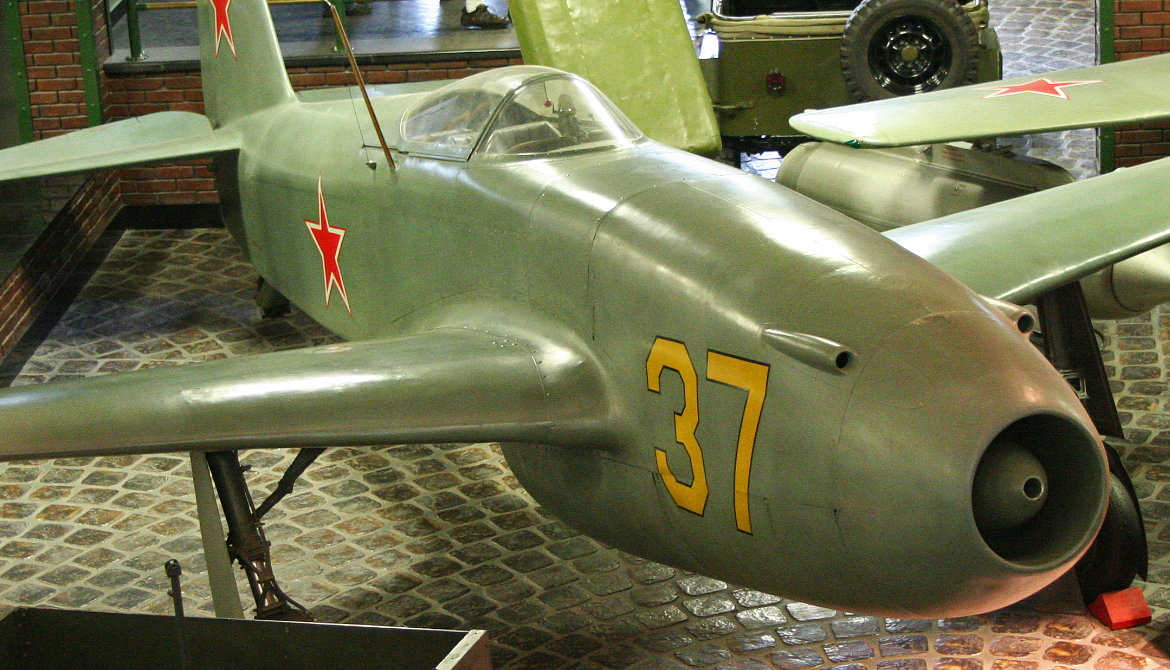
Only one Yak-15 survives, 'Yellow 37' at the Vadim Zadorozhny Technical Museum outside Moscow. It was purchased by the technical museum when the Yakovlev OKB's museum was liquidated in 2006.
Variants
Data from: OKB Yakovlev
- Yak-Jumo (Yak-3-Jumo): The first prototypes of the Yak-15 series, powered by captured Jumo 004 engines.
- Yak-15-RD10: (also referred to as Yak-RD) Initial designation of prototypes and early production aircraft powered by Soviet-built RD-10 engines (copies of the Jumo 004), with no or reduced armament.
- Yak-15: Production aircraft with full armament
- Yak-21: Two-seat training version of Yak-15. One built, but not proceeded with because of the success of the trainer version of the Yak-17.
- Yak-15V: (V - Vyvozny - familiarisation trainer) Alternative designation for the Yak-21.
- Yak-15U: (U - Uchebnotrenirovochnyy - training) Alternative designation for the Yak-21.
- Yak-15U (Yakovlev Yak-15U-RD10): (U - uloochshenny - improved) Improved Yak-15 with tricycle undercarriage and drop tanks, became the prototype of the Yak-17 proper.
0
KmCeiling
0
KmCombat RANGE
0
Km/hAircraft Speed
0
Max Crew
Photo Gallery
JSC A.S. Yakovlev Design Bureau Yakovlev Yak-15
( NATO reporting name: Feather),USAF/DOD designation Type 2


JSC A.S. Yakovlev Design Bureau
Yakovlev Yak-15
(NATO reporting name: "Feather")
General Info
-
-
-
- Crew: one
- Length: 8.7 m (28 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 9.2 m (30 ft 2 in)
- Wing area: 14.85 m2 (159.8 sq ft)
-
-
Powerplant
-
-
-
- Empty weight: 1,852 kg (4,083 lb)
- Gross weight: 2,638 kg (5,816 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 590 kg (1,300 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Klimov RD-10 turbojet, 8.8 kN (2,000 lbf) thrust
-
-
Performance
- Maximum speed: 786 km/h
- Combat range: 510 km
- Service ceiling: 12,000 m
.
Links to Youtube & Others
On 29 April 1946, five days after the Mikoyan-Gurevich I-300 (MiG-9 Prototype) and the Yak-Jumo made their first flights, the Council of Ministers ordered that the Yakovlev OKB begin design of a new aircraft similar to the Yak-Jumo, using the RD-10 engine with improved aerodynamics. This generally resembled the original aircraft, but the wings were entirely redesigned with laminar flow airfoils, the tail structure was enlarged and an ejection seat was fitted.
Yakovlev Yak-15/17 Feather
At an altitude of 5000 meters, the Yak-17-RD10, as the new fighter was designated, was expected to have a top speed of 822 km/h (511 mph);
Youtube Link
On 9 April 1945, the Council of People's Commissars ordered the Yakovlev OKB to develop a single-seat jet fighter to be equipped with a single German Jumo 004 engine.









.png)
.png)



